Abstract
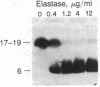
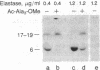
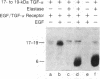
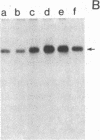
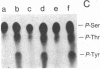
Retrovirus-transformed rat cells that actively express transforming growth factor type alpha (TGF-alpha) release into the medium a soluble protein of 17-19 kDa that has been identified as a precursor for TGF-alpha. The identification of this protein as a TGF-alpha precursor is based on its recognition by specific antibodies and by the ability of elastase to convert this protein into a 6-kDa polypeptide with the properties of mature TGF-alpha. This TGF-alpha precursor binds to epidermal growth factor/TGF-alpha receptors and activates the receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity in intact cells. The biological potency of this precursor is not markedly increased by conversion into mature TGF-alpha in vitro. These studies demonstrate the ability of transformed cells to release a TGF-alpha precursor capable of strong mitogenic action in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters cause the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal human fibroblasts at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1974–1978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R., Like B., Massagué J. Modulation of type alpha transforming growth factor receptors by a phorbol ester tumor promoter. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(1):23–30. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Larco J. E., Preston Y. A., Todaro G. J. Properties of a sarcoma-growth-factor-like peptide from cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive sarcoma virus. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Oct;109(1):143–152. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geneste P., Bender M. L. Esterolytic activity of elastase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):683–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rose T. M., Webb N. R., Todaro G. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for rat transforming growth factor-alpha. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):489–491. doi: 10.1038/313489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Hargreaves W. R., Twardzik D. R., Todaro G. J. Detection of larger polypeptides structurally and functionally related to type I transforming growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):356–360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Todaro G. J. Rat transforming growth factor type 1: structure and relation to epidermal growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1079–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6320373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Twardzik D. R., De Larco J. E., Stephenson J. R., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors produced by retrovirus-transformed rodent fibroblasts and human melanoma cells: amino acid sequence homology with epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Epidermal growth factor-like transforming growth factor. II. Interaction with epidermal growth factor receptors in human placenta membranes and A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13614–13620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Hash J. H., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7669–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Derynck R., Winkler M. E., Gregory H. Human transforming growth factor-alpha causes precocious eyelid opening in newborn mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):515–516. doi: 10.1038/315515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Todaro G. J. Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):878–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Green N., Liu F. T., Niman H. L., Lerner R. A. Chemical synthesis of a polypeptide predicted from nucleotide sequence allows detection of a new retroviral gene product. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):801–805. doi: 10.1038/287801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam J. P. Physiological effects of transforming growth factor in the newborn mouse. Science. 1985 Aug 16;229(4714):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.3860952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Fryling C., De Larco J. E. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Kimball E. S., Sherwin S. A., Ranchalis J. E., Todaro G. J. Comparison of growth factors functionally related to epidermal growth factor in the urine of normal and human tumor-bearing athymic mice. Cancer Res. 1985 May;45(5):1934–1939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Sherwin S. A., Ranchalis J., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors in the urine of normal, pregnant, and tumor-bearing humans. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Oct;69(4):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Todaro G. J., Marquardt H., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Transformation induced by Abelson murine leukemia virus involves production of a polypeptide growth factor. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):894–897. doi: 10.1126/science.6177040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Growth factors from murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4001–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]