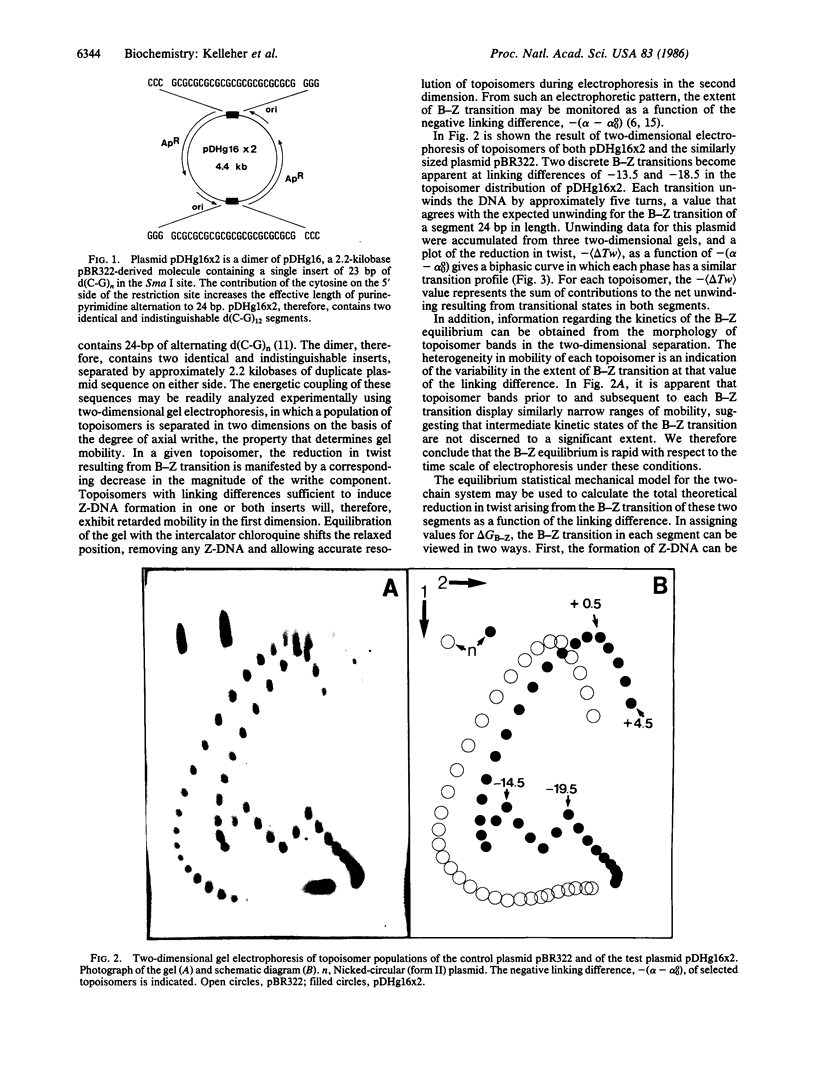
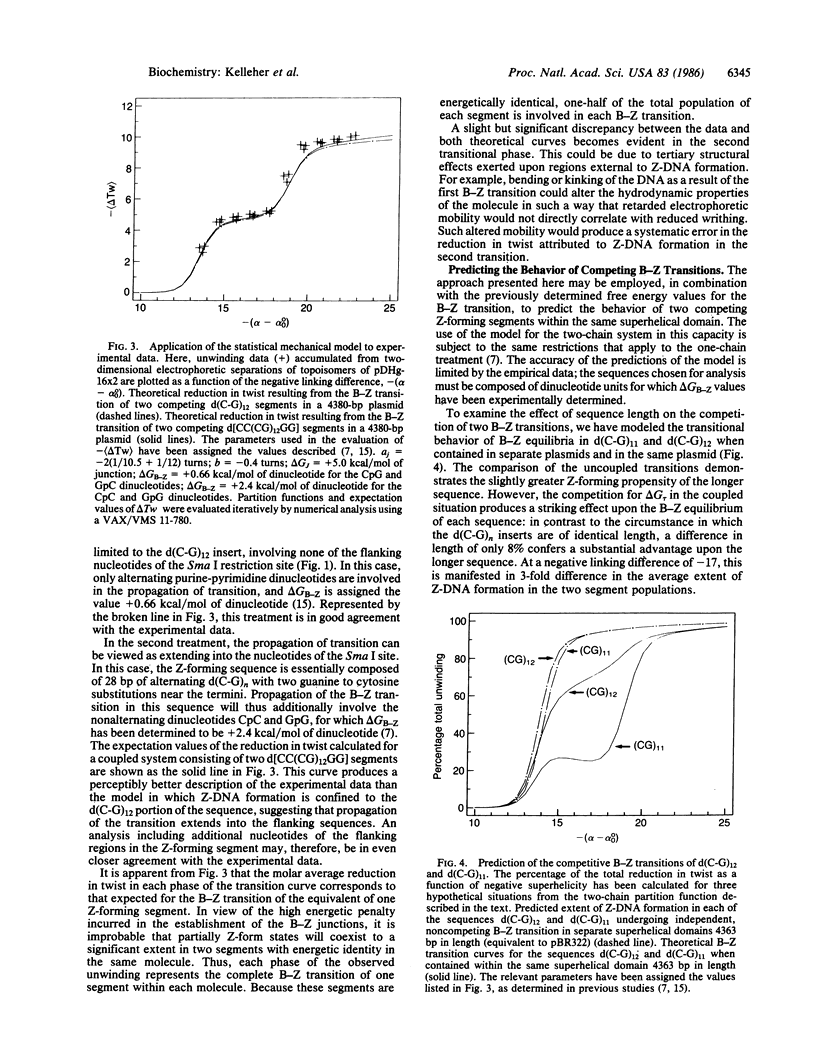
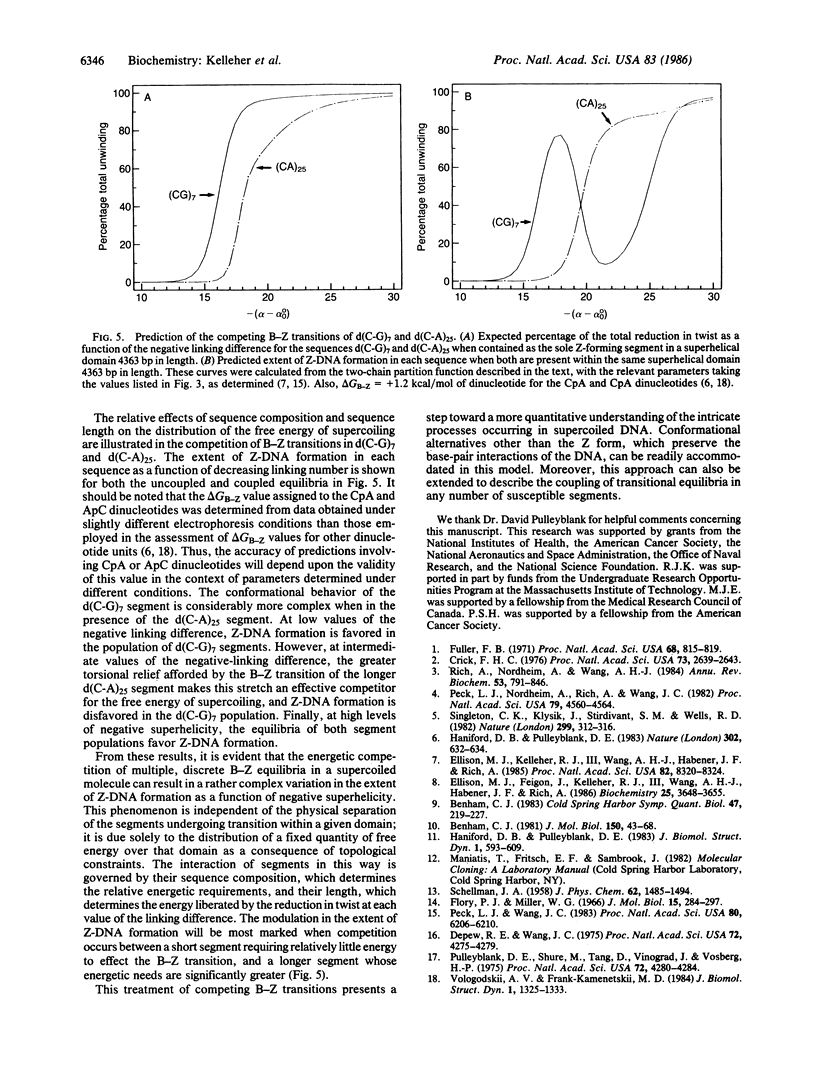
Abstract
Conformational transitions in topologically constrained duplex DNA necessarily affect and are affected by other transitional processes throughout the entire molecule. This conformational interdependence of discrete sequences within a given superhelical domain arises through a requisite competition for the free energy of supercoiling. Here we present a generalized statistical mechanical analysis of multiple, competing conformational equilibria in superhelical DNA. This model has been applied, using experimentally determined parameters, to the energetic coupling of two independent B-Z transitions. Specifically, we have monitored the extent of B-Z transition, as a function of negative superhelicity, in topoisomers of a plasmid containing two identical d(C-G)n inserts using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. The theoretical results were found to be in good agreement with the experimental data, and we have used this model to predict the competitive behavior of B-Z transitions within sequences differing in length and sequence composition. This competition is shown to have a profound effect upon the B-Z equilibria of those sequences analyzed, resulting in a complex modulation in the extent of Z-DNA formation as a function of negative superhelicity. These theoretical and experimental results show that DNA sequences separated by large distances are capable of communicating structural information.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. J. Statistical mechanical analysis of competing conformational transitions in superhelical DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):219–227. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Theoretical analysis of competitive conformational transitions in torsionally stressed DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):43–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90324-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H. Linking numbers and nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2639–2643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew D. E., Wang J. C. Conformational fluctuations of DNA helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. J., Feigon J., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Wang A. H., Habener J. F., Rich A. An assessment of the Z-DNA forming potential of alternating dA-dT stretches in supercoiled plasmids. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3648–3655. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. J., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Wang A. H., Habener J. F., Rich A. Sequence-dependent energetics of the B-Z transition in supercoiled DNA containing nonalternating purine-pyrimidine sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8320–8324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory P. J., Miller W. G. A general treatment of helix-coil equilibria in macromolecular systems. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):284–297. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F. B. The writhing number of a space curve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):815–819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. The in-vivo occurrence of Z DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):593–609. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Nordheim A., Rich A., Wang J. C. Flipping of cloned d(pCpG)n.d(pCpG)n DNA sequences from right- to left-handed helical structure by salt, Co(III), or negative supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4560–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Energetics of B-to-Z transition in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Shure M., Tang D., Vinograd J., Vosberg H. P. Action of nicking-closing enzyme on supercoiled and nonsupercoiled closed circular DNA: formation of a Boltzmann distribution of topological isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA is induced by supercoiling in physiological ionic conditions. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):312–316. doi: 10.1038/299312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Left-handed Z form in superhelical DNA: a theoretical study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Jun;1(6):1325–1333. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]