Abstract
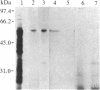
The expression of a gene encoding the cell wall-degrading enzyme polygalacturonase [poly(1,4-α-D-galacturonide) glucanohydrolase, EC 3.2.1.15] was characterized during tomato fruit ripening. Polygalacturonase was purified from ripe tomato fruit and used to produce highly specific antiserum. Immunoblot analyses detected a 45- and a 46-kDa protein in ripe fruit but immunoprecipitation of in vitro translation products of mRNA from ripe tomato fruit yielded a single 54-kDa polypeptide, suggesting post-translational processing. A plasmid cDNA library was prepared from poly(A)+ RNA isolated from ripe tomato fruit. The cDNA library was inserted into a λ-based expression vector, and polygalacturonase cDNA clones were identified by immunological screening. Hybrid-select translation experiments indicated that the cDNAs encode a 54-kDa in vitro translation product that is specifically immunoprecipitated with polygalacturonase antiserum. RNA-blot analysis indicated that the 1.9-kilobase polygalacturonase mRNA was virtually absent from immature-green fruit, accumulated steadily during the ripening process, and was at its highest level in red-ripe fruit. There was at least a 2000-fold increase in the level of polygalacturonase mRNA between immature-green and red-ripe tomato fruit. These studies show that the levels of polygalacturonase mRNA are developmentally regulated during tomato fruit ripening.
Keywords: cDNA, mRNA induction, ethylene, pectic enzyme
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander D. C., McKnight T. D., Williams B. G. A simplified and efficient vector-primer cDNA cloning system. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Straus J. W., Dudock B. S. Preparation of a cell-free protein-synthesizing system from wheat germ. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:635–644. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Varner J. E. An extracellular matrix protein in plants: characterization of a genomic clone for carrot extensin. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2145–2151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crookes P. R., Grierson D. Ultrastructure of tomato fruit ripening and the role of polygalacturonase isoenzymes in cell wall degradation. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1088–1093. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Elzen P., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Differential expression of the eight genes of the petunia ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit multi-gene family. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3055–3061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., van den Elzen P., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Linkage and homology analysis divides the eight genes for the small subunit of petunia ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase into three gene families. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4964–4968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della-Penna D., Christoffersen R. E., Bennett A. B. Biotinylated proteins as molecular weight standards on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen G., Rubenstein I. Complex organization of zein genes in maize. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCHSINGER W. W., CORNESKY R. A. Reducing power by the dinitrosalicylic acid method. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:346–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer T. J. Partial purification and characterization of the mRNA for alpha-amylase from barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):834–837. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushing J. W., Huber D. J. In vitro characterization of tomato fruit softening : the use of enzymically active cell walls. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):891–894. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Themmen A. P., Tucker G. A., Grierson D. Degradation of isolated tomato cell walls by purified polygalacturonase in vitro. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jan;69(1):122–124. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker G. A., Robertson N. G., Grierson D. Changes in polygalacturonase isoenzymes during the 'ripening' of normal and mutant tomato fruit. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(1):119–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner S. J., Bloom H. L. Characteristics of tomato cell wall degradation in vitro: implications for the study of fruit-softening enzymes. Plant Physiol. 1977 Aug;60(2):207–210. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]