Abstract
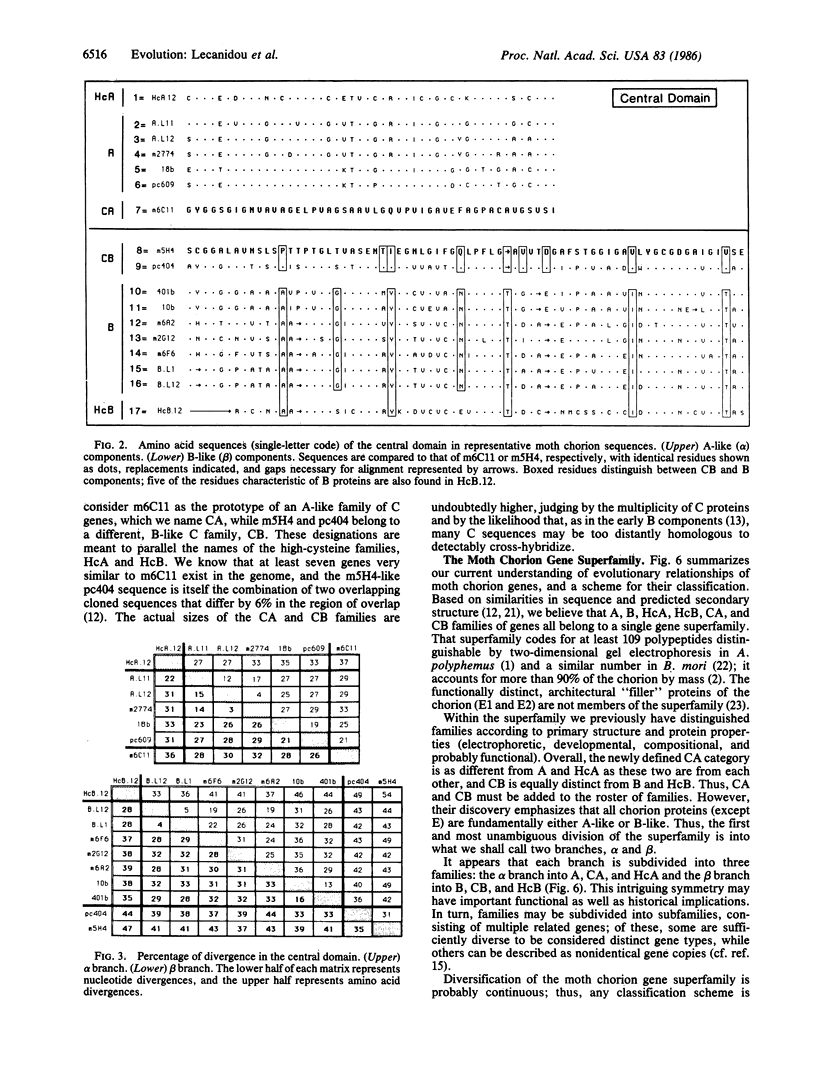
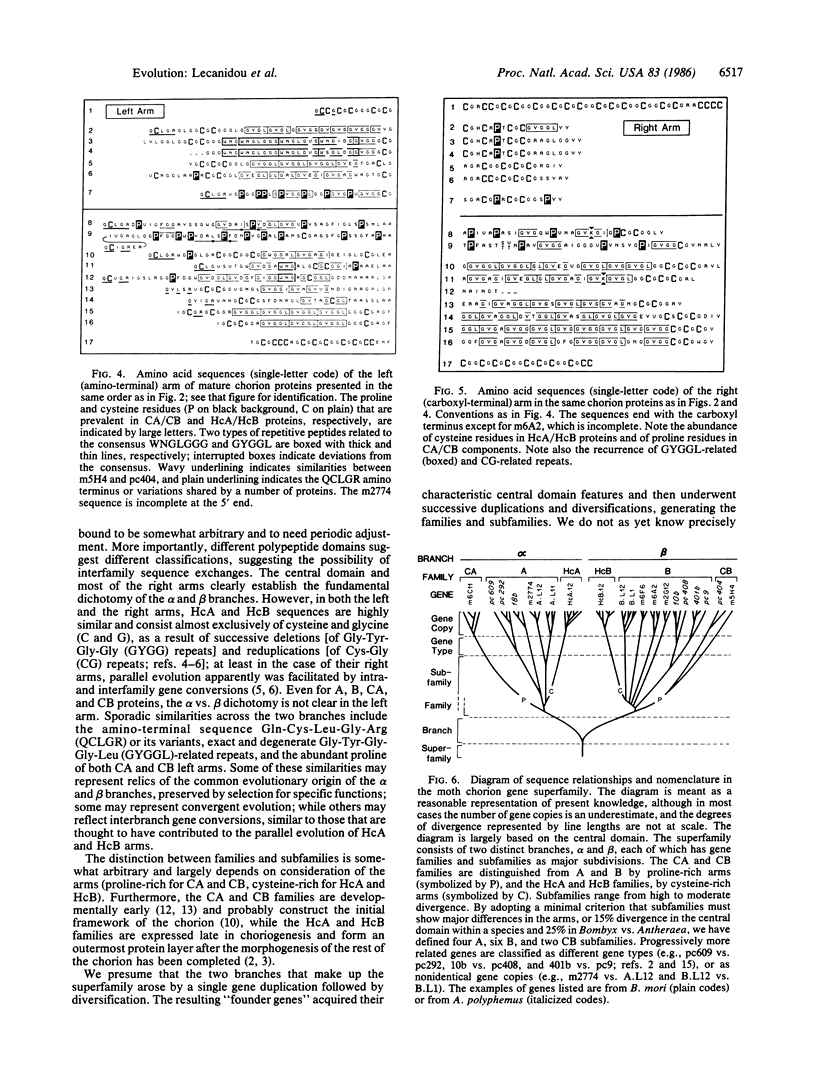
The nucleotide sequences of two developmentally early chorion cDNA clones from Bombyx mori define two distinct proline-rich chorion protein families, which we name CA and CB to indicate their homologies to the previously defined chorion protein families A and B, as well as the developmentally late and cysteine-rich HcA and HcB chorion families. Thus, the chorion gene superfamily has two symmetrical branches, each consisting of three families: the alpha branch (A, CA, HcA families) and the beta branch (B, CB, HcB families). The evolution of the superfamily is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eickbush T. H., Rodakis G. C., Lecanidou R., Kafatos F. C. A complex set of early chorion DNA sequences from Bombyx mori. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. R., Kafatos F. C. Developmentally regulated genes in silkmoths. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:443–487. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamodrakas S. J., Etmektzoglou T., Kafatos F. C. Amino acid periodicities and their structural implications for the evolutionarily conservative central domain of some silkmoth chorion proteins. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Tsitilou S. G., Kafatos F. C. DNA sequence transfer between two high-cysteine chorion gene families in the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4452–4456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Kafatos F. C. Accepted mutations in a gene family: evolutionary diversification of duplicated DNA. J Mol Evol. 1982;19(1):87–103. doi: 10.1007/BF02100227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Rosenthal N., Rodakis G. C., Kafatos F. C. Evolution of two major chorion multigene families as inferred from cloned cDNA and protein sequences. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1317–1332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecanidou R., Eickbush T. H., Rodakis G. C., Kafatos F. C. Novel B family sequence from an early chorion cDNA library of Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1955–1959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel M. R., Goldsmith M. R., Goplerud J., Kafatos F. C. Specific protein synthesis in cellular differentiation. V. A secretory defect of chorion formation in the Grcol mutant of Bombyx mori. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar;75(1):41–58. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):643–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier J. C., Kafatos F. C., Hamodrakas S. J. Silkmoth chorion multigene families constitute a superfamily: comparison of C and B family sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1043–1047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier J. C., Mazur G. D., Kafatos F. C., Paul M. Morphogenesis of silkmoth chorion: initial framework formation and its relation to synthesis of specific proteins. Dev Biol. 1982 Jul;92(1):159–174. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier J. C., Mazur G. D., Kafatos F. C. The silkmoth chorion: morphological and biochemical characterization of four surface regions. Dev Biol. 1980 May;76(2):286–304. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier J. C., Pacholski P. Nucleotide sequence of an unusual regionally expressed silkmoth chorion RNA: predicted primary and secondary structures of an architectural protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6035–6039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodakis G. C., Kafatos F. C. Origin of evolutionary novelty in proteins: how a high-cysteine chorion protein has evolved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3551–3555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodakis G. C., Moschonas N. K., Kafatos F. C. Evolution of a multigene family of chorion proteins in silkmoths. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 May;2(5):554–563. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.5.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodakis G. C., Moschonas N. K., Regier J. C., Kafatos F. C. The B multigene family of chorion proteins in saturniid silkmoths. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(5):322–332. doi: 10.1007/BF02101635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsitilou S. G., Regier J. C., Kafatos F. C. Selection and sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding a known chorion protein of the A family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1987–1997. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsitilou S. G., Rodakis G. C., Alexopoulou M., Kafatos F. C., Ito K., Iatrou K. Structural features of B family chorion sequences in the silkmoth Bombyx mori, and their evolutionary implications. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1845–1852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




