Abstract
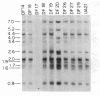
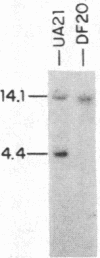
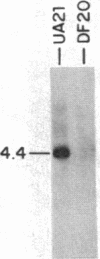
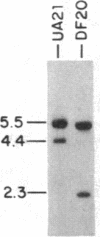
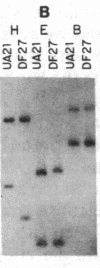
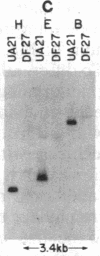
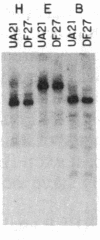
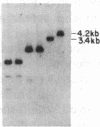
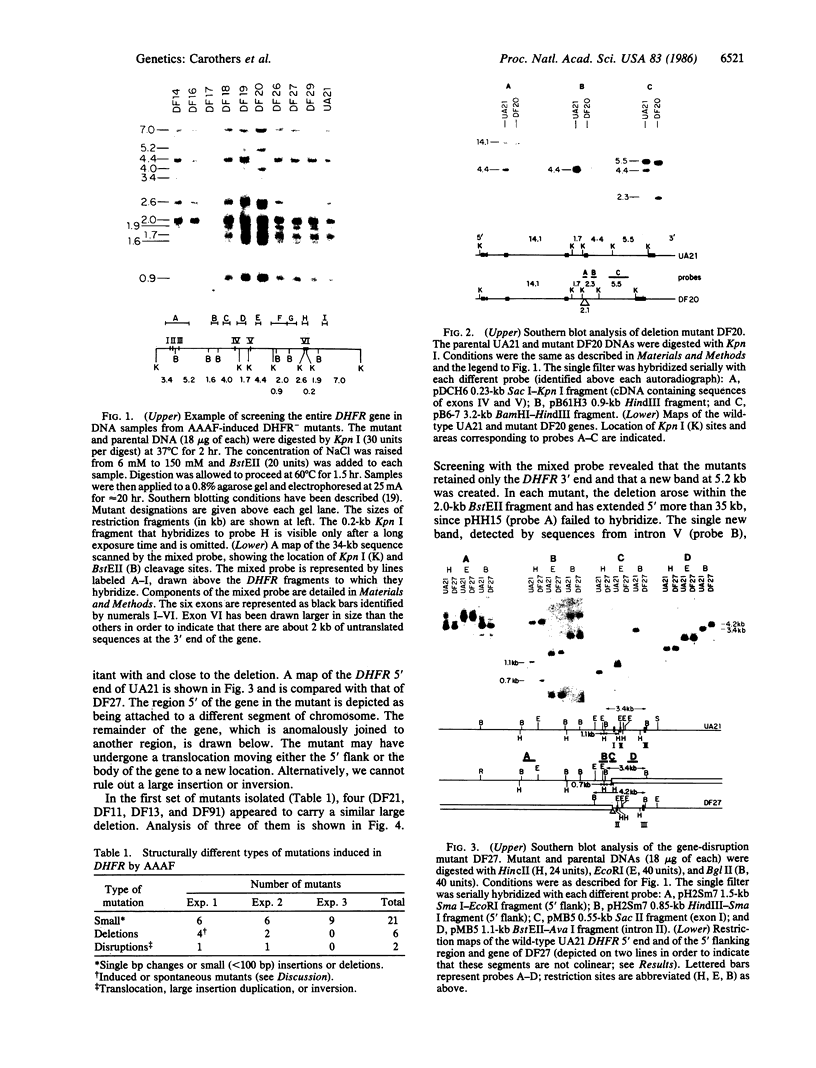
To determine the types of alterations in gene structure that are induced by the carcinogen 2-(N-acetoxy-N-acetyl)aminofluorene, we used this compound to generate mutations at the dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) locus (DHFR) in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Twenty-nine independent enzyme-deficient mutants were isolated. A profile of the 26-kilobase (kb)-long gene was obtained by Southern blot analysis of the mutant and parental DNAs digested with BstEII/Kpn I. Hybridization to a mixed probe of 10 DHFR genomic and cDNA fragments revealed 12 bands that scan 34 kb. Twenty-one DHFR- clones (72%) contained small mutations (changes less than 100 base pairs in size). Large or small deletions involving various parts of the gene occurred in eight of the mutants (28%). A large deletion (greater than 35 kb) with 5' and 3' breakpoints mapping to approximately the same location was noted in four mutants. One mutant has undergone a deletion of 550-900 bp that eliminated the first coding exon. Concomitantly, a chromosomal event (either translocation, insertion, or inversion) has separated the 5' flank from the body of the gene. In another mutant, four deletions have occurred at the DHFR 5' end and internally. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the mutant DNAs with exon-specific probes localized three mutations. One mutant has lost a Taq I (TCGA) site, and another has lost a Sac I (GAGCTC) site. In a third, a GC----TA transversion has created a BstEII (GGTNACC) site. Finally, we used HPLC to determine the ratio of acetylated (12%) to deacetylated (88%) 2-aminofluorene adducts formed in the parental cells. A correlation between the mutational specificities and the conformational changes induced by the two types of DNA adducts is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Durston W. E., Yamasaki E., Lee F. D. Carcinogens are mutagens: a simple test system combining liver homogenates for activation and bacteria for detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aust A. E., Drinkwater N. R., Debien K., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Comparison of the frequency of diphtheria toxin and thioguanine resistance induced by a series of carcinogens to analyze their mutational specificities in diploid human fibroblasts. Mutat Res. 1984 Jan;125(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(84)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichara M., Fuchs R. P. DNA binding and mutation spectra of the carcinogen N-2-aminofluorene in Escherichia coli. A correlation between the conformation of the premutagenic lesion and the mutation specificity. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Urlaub G., Ellis N., Chasin L. A. Structure of the dihydrofolate reductase gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):1997–2012. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., ar-Rushdi A., Drwinga H. L., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Transcriptional activation of the translocated c-myc oncogene in burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson P. M., Kit S., Dubbs D. R. Induction of dihydrofolate reductase activity by SV40 and polyoma virus. Cancer Res. 1966 Aug;26(8):1653–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Daune M. Physical studies on deoxyribonucleic acid after covalent binding of a carcinogen. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2659–2666. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuscoe J. C., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Ledbetter D. H., Caskey C. T. Deletion and amplification of the HGPRT locus in Chinese hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1086–1096. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Casciano D. A., Couch D. B., Krahn D. F., O'Neill J. P., Whitfield B. L. The use of Chinese hamster ovary cells to quantify specific locus mutation and to determine mutagenicity of chemicals. A report of the gene-tox program. Mutat Res. 1981 Mar;86(2):193–214. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(81)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H. W., Brookes P. On the mechanism of induction of resistance to 6-thioguanine in Chinese hamster V79 cells by 3-methylcholanthrene-diolepoxide. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Oct;6(10):1471–1476. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.10.1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King H. W., Brookes P. On the nature of the mutations induced by the diolepoxide of benzo[a]pyrene in mammalian cells. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Jul;5(7):965–970. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.7.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Klein E. Evolution of tumours and the impact of molecular oncology. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):190–195. doi: 10.1038/315190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffel-Schwartz N., Verdier J. M., Bichara M., Freund A. M., Daune M. P., Fuchs R. P. Carcinogen-induced mutation spectrum in wild-type, uvrA and umuC strains of Escherichia coli. Strain specificity and mutation-prone sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 25;177(1):33–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Kanda N., Schreck R. R., Bruns G., Latt S. A., Gilbert F., Alt F. W. Transposition and amplification of oncogene-related sequences in human neuroblastomas. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. C., Miller J. A., Miller E. C., Liem A. N-sulfoöxy-2-aminofluorene is the major ultimate electrophilic and carcinogenic metabolite of N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofluorene in the livers of infant male C57BL/6J x C3H/HeJ F1 (B6C3F1) mice. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Jul;6(7):1037–1045. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.7.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacInnes M. A., Friedrich U., van Daalen Wetters T., Coffino P. Quantitative forward-mutation specificity of mono-functional alkylating agents, ICR-191, and aflatoxin B1 in mouse lymphoma cells. Mutat Res. 1982 Aug;95(2-3):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melera P. W., Davide J. P., Hession C. A., Scotto K. W. Phenotypic expression in Escherichia coli and nucleotide sequence of two Chinese hamster lung cell cDNAs encoding different dihydrofolate reductases. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. D., Azizkhan J. C., Hamlin J. L. Amplification of a cloned Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene after transfer into a dihydrofolate reductase-deficient cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1274–1282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Carothers A. M., Han J. H., Harding J. D., Kas E., Venolia L., Chasin L. A. Multiple transcription start sites, DNase I-hypersensitive sites, and an opposite-strand exon in the 5' region of the CHO dhfr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):425–440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Urlaub G., Chasin L. Spontaneous splicing mutations at the dihydrofolate reductase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Goncalves O., Meuth M. Structure of mutant alleles at the aprt locus of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):575–594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Givol D., Canaani E. Activation of a cellular oncogene by DNA rearrangement: possible involvement of an IS-like element. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):607–611. doi: 10.1038/300607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santella R. M., Kriek E., Grunberger D. Circular dichroism and proton magnetic resonance studies of dApdG modified with 2-aminofluorene and 2-acetylaminofluorene. Carcinogenesis. 1980;1(11):897–902. doi: 10.1093/carcin/1.11.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spodheim-Maurizot M., Saint-Ruf G., Leng M. Conformational changes induced in DNA by in vitro reaction with N-hydroxy-N-2-aminofluorene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1683–1694. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theall G., Eisinger M., Grunberger D. Metabolism of benzo[a]pyrene and DNA adduct formation in cultured human epidermal keratinocytes. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(7):581–587. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.7.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Käs E., Carothers A. M., Chasin L. A. Deletion of the diploid dihydrofolate reductase locus from cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90422-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Landzberg M., Chasin L. A. Selective killing of methotrexate-resistant cells carrying amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1594–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., McDowell J., Chasin L. A. Use of fluorescence-activated cell sorter to isolate mutant mammalian cells deficient in an internal protein, dihydrofolate reductase. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF01534736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Pulkrabek P., Grunberger D., Weinstein I. B. Differential excision from DNA of the C-8 and N2 guanosine adducts of N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene by single strand-specific endonucleases. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3756–3760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarbl H., Sukumar S., Arthur A. V., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Direct mutagenesis of Ha-ras-1 oncogenes by N-nitroso-N-methylurea during initiation of mammary carcinogenesis in rats. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):382–385. doi: 10.1038/315382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]