Abstract
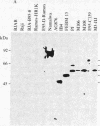
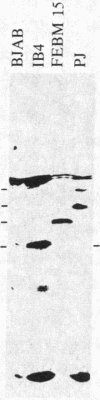
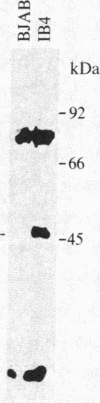
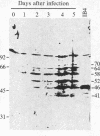
Four peptides were synthesized on the basis of amino acid sequences deduced from a highly spliced transcript encoded by the Bam W, Y, and H fragments of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome [Bodescot, M., Chambraud, J. B., Farrell, P. J. & Perricaudet, M. (1984) EMBO J. 3, 1913-1917]. Rabbit antisera against three of the four peptides identified a nuclear polypeptide that varied between 22 and 70 kDa in molecular size. Four of 20 EBV-positive human sera contained antibodies against this polypeptide. Since this is the fifth EBV-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) discovered in growth-transformed cells, it is designated EBNA5. The antigen was detected in virus nonproducer lines (less than 0.01% EBV early antigen expression) and is thus not dependent on the viral cycle. It was differentially expressed depending on the origin of the lines. All 10 lymphoblastoid cell lines tested expressed EBNA5, but it could not be detected in 10 of 11 EBV-carrying Burkitt lymphoma lines. Infection of tonsillar lymphocytes with the B95-8 strain of EBV induced six EBNA5-specific polypeptides that varied between 41 and 70 kDa in molecular size with regular increments of 6 kDa. This may be due to the fact that the EBNA5 coding sequence includes the Bam W internal repeat. Parallel infection of the EBV-negative Burkitt lymphoma line Ramos with the same viral substrain did not induce detectable levels of EBNA5, nor was this antigen present in permanently EBV-converted Ramos sublines. These findings imply that the expression of the viral genome varies among B cells having different phenotypes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aman P., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G. Epstein-Barr virus susceptibility of normal human B lymphocyte populations. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):208–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Bornkamm G. W. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus. III. Comparison of a transforming and a nontransforming virus by partial denaturation mapping of their DNAs. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.81-89.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Rymo L., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G. The Epstein-Barr virus determined nuclear antigen is composed of at least three different antigens. Int J Cancer. 1986 Feb 15;37(2):195–200. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910370205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Timar L., Klein G. Characterization of a second Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen associated with the BamHI WYH region of EBV DNA. Int J Cancer. 1985 Mar 15;35(3):359–366. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Klein G., Jörnvall H., Alexander H., Lerner R. Antibodies against synthetic peptides react with the second Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1813–1818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn L., Ernberg I. Induction of EBNA precedes the first cellular S-phase after EBV-infection of human lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1978 Feb 15;21(2):157–160. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Andersson-Anvret M., Klein G., Lundin L., Killanger D. Relationship between amount of Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen per cell and number of EBV-DNA copies per cell. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):269–271. doi: 10.1038/266269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Recovery of transforming EBV from non-producer cells after superinfection with non-transforming P3HR-1 EBV. Int J Cancer. 1978 Oct 15;22(4):378–383. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Dambaugh T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA. IX. Variation among viral DNAs from producer and nonproducer infected cells. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):632–648. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.632-648.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L. Efficiency of transformation of lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):152–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Kieff E. A third viral nuclear protein in lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5944–5948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Dillner J., Ernberg I., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Rosén A., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G. Four virally determined nuclear antigens are expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katamine S., Otsu M., Tada K., Tsuchiya S., Sato T., Ishida N., Honjo T., Ono Y. Epstein-Barr virus transforms precursor B cells even before immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):369–372. doi: 10.1038/309369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G. Biological differences between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) strains with regard to lymphocyte transforming ability, superinfection and antigen induction. Exp Cell Res. 1975 May;92(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymo L., Klein G., Ricksten A. Expression of a second Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen in mouse cells after gene transfer with a cloned fragment of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3435–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Farley J., Strominger J. L., Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Transformation by Epstein-Barr virus requires DNA sequences in the region of BamHI fragments Y and H. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.286-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T. C., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen by fluoroimmunoelectrophoresis and radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.996-1004.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima Y., Marczynska B., Nonoyama M. Transforming activity of Epstein-Barr virus obtained by superinfection of Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2008–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]