Abstract
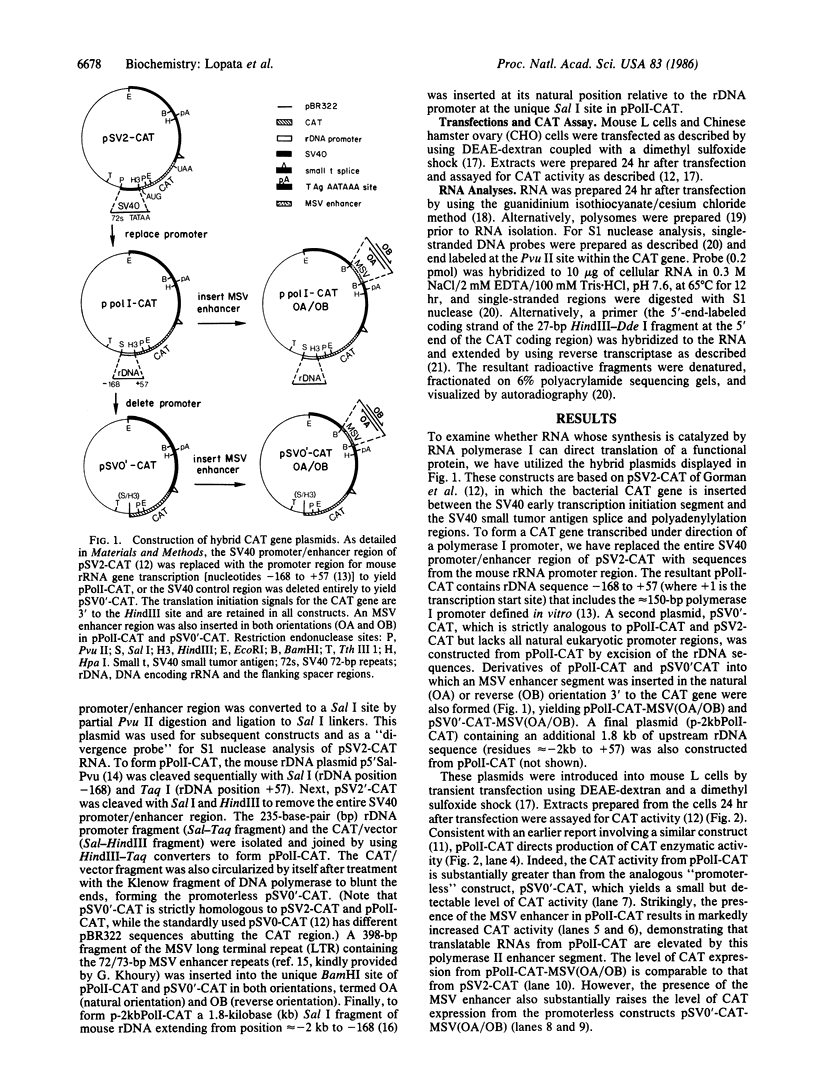
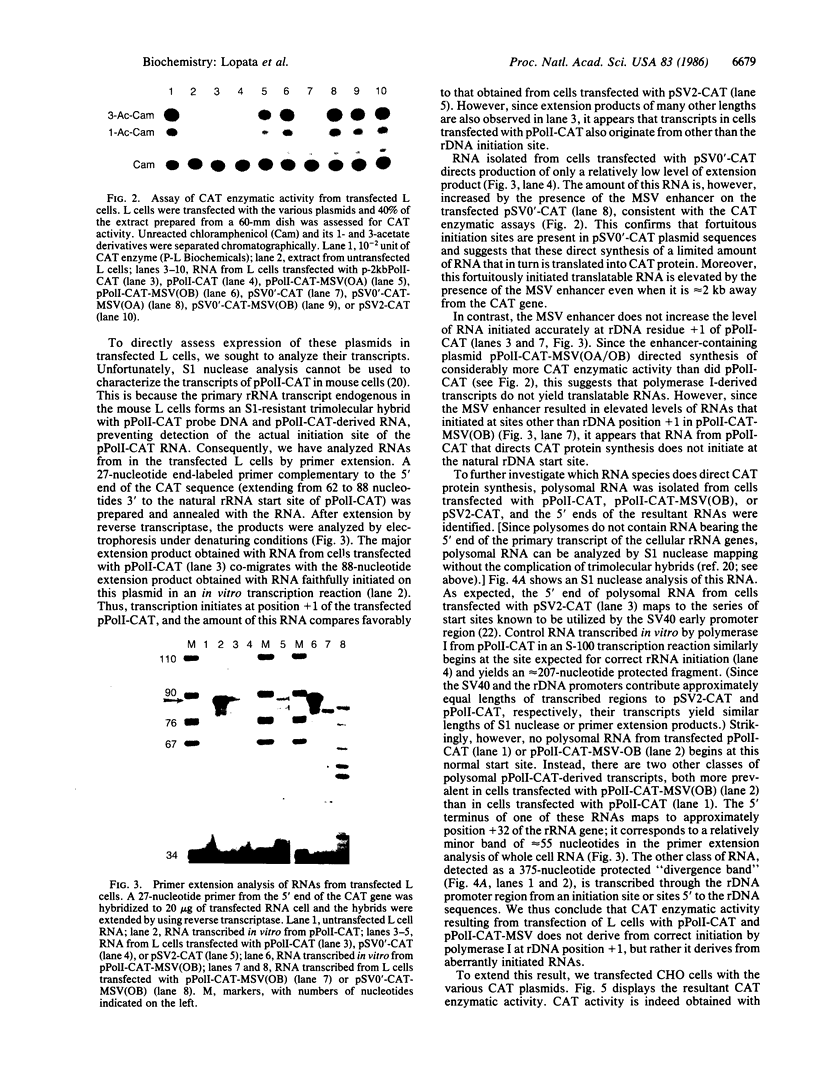
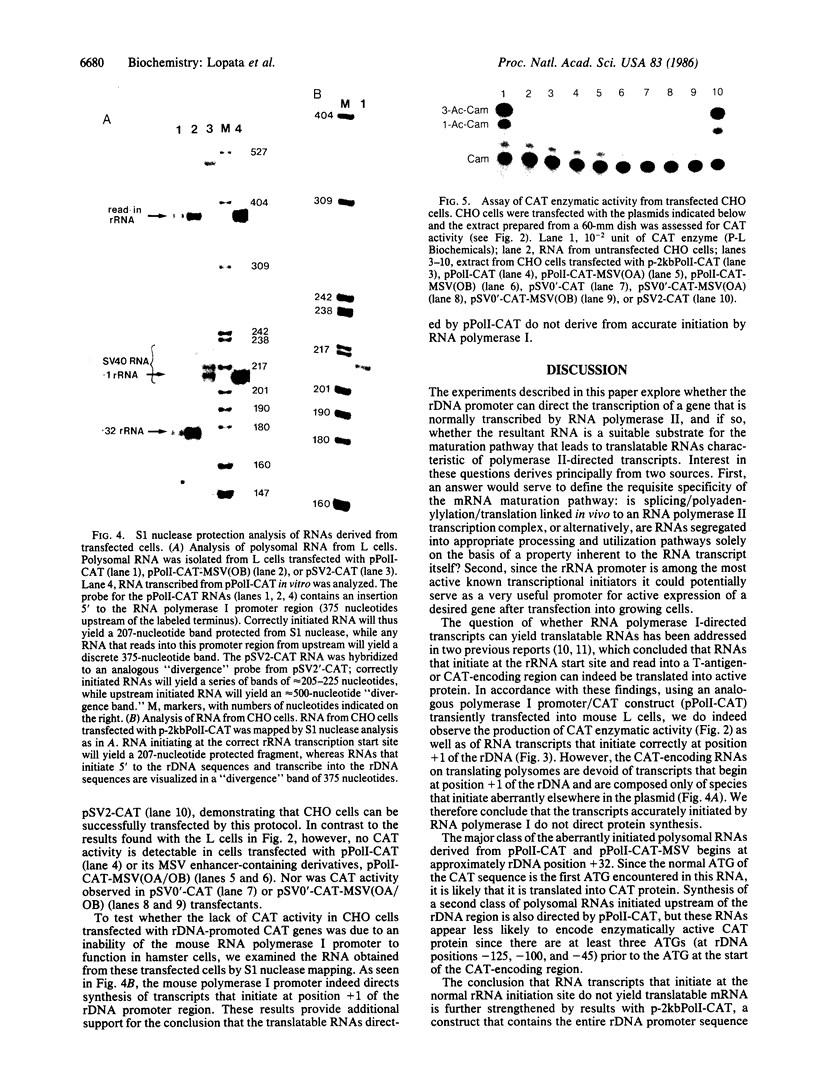
To examine the RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.6) specificity of RNA maturation/utilization and transcriptional enhancement, we constructed a chimeric plasmid (pPolI-CAT) in which a promoter for mouse rRNA gene transcription was placed adjacent the coding sequences for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT; EC 2.3.1.28). A number of other constructs, including plasmids also containing a murine sarcoma virus enhancer or lacking any natural eukaryotic promoter sequences, were also prepared. In apparent agreement with earlier conclusions that an RNA polymerase I transcript can act as a messenger RNA, transient transfection of mouse L cells with pPolI-CAT yielded both high levels of transcription from the RNA polymerase I promoter and enzymatically active CAT protein. However, further examination revealed that CAT protein is not translated from RNA that begins at the normal rRNA transcription initiation site. Polysomal RNA is devoid of such RNA and instead consists of CAT-encoding transcripts that begin elsewhere in the mouse ribosomal DNA (rDNA) region. Since transcription of these aberrant RNAs is stimulated by the addition of a murine sarcoma virus enhancer segment, they are probably transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Transcripts that map to the authentic rRNA start site are not similarly enhanced. Moreover, unlike the RNAs deriving from the rRNA initiation site, these aberrant RNAs are more stable and the level of translatable CAT transcripts is suppressed by inclusion of larger segments of the rDNA promoter regions. Fortuitously initiated mRNAs are also formed in the absence of any natural eukaryotic promoter sequence. From these data we conclude that there is no evidence that normal RNA polymerase I transcription yields functional mRNA and that transcriptional enhancement appears to be RNA polymerase specific.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlson D. P., Ross J. Human beta-globin promoter and coding sequences transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):857–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90543-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. P., Ross J. alpha-Amanitin-insensitive transcription of mouse beta major-globin 5'-flanking and structural gene sequences correlates with mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7782–7786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar V. N., Miller D. A., Miller O. J. Transcription of mouse rDNA and associated formation of the nucleolus organizer region after gene transfer and amplification in Chinese hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2943–2950. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Grummt I. Expression of an mRNA coding gene under the control of an RNA polymerase I promoter. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2319–2322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg C. J., Raskas H. J. In vitro splicing of purified precursor RNAs specified by early region 2 of the adenovirus 2 genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5430–5434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Skinner J. A. Efficient transcription of a protein-coding gene from the RNA polymerase I promoter in transfected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):722–726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T. M., Brownlee G. G., Milstein C. Studies on polysome-membrane interactions in mouse myeloma cells. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):613–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M., Arnheim N. Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):211–224. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Tjian R. In vitro transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Sollner-Webb B., Cleveland D. W. Surprising S1-resistant trimolecular hybrids: potential complication in interpretation of S1 mapping analyses. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2842–2846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. A complex control region of the mouse rRNA gene directs accurate initiation by RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):554–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. Transcription of herpes simplex virus tk sequences under the control of wild-type and mutant human RNA polymerase I promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):352–362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]