Abstract
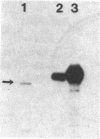
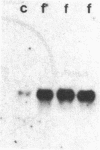
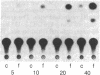
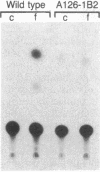
We have examined the regulation of somatostatin gene expression by cAMP in PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells transfected with the rat somatostatin gene. Forskolin at 10 microM caused a 4-fold increase in somatostatin mRNA levels within 4 hr of treatment in stably transfected cells. Chimeric genes containing the somatostatin gene promoter fused to the bacterial reporter gene encoding chloramphenicol acetyltransferase were also induced by cAMP in PC12 cells. To delineate the sequences required for response to cAMP, we constructed a series of promoter deletion mutants. Our studies defined a region between 60 and 29 base pairs upstream from the transcriptional initiation site that conferred cAMP responsiveness when placed adjacent to the simian virus 40 promoter. Within the cAMP-responsive element of the somatostatin gene, we observed an 8-base palindrome, 5'-TGACGTCA-3', which is highly conserved in many other genes whose expression is regulated by cAMP. cAMP responsiveness was greatly reduced when the somatostatin fusion genes were transfected into the mutant PC12 line A126-1B2, which is deficient in cAMP-dependent protein kinase 2. Our studies indicate that transcriptional regulation of the somatostatin gene by cAMP requires protein kinase 2 activity and may depend upon a highly conserved promoter element.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aron D. C., Muszynski M., Birnbaum R. S., Sabo S. W., Roos B. A. Somatostatin elaboration by monolayer cell cultures derived from transplantable rat medullary thyroid carcinoma: synergistic stimulatory effects of glucagon and calcium. Endocrinology. 1981 Dec;109(6):1830–1834. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-6-1830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boney C., Fink D., Schlichter D., Carr K., Wicks W. D. Direct evidence that the protein kinase catalytic subunit mediates the effects of cAMP on tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4911–4918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chihara K., Arimura A., Schally A. V. Effect of intraventricular injection of dopamine, noreprinephrine, acetylcholine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine on immunoreactive somatostatin release into rat hypophyseal portal blood. Endocrinology. 1979 Jun;104(6):1656–1662. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-6-1656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou A. I., Squinto S. P., Jungmann R. A. The phosphoform of the regulatory subunit RII of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase possesses intrinsic topoisomerase activity. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell R. B., Boime I. Differential expression of the human gonadotropin alpha gene in ectopic and eutopic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3157–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Possible role for cyclic nucleotides and phosphorylated membrane proteins in postsynaptic actions of neurotransmitters. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):101–108. doi: 10.1038/260101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Dickens G., End D., Londos C. The action of adenosine analogs on PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1981 Dec;37(6):1431–1439. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb06312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Tank A. W., Weiner N., Chikaraishi D. M. Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA by glucocorticoid and cyclic AMP in a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Isolation of a cDNA clone for tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14632–14637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Goodman R. H., Horovitch S. J., Habener J. F. Primary structure of the gene encoding rat preprosomatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3337–3340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Low M. J., Tapia-Arancibia L., Reichlin S., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Cyclic AMP regulates somatostatin mRNA accumulation in primary diencephalic cultures and in transfected fibroblast cells. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):1171–1176. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-01171.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Ohishi H. Long terminal repeat sequences of intracisternal A particle genes in the Syrian hamster genome: identification of tRNAPhe as a putative primer tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7169–7179. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Reichlin S. Somatostatin in hypothalamus, extrahypothalamic brain, and peripheral tissues of the rat. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):523–530. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Weir L., Leder P. Enhancer-dependent expression of human kappa immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7161–7165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. P., Rutter W. J. Sequence of the human somatostatin I gene. Science. 1984 Apr 13;224(4645):168–171. doi: 10.1126/science.6142531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimatsu A., Kato Y., Matsushita N., Katakami H., Yanaihara N., Imura H. Effects of glucagon, Neurotensin, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on somatostatin release from perifused rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1982 Jun;110(6):2113–2117. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-6-2113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Golde D. W., Miwa M., Sugimura T., Chen I. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the long terminal repeat of human T-cell leukemia virus type II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1079–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Kelley-Geraghty D. C., Kuettel M. R., Jungmann R. A. Ultrastructural localization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in regenerating rat hepatocytes using immunogold electron microscopy. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(1):65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapia-Arancibia L., Reichlin S. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and PHI stimulate somatostatin release from rat cerebral cortical and diencephalic cells in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1985 Jun 10;336(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavianini M. A., Hayes T. E., Magazin M. D., Minth C. D., Dixon J. E. Isolation, characterization, and DNA sequence of the rat somatostatin gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11798–11803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao M., Watanabe Y., Mishina M., Numa S. Sequence requirement for transcription in vivo of the human preproenkephalin A gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2223–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced process formation by cultured rat pheochromocytoma cells. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):341–342. doi: 10.1038/258341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsimanis A., Bichko V., Dreilina D., Meldrais J., Lozha V., Kukaine R., Gren E. The structure of cloned 3'-terminal RNA region of bovine leukemia virus (BLV). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):6079–6087. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.6079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Horovitch S. J., Montminy M. R., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Structure of the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide gene. DNA. 1985 Aug;4(4):293–300. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Buskirk R., Corcoran T., Wagner J. A. Clonal variants of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells with defects in cAMP-dependent protein kinases induce ornithine decarboxylase in response to nerve growth factor but not to adenosine agonists. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1984–1992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. A., Gordon D. F., Kissil M. S., Mead D. A., Kemper B. Isolation and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for bovine parathyroid hormone. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynshaw-Boris A., Lugo T. G., Short J. M., Fournier R. E., Hanson R. W. Identification of a cAMP regulatory region in the gene for rat cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Use of chimeric genes transfected into hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12161–12169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]