Abstract
The development of convenient, real-time probes for monitoring protein function in biological samples represents an important challenge of the postgenomic era. In response, we introduce here “transcription factor beacons,” binding-activated fluorescent DNA probes that signal the presence of specific DNA-binding activities. As a proof of principle, we present beacons for the rapid, sensitive detection of three transcription factors (TATA Binding Protein, Myc-Max, and NF-κB), and measure binding activity directly in crude nuclear extracts.
One of the most important challenges of the postgenomic era is the development of probes that support the rapid, real-time monitoring of protein function directly in native cellular environments or crude cellular extracts (functional proteomics).1–4 Ideally, such probes should respond to endogenous target (i.e., the naturally occurring protein rather than a recombinant fusion protein), work directly under complex in vitro or in vivo conditions, and be versatile enough to support the detection of a wide range of protein functions.1–4 The availability of such probes would enhance our ability to elucidate the role of protein function in healthy or disease states, and would improve drug screening assays by enabling the identification of inhibitors directly in biologically relevant samples.1–4
An increasingly important approach to functional genomics has been the development of activity-based probes that respond to the function of the targeted protein, rather than just its presence. Successful examples include “tagged-chemical” activity-based probes, which have been adapted to detect a range of enzyme functions,3,4 and structure-switching sensors, which are activated via covalent modification5 or via binding-induced conformational changes.5–9 Expanding on this theme, here we describe a novel class of structure-switching molecular probes that are activated upon binding to specific DNA-binding proteins.
DNA-binding activity is ubiquitous; more than 10% of the ~25 000 human genes encode DNA-binding proteins, the majority of which function as transcription factors (TF)10 that control crucial biological mechanisms such as cell proliferation and apoptosis. Unfortunately, current methods for monitoring DNA-binding activity are generally slow and cumbersome.11 Immunochemical approaches, for example, such as ELISAs and Western blots, are multistep, reagent intensive techniques that require specific antibodies against each new protein target. Fluorescently labeled antibodies, the traditional method of intracellular localization of DNA binding proteins, generally fail to distinguish between binding-competent and binding-inhibited forms, reducing their specificity, and suffer from constitutive fluorescence, reducing their sensitivity. While widespread, other in vitro methods for the detection of DNA binding activity such as gel shift assay12 and fluorescence anisotropy suffer from being time- and labor-intensive or are limited to the study of purified materials.11 In response, Heyduk and co-workers have recently developed bimolecular proximity assays, a convenient approach to the detection of some TFs that employs the binding-induced association of a two-part DNA recognition element.13 The number of target proteins amenable to this approach, however, is limited as the assay requires the presence of a covalent break within the DNA recognition element.11 Finally, Tan and coworkers have reported a molecular beacon for the detection of single-stranded DNA-binding proteins.5,9 This does not, however, support the detection of transcription factors, which only bind double-stranded DNA. In short, there remains a pressing need for improved methods of detecting and quantifying the DNA binding activity of transcription factors and other DNA binding proteins.
We have developed a versatile new class of fluorescent sensors we have termed Transcription Factor (TF) Beacons. The TF beacon strategy is inspired by molecular and aptamer beacons,5,8,9,14,15 structure-switching oligonucleotide probes that, like naturally occurring biomolecular switches,6 employ binding-induced structural change to signal the presence of a specific molecular target or its functioning. Critically, because their signaling is induced only by the formation of a highly specific probe–target complex, such conformation-linked sensors generally work well even when deployed in complex environments, including inside living cells.6,16
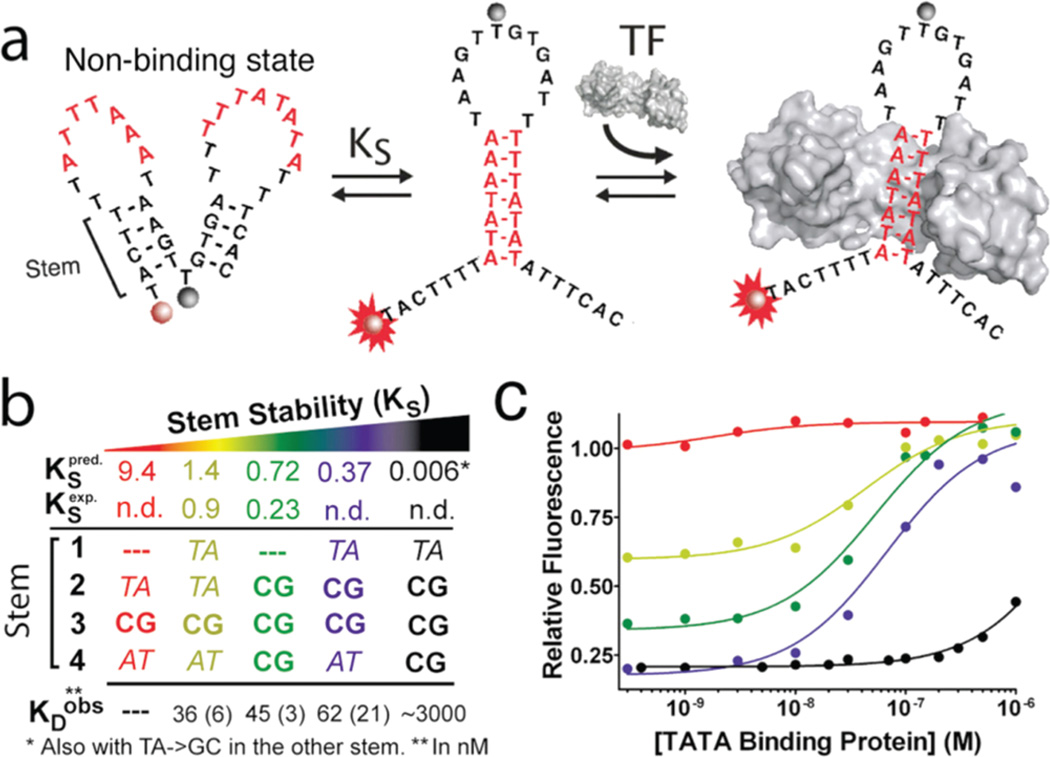
The design of TF beacons requires that we convert a specific double-stranded DNA binding sequences into a molecular switch. This starts by selecting a consensus, double-stranded DNA binding sequence that specifically recognizes the target TF (these are known for most transcription factors of interest).18,19 Using freely available software,20 which predicts DNA conformation thermodynamics with relative accuracy (compare KSpred. to KSexp in Figure 1b), we then incorporate additional nucleotide sequences to create a construct that interconverts between two distinct conformations: a stem-loop structure containing the specific DNA binding sequence of the target protein (red stem), and a double stem-loop “nonbinding” structure that lacks this recognition element (Figure 1a and Supporting Methods). Binding of the target TF drives this conformational equilibrium toward the binding-competent, stem-loop state via a population-shift mechanism.17 By attaching a fluorophore/quencher pair to one of the two stems in the nonbinding state, this conformational shift is signaled via a large increase in fluorescence emission, enabling the quantitative detection of the target protein (Figure 1a).
Figure 1.
Transcription factor (TF) beacons for the quantitative detection of DNA binding activity. (a) DNA sequences containing the recognition site for a specific DNA binding protein (here shown, red stem, for TATA binding protein (TBP)) are engineered into switches by stabilizing an alternative “non-binding” conformation or state (left). Binding of the protein thus shifts the switch’s conformational equilibrium toward the binding-competent state, which, in turn, is linked to an increase in fluorescence. (b and c) Optimal detection limits are achieved at intermediate values of the switching equilibrium constant (KS) as this produces a switch that, in the absence of target, is predominantly in its dark “non-binding” state without overstabilizing it, which would reduce the beacon’s affinity (Supporting Figure 1).17
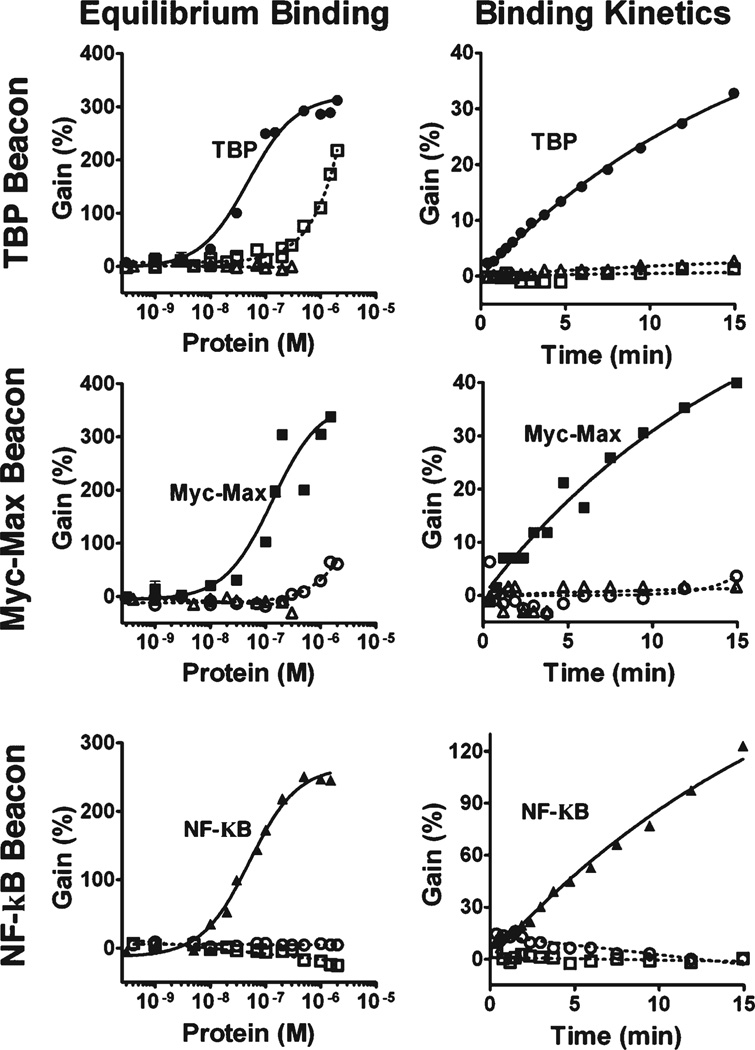
As our first proof-of-principle, we fabricated a TF beacon that detects the DNA binding activity of TATA binding protein (TBP), a TF present in virtually all eukaryotic cells.21 As predicted via simulation (Supporting Figure 1),17 the beacon achieves near optimal detection limits at a switching equilibrium constant, KS, between 0.2 and 1 (Figure 1b,c). This balances the trade-off between signal gain (optimal at lower KS) and DNA binding affinity (optimal at higherKS) (Supporting Figure 2).17 TheKS-optimized TF beacon exhibits a fluorescence gain of about 300% at saturating TBP concentrations and readily detects nanomolar target in less than 10 min (Figure 2, top-right). The sensor exhibits little (but, due to cross-specificity of TF binding, not zero18,19) cross reactivity with other TFs (Figure 2, top panels).
Figure 2.
TF beacons are versatile, specific, sensitive and rapid. (Left) TF beacons for the detection of TBP (circles, KD = 45 ± 3 nM), Myc-Max (squares, KD = 134 ± 41 nM), and NF-κB (triangles, KD = 53 ± 12 nM) exhibit nanomolar detection limits and little (but, as expected, not zero18,19) cross reactivity with the other targets (open symbols). (Right) TF beacons respond rapidly to their specific targets (at 10 nM for TBP and 40 nM for Myc-Max and NF-κB) while, again, exhibiting little cross reactivity with other targets (other targets at 40 nM). The switching equilibrium constants (KS) of the sensors employed here are 0.2, 0.3, and 0.3 respectively, and represent optimal trade-offs between sensor gain and DNA binding affinity (Supporting Figure 1).17
Motivated by our success in the detection of TBP, we designed TF beacons targeting Myc-Max and NF-κB (Figure 2, middle, bottom panels), two unrelated TFs that are potential targets for the treatment of cancer and immune system diseases.22,23 Both achieve similarly sensitive and rapid detection of their target DNA binding proteins and exhibit little (but again, as expected, not zero18,19) cross reactivity with other TFs (Figure 2, middle, bottom panels).
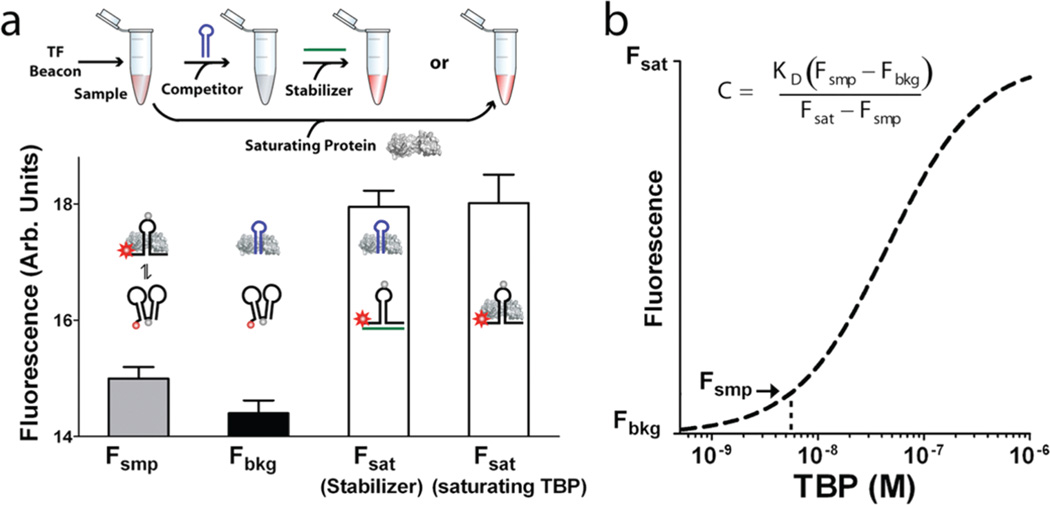
The specificity and selectivity of switch-based sensors6 is such that TF beacons enable the rapid, convenient quantification of active DNA binding proteins directly in crude nuclear extract (Supporting Figure 3 and Figure 3). Indeed, we have used them to develop a single tube assay that requires only three fluorescence measurements to, respectively, establish the fluorescence of the beacon when it is in equilibrium with the endogenous TF in the sample, when it is fully unbound, and when it is fully in its emissive conformation (Figure 3a and Supporting Methods). This assay consists of adding the TF beacon to the sample and measuring its fluorescence signal when in equilibrium with the TF. Then, an excess of a nonfluorescent, nonswitching double-stranded DNA is added as a competitor to determine the fluorescence of the fully unbound beacon. This is followed by the addition of a single-stranded DNA that binds to and stabilizes the beacon in its fully emissive configuration. Using this simple, single-tube, three-measurement assay, we have determined the endogenous TBP concentration in crude, 250 µg/mL HeLa nuclear extract to be 5.8 ± 1.6 nM (Figure 3b; the confidence interval represents the standard error of 4 independent measurements). This value is in close agreement with the ~5 nM concentration obtained using gel shift assay (Supporting Figure 4); however, our single-tube assay requires approximately a fifth of the time, half the sample, and many fold less effort than is required by the “gold standard” gel shift approach.
Figure 3.
TF beacons support the quantification of DNA-binding activity directly in crude nuclear extracts. (a) This requires three fluorescence measurements, which are performed in a single tube: Fsmp, the fluorescence of the TF beacon in equilibrium with the endogenous target in the sample; Fbkg, the fluorescence of the TF beacon when unbound, obtained by adding a saturating concentration of a competitor DNA (blue); and Fsat, the fluorescence of the TF beacon in its fully bound state, which is obtained by adding either a DNA “stabilizer” (green) or excess target, each of which stabilize the beacon’s emissive conformation. (b) From the known dissociation constant of the beacon, we then estimate the target concentration. For active TBP, we measure a concentration of 5.8 ± 1.6 nM (or 5.7 ± 1.7 nM if Fsat is obtained using saturating TBP) in HeLa nuclear extract, which is within error of the value obtained using a traditional gel shift assay (Supporting Methods and Supporting Figure 4).
The TF beacons we have described herein represent a versatile new class of binding-activated probes for the monitoring of specific DNA binding activity. These new probes achieve biologically relevant specificities and detection limits. They are also convenient and quantitative; using them we have measured the concentration of a specific, active TF directly in crude nuclear extract in an inexpensive, three-measurement, single-tube assay. Finally, using free software tools20 (Supporting Methods) and commercial, automated DNA synthesis, TF beacons are easily designed and conveniently obtained for a wide range of DNA binding proteins. This convenience and ease of fabrication suggests that TF beacons would be amenable to high-throughput analysis, and their use of commercial dye–quencher pairs should enable facile multiplexing.
TF beacons appear to provide significant advantages over existing methods for the detection of DNA binding activity. For example, the reagentless, activatable format of TF beacons drastically simplifies the detection of active DNA binding proteins by eliminating washing and/or transfer steps (e.g., ELISA, Western blots), electrophoresis (e.g., gel shift assay), and the need to generate specific antibodies (e.g., ELISAs). TF beacons are likewise much more selective than fluorescence anisotropy-based detection approaches, which are limited to use in highly purified samples11 and more general than, for example, the “switch-like” proximity assay of Heyduk et al.,13 which requires two covalent breaks within the DNA recognition sequence, limiting the number of target proteins it can detect.11 Finally, given their binding-induced signal activation, TF beacons should provide an ideal quantitative probe for the in vivo monitoring of DNA-binding activity as they likely exhibit much greater contrast than “constitutively on” antibody-based imaging technologies (see, by analogy, the successes of molecular beacons for intracellular use16). Given these attributes, we believe that TF beacons may prove of significant utility in a range of applications, including drug screening, cancer diagnostics, and developmental biology, where interest in the quantitative regulation of TFs is rapidly growing.22–25
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors wish to thank Brett and Ron Cook of Biosearch Technology and Aaron Rowe and Anna Simon for helpful discussions regarding this work. This work was supported by NIH grant R01EB007689. A.V.-B. is a Fond Québécois de la Recherche sur la Nature et les Technologies Fellow. A.J.B. is a Tri-County Blood Bank Santa Barbara Foundation Fellow.
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
Supporting Information. Supporting methods, figures, DNA sequences and complete ref 18. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
REFERENCES
- 1.Patricelli MP. Briefings Funct. Genomics Proteomics. 2002;1:151–158. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/1.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simon GM, Cravatt BF. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008;4:639–642. doi: 10.1038/nchembio1108-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Speers AE, Adam GC, Cravatt BF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:4686–4687. doi: 10.1021/ja034490h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cravatt BF, Wright AT, Kozarich JW. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008;77:383–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.101304.124125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wang K, Tang Z, Yang CJ, Kim Y, Fang X, Li W, Wu Y, Medley CD, Cao Z, Li J, Colon P, Lin H, Tan W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009;48:856–870. doi: 10.1002/anie.200800370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vallée-Bélisle A, Plaxco KW. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2010;20:518–526. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2010.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nutiu R, Li YJ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:4771–4778. doi: 10.1021/ja028962o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stojanovic MN, Kolpashchikov DM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:9266–9270. doi: 10.1021/ja032013t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fang X, Li JJ, Tan W. Anal. Chem. 2000;72:3280–3285. doi: 10.1021/ac991434j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Babu MM, Luscombe NM, Aravind L, Gerstein M, Teichmann SA. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004;14:283–291. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jantz D, Berg JM. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002;20:126–127. doi: 10.1038/nbt0202-126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Garner MM, Revzin A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981;9:3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Heyduk T, Heyduk E. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002;20:171–176. doi: 10.1038/nbt0202-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tyagi S, Kramer FR. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996;14:303–308. doi: 10.1038/nbt0396-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hamaguchi N, Ellington A, Stanton M. Anal. Biochem. 2001;294:126–131. doi: 10.1006/abio.2001.5169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tyagi S. Nat. Methods. 2009;6:331–338. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vallee-Belisle A, Ricci F, Plaxco KW. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2009;106:13802–13807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0904005106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Badis G, et al. Science. 2009;324:1720–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.1162327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sandelin A, Alkema W, Engstrom P, Wasserman WW, Lenhard B. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:D91–D94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rouillard JM, Zuker M, Gulari E. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3057–3062. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hernandez N. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1291–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Darnell JE., Jr Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:740–749. doi: 10.1038/nrc906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hermeking H. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2003;3:163–175. doi: 10.2174/1568009033481949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Latchman DS. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;334:28–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199601043340108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2006;5:993–996. doi: 10.1038/nrd2199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.