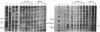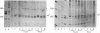Abstract
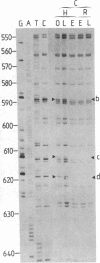
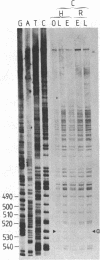
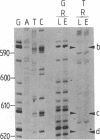
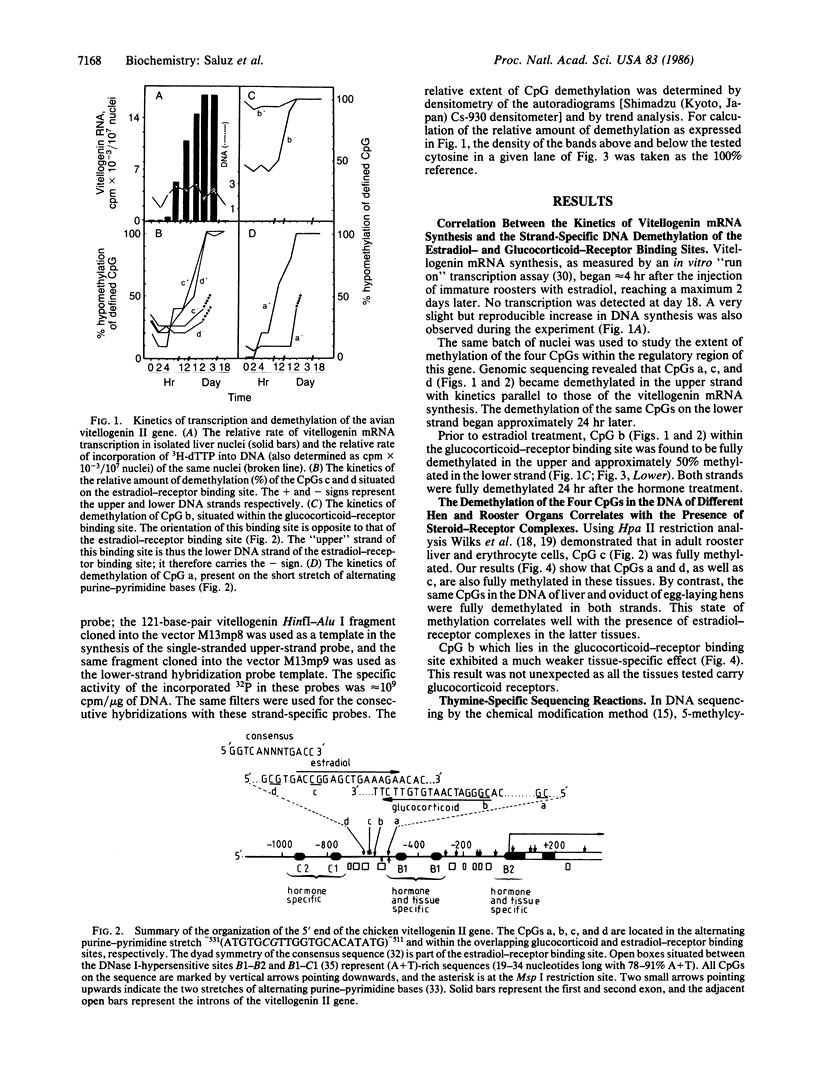
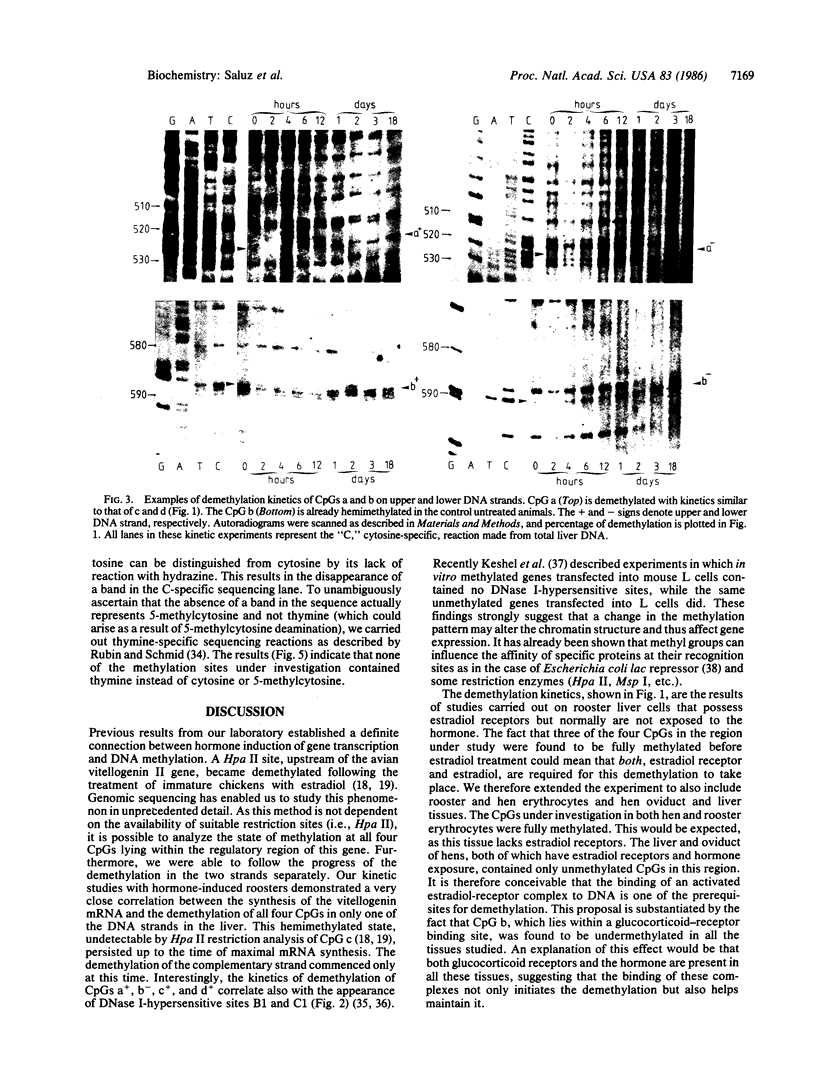
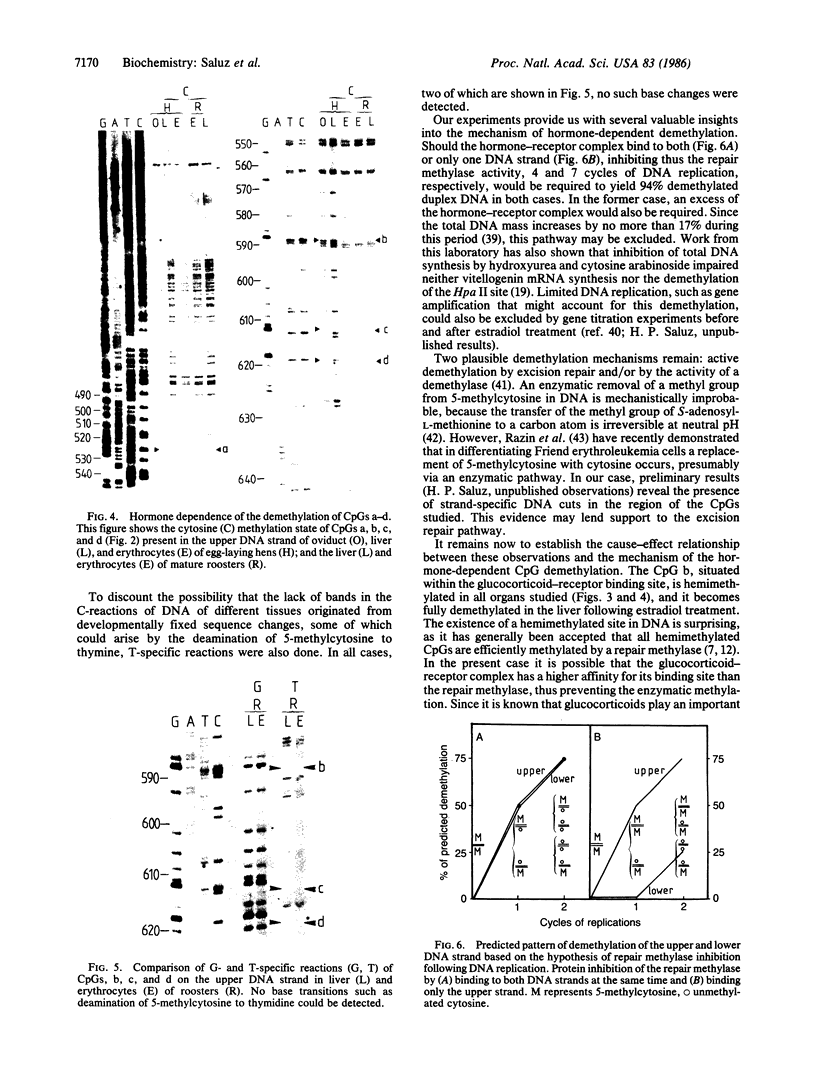
Genomic sequencing was used to study the extent of cytosine methylation of four CpG sites within the regulatory region of the estradiol-inducible avian vitellogenin II gene. Three of these sites, two of which lie within the estradiol-receptor binding site and one in a short stretch of alternating purines and pyrimidines, were initially fully methylated. Analysis of DNA isolated from liver nuclei revealed that hormone treatment of immature White Leghorn roosters resulted in a demethylation of these sites, which occurred initially in only one DNA strand. This demethylation correlated well with the induction of vitellogenin mRNA synthesis. The demethylation of the complementary DNA strand lagged approximately equal to 24 hr behind. The fourth CpG, located within an overlapping glucocorticoid-receptor binding site, was already hemimethylated at the onset of the experiment. The demethylation of this site also occurred with kinetics similar to the rate of vitellogenin mRNA synthesis. All four CpGs remained demethylated even after cessation of gene transcription. A comparison of the methylation state of these four sites in DNA from different tissues demonstrated a clear dependence of the demethylation on estradiol. Our results suggest that this hormone-dependent event occurs via an active pathway through excision repair and/or enzymatic demethylation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. Methylation of the genes for 18S, 28S, and 5S ribosomal RNA. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;108:129–141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69370-0_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B. Identification and sequence analysis of the 5' end of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1117–1135. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Udell D. S., Burns A. T., Gordon J. I., Goldberger R. F. Kinetics of avian vitellogenin messenger RNA induction. Comparison between primary and secondary response to estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7913–7915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Wang R. Y. 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1981 Jun 19;212(4501):1350–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.6262918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. Methylation and gene control. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):602–603. doi: 10.1038/296602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H. Studies on gene control regions XII. The functional significance of a lac operator constitutive mutation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):401–416. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser M., Mattaj I. W., Wilks A. F., Seldran M., Jost J. P. Structure and sequence of the promoter area and of a 5' upstream demethylation site of the estrogen-regulated chicken vitellogenin ii gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):9024–9030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjerset R. A., Martin D. W., Jr Presence of a DNA demethylating activity in the nucleus of murine erythroleukemic cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8581–8583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Cedar H., Razin A. Restriction enzyme digestion of hemimethylated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2509–2515. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward M. A., Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Activation of vitellogenin gene transcription is a direct response to estrogen in Xenopus laevis liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8273–8284. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers H. G., Hue L. Gluconeogenesis and related aspects of glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:617–653. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Pugh J. E. DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Jähner D. Methylation, expression and chromosomal position of genes in mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 15;782(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Geiser M., Seldran M. Specific modulation of the transcription of cloned avian vitellogenin II gene by estradiol-receptor complex in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):988–991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Keller R., Dierks-Ventling C. Deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid synthesis during phosvitin induction by 17beta-estradiol in immature chicks. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5262–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Moncharmont B., Jiricny J., Saluz H., Hertner T. In vitro secondary activation (memory effect) of avian vitellogenin II gene in isolated liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Ohno T., Panyim S., Schuerch A. R. Appearance of vitellogenin mRNA sequences and rate of vitellogenin synthesis in chicken liver following primary and secondary stimulation by 17 beta-estradiol. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Schuerch A. R., Walz A. Reiteration frequency of vitellogenin gene in avian liver before and after estradiol treatment. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F. C., Philipsen J. N., Gruber M., Ab G. Methylation of the chicken vitellogenin gene: influence of estradiol administration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1361–1373. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod J. J., Bourgeois S., Defer N., Crépin M. Demethylation and expression of murine mammary tumor proviruses in mouse thymoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):110–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Yuan R. DNA restriction enzyme from E. coli. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1110–1114. doi: 10.1038/2171110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Ohno T., Jost J. P. In vitro RNA synthesis and expression of vitellogenin gene in isolated chicken liver nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1353–1370. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Friedman J. DNA methylation and its possible biological roles. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:33–52. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Szyf M., Kafri T., Roll M., Giloh H., Scarpa S., Carotti D., Cantoni G. L. Replacement of 5-methylcytosine by cytosine: a possible mechanism for transient DNA demethylation during differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Schmid C. W. Pyrimidine-specific chemical reactions useful for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4613–4619. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Wahli W., Weber R. Quantitation of vitellogenin messenger RNA in the liver of male Xenopus toads during primary and secondary stimulation by estrogen. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Kitchin R. Selective silencing of eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1975 Aug 8;189(4201):426–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H., Jost J. P. Optimized genomic sequencing as a tool for the study of cytosine methylation in the regulatory region of the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Gene. 1986;42(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer G., Cadepond-Vincent F., Baulieu E. E. Nuclear synthesis of egg white protein messenger ribonucleic acids in chick oviduct: effects of the anti-estrogen tamoxifen on estrogen-, progesterone-, and dexamethasone-induced synthesis. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 26;24(7):1742–1749. doi: 10.1021/bi00328a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Tata J. R. Vitellogenin gene expression in male Xenopus hepatocytes during primary and secondary stimulation with estrogen in cell cultures. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):741–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Cozens P. J., Mattaj I. W., Jost J. P. Estrogen induces a demethylation at the 5' end region of the chicken vitellogenin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4252–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A., Cato A. C., Cozens P. J., Mattaj I. W., Jost J. P. Isolation and fine structure organisation of an avian vitellogenin gene coding for the major estrogen-inducible mRNA. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A., Seldran M., Jost J. P. An estrogen-dependent demethylation at the 5' end of the chicken vitellogenin gene is independent of DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1163–1177. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]