Abstract
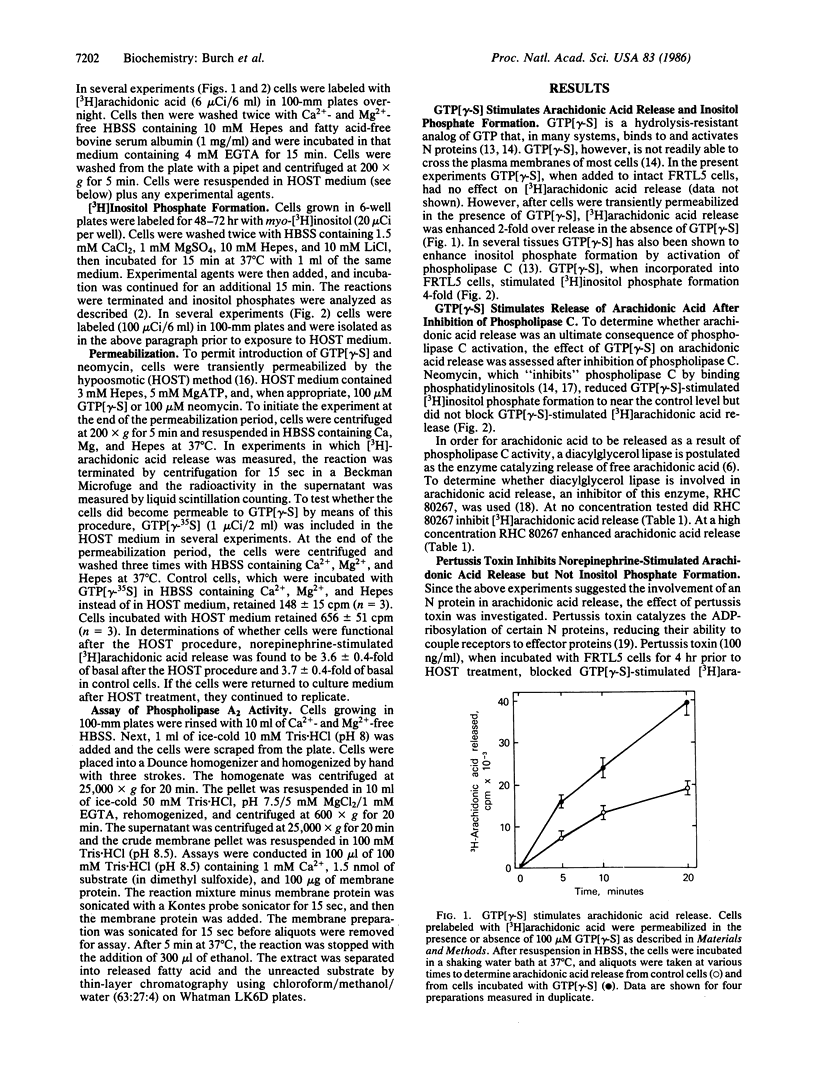
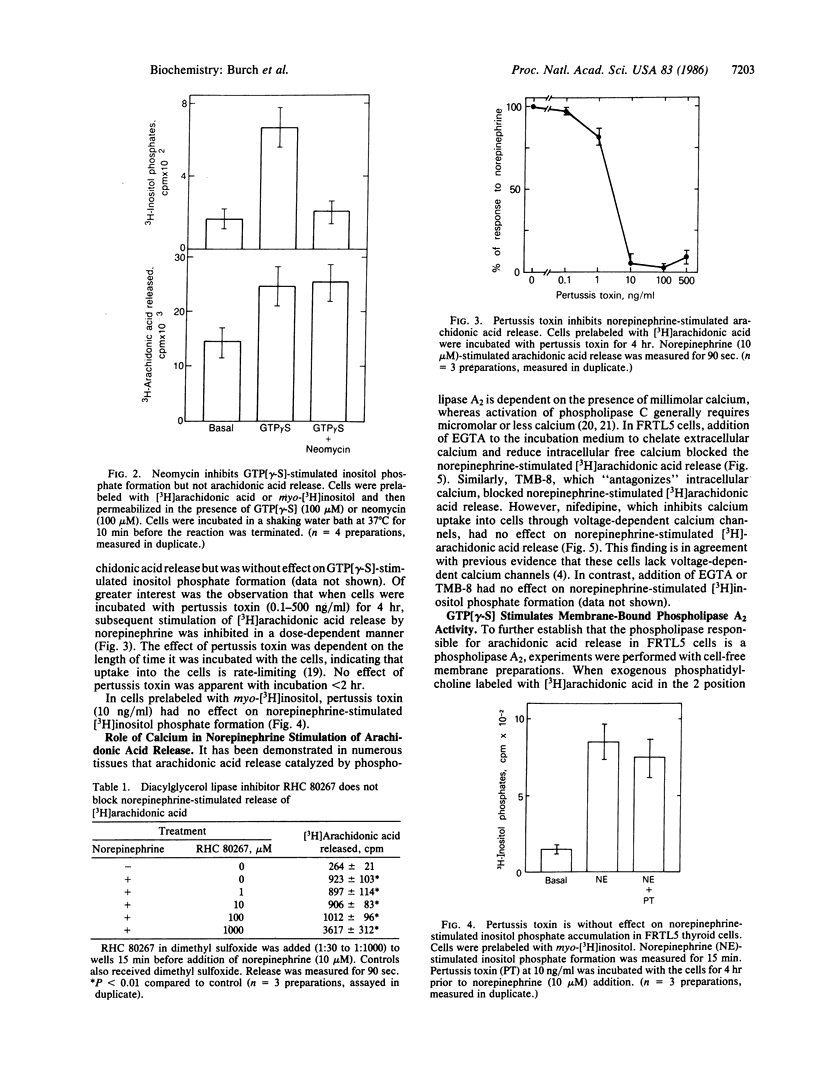
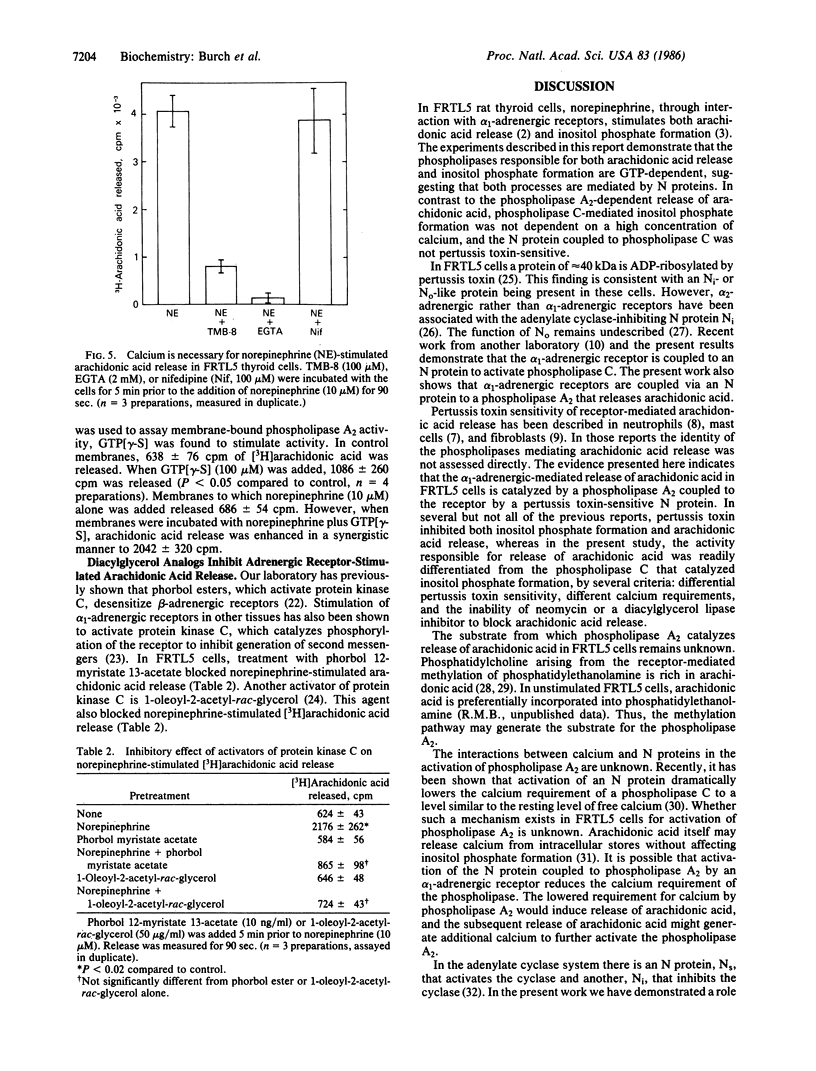
In FRTL5 rat thyroid cells, norepinephrine, by interacting with alpha 1-adrenergic receptors, stimulates inositol phosphate formation, through activation of phospholipase C, and arachidonic acid release. Recent studies have shown that GTP-binding proteins couple several types of receptors to phospholipase C activation. The present study was undertaken to determine whether GTP-binding proteins couple alpha 1-adrenergic receptors to stimulation of phospholipase C activity and arachidonic acid release. When introduced into permeabilized FRTL5 cells, guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[gamma-S]), which activates many GTP-binding proteins, stimulated inositol phosphate formation and arachidonic acid release. Neomycin inhibited GTP[gamma-S]-stimulated inositol phosphate formation but was without effect on GTP[gamma-S]-stimulated arachidonic acid release, suggesting that separate GTP-binding proteins mediate each process. In addition, pertussis toxin inhibited norepinephrine-stimulated arachidonic acid release but not norepinephrine-stimulated inositol phosphate formation. Norepinephrine-stimulated arachidonic acid release but not inositol phosphate formation was also inhibited by decreased extracellular calcium and by TMB-8, suggesting a role for a phospholipase A2. To confirm that arachidonic acid was released by a phospholipase A2, FRTL5 membranes were incubated with 1-acyl-2-[3H]arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. GTP[gamma-S] slightly stimulated arachidonic acid release, whereas norepinephrine acted synergistically with GTP[gamma-S] to stimulate arachidonic acid release. The results show that phospholipase C and phospholipase A2 are activated by alpha 1-adrenergic agonists. Both phospholipases are coupled to the receptor by GTP-binding proteins. That coupled to phospholipase A2 is pertussis toxin-sensitive, whereas that coupled to phospholipase C is pertussis toxin-insensitive.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B., Snowdowne K. W. Measurement of intracellular free calcium in monkey kidney cells with aequorin. Science. 1982 Jul 16;217(4556):252–254. doi: 10.1126/science.6806904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda D., Kohn L. D. Thyrotropin upregulates alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in rat FRTL-5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8677–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda D., Marcocci C., Kohn L. D., Axelrod J., Luini A. Association of the changes in cytosolic Ca2+ and iodide efflux induced by thyrotropin and by the stimulation of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in cultured rat thyroid cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9230–9236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews F. T., Morita Y., McGivney A., Hirata F., Siraganian R. P., Axelrod J. IgE-mediated histamine release in rat basophilic leukemia cells: receptor activation, phospholipid methylation, Ca2+ flux, and release of arachidonic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Dec;212(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. The importance of phospholipase-A2 in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Feb 1;25(3):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. L., Ueda T., Chueh S. H., Noel M. W. Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum is mediated by a guanine nucleotide regulatory mechanism. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):461–464. doi: 10.1038/320461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., Lomasney J. W., DeBernardis J. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Phorbol esters promote alpha 1-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and receptor uncoupling from inositol phospholipid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5651–5655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallorga P., Tallman J. F., Henneberry R. C., Hirata F., Strittmatter W. T., Axelrod J. Mepacrine blocks beta-adrenergic agonist-induced desensitization in astrocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1341–1345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase and stimulation of arachidonic acid release in 3T3 fibroblasts. Selective susceptibility to islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7226–7233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philp N. J., Grollman E. F. Thyrotropin and norepinephrine stimulate the metabolism of phosphoinositides in FRTL-5 thyroid cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 7;202(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A. F., LANDS W. E. Positional specificites in phospholipid hydrolyses. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:804–810. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Inhibition by neomycin of polyphosphoinositide turnover in subcellular fractions of guinea-pig cerebral cortex in vitro. J Neurochem. 1976 Nov;27(5):1119–1124. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb00318.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Properties and distribution of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in human and horse platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 12;752(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Cox C. C., Snyderman R. Receptor-coupled activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C by an N protein. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):97–100. doi: 10.1126/science.3006254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Gershengorn M. C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and GTP activate inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes isolated from rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2712–2717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland C. A., Amin D. Relative activities of rat and dog platelet phospholipase A2 and diglyceride lipase. Selective inhibition of diglyceride lipase by RHC 80267. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14006–14010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacconi M., Wurtman R. J. Phosphatidylcholine produced in rat synaptosomes by N-methylation is enriched in polyunsaturated fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4828–4831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. A., Fain J. N. Guanosine 5'-O-thiotriphosphate stimulates phospholipase C activity in plasma membranes of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9527–9530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Philp N. J., Grollman E. F. Effect of thyrotropin on iodide efflux in FRTL-5 cells mediated by Ca2+. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1108–1113. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Turk J., Sherman W. R., McDaniel M. L. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization by arachidonic acid. Comparison with myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in isolated pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3501–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



