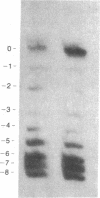
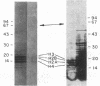
Abstract
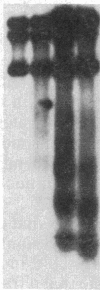
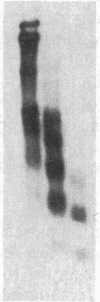
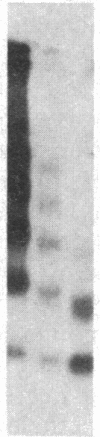
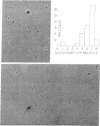
A multicopy yeast plasmid containing the TRP1 gene (coding for N-5'-phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase) and ARS1 (autonomously replicating sequence 1) has been purified as chromatin. Electrophoretic analysis of nucleic acid and proteins and electron microscopy show that the plasmid chromatin is largely free of contaminants. Electron-microscopic and linking-number analyses indicate that the plasmid chromatin contains seven nucleosomes, as predicted by the indirect end-label analyses of Thoma, Bergman, and Simpson [J. Mol. Biol. (1984) 177, 715-733]. Indirect end label mapping of micrococcal nuclease cuts demonstrates that nucleosome positions and nuclease-sensitive regions are not altered by the purification. The plasmid chromatin behaves homogeneously with respect to its elution from nuclei, template activity, and intrinsic buoyant density. Taken together, these observations suggest that different copies of the TRP1ARS1 plasmid do not differ from each other grossly in chromatin structure. We discuss the potential for understanding eukaryotic gene regulation offered by the ability to isolate unique genes as chromatin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausio J., Seger D., Eisenberg H. Nucleosome core particle stability and conformational change. Effect of temperature, particle and NaCl concentrations, and crosslinking of histone H3 sulfhydryl groups. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):77–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celniker S. E., Sweder K., Srienc F., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. Deletion mutations affecting autonomously replicating sequence ARS1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2455–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. W., Hamkalo B. A. Nucleosome dissociation at physiological ionic strengths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):445–457. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Wides R. J., Sollner-Webb B. Eucaryotic transcription complexes are specifically associated in large sedimentable structures: rapid isolation of polymerase I, II, and III transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1582–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Transcription occurs at a nucleoskeleton. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):919–925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Koller T. Electron microscope specimen preparation of rat liver chromatin by a modified Miller spreading technique. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;24(2):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. M., Brajkovich C. M., Scott J. F. Alternative model for chromatin organization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomal DNA plasmid TRP1 RI circle (YARp1). Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3124–3130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Georgiev G. P. Non-random cleavage of SV40 DNA in the compact minichromosome and free in solution by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. S., Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Core particle, fiber, and transcriptionally active chromatin structure. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:117–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson D. S., Yao M. C., Kimmel A. R., Gorovsky M. A. Sequence organization within and flanking clusters of 5S ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):3003–3021. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.3003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashkin J. A., Zeigel R. F., Huberman J. A. Isolation and initial characterization of residual nuclear structures from yeast. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Aug;153(2):374–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90607-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdson D. C., Gaarder M. E., Livingston D. M. Characterization of the transmission during cytoductant formation of the 2 micrometers DNA plasmid from Saccharomyces. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(1):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00270139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Thoma F., Brubaker J. M. Chromatin reconstituted from tandemly repeated cloned DNA fragments and core histones: a model system for study of higher order structure. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srienc F., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. Effect of ARS1 mutations on chromosome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1676–1684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. R. Analytical methods for yeasts. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:111–147. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60955-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Bergman L. W., Simpson R. T. Nuclease digestion of circular TRP1ARS1 chromatin reveals positioned nucleosomes separated by nuclease-sensitive regions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):715–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A., Scott J. F. Construction, replication, and chromatin structure of TRP1 RI circle, a multiple-copy synthetic plasmid derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):221–232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]