Abstract
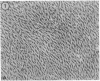
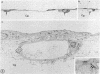
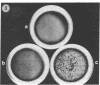
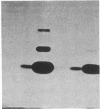
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are potent mitogens for vascular and capillary endothelial cells in vitro and can stimulate the formation of blood capillaries (angiogenesis) in vivo. A crucial event in this process is the invasion of the perivascular extracellular matrix by sprouting endothelial cells. Using a recently developed in vitro model of angiogenesis, we show here that highly purified basic pituitary FGF can induce capillary endothelial cells to invade a three-dimensional collagen matrix and to organize themselves to form characteristic tubules that resemble blood capillaries. We also show that basic FGF concomitantly stimulates endothelial cells to produce a urokinase-type plasminogen activator, a protease that has been implicated in the neovascular response. The results demonstrate that basic FGF can stimulate processes that are characteristic of angiogenesis in vivo, including endothelial cell migration, invasion, and production of plasminogen activator.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessandri G., Raju K., Gullino P. M. Mobilization of capillary endothelium in vitro induced by effectors of angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1790–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausprunk D. H., Folkman J. Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jul;14(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banda M. J., Knighton D. R., Hunt T. K., Werb Z. Isolation of a nonmitogenic angiogenesis factor from wound fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M. In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 1. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1980 Dec;8(2):153–197. doi: 10.3109/10408448009037493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Karnovsky M. J., Spiegelman B. M. Differentiation-dependent stimulation of neovascularization and endothelial cell chemotaxis by 3T3 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5597–5601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellot J. J., Jr, Karnovsky M. J., Spiegelman B. M. Potent stimulation of vascular endothelial cell growth by differentiated 3T3 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6007–6011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A., Glaser B. M., Brunson S. K., Fenselau A. H. Angiogenic activity from bovine retina: partial purification and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3068–3072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L., O'Brien T. G., Baird W. M. Tumor promoters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Adv Cancer Res. 1980;32:1–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60360-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Ueno N., Baird A., Hill F., Denoroy L., Ling N., Gospodarowicz D., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine brain acidic fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90942-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. C., Zetter B. R. Long-term culture of capillary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;43:175–203. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie M. B., Cramer E. B., Naprstek B. L., Silverstein S. C. Cultured endothelial cell monolayers that restrict the transendothelial passage of macromolecules and electrical current. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1033–1041. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Leapman S. B., Folkman J. Tumor growth and neovascularization: an experimental model using the rabbit cornea. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):413–427. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Bialecki H., Thakral T. K. The angiogenic activity of the fibroblast and epidermal growth factor. Exp Eye Res. 1979 May;28(5):501–514. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(79)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Böhlent P. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6963–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Moscatelli D., Jaffe E. A., Rifkin D. B. Plasminogen activator and collagenase production by cultured capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):974–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. Increased capillary endothelial cell protease activity in response to angiogenic stimuli in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Knighton D., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis activity in cells grown in tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1976 Jan;36(1):110–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Orci L. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters induce angiogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):469–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins D. E., Rifkin D. B. Stimulation of motility in cultured bovine capillary endothelial cells by angiogenic preparations. J Cell Physiol. 1984 May;119(2):247–254. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041190216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor A. M., Schor S. L., Weiss J. B., Brown R. A., Kumar S., Phillips P. Stimulation by a low-molecular-weight angiogenic factor of capillary endothelial cells in culture. Br J Cancer. 1980 May;41(5):790–799. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyama Y., Tanimoto T., Hoshijima M., Kaibuchi K., Ohyanagi H., Saitoh Y., Takai Y. Enhancement of fibroblast growth factor-induced diacylglycerol formation and protein kinase C activation by colon tumor-promoting bile acid in Swiss 3T3 cells. Different modes of action between bile acid and phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Giménez-Gallego G., DiSalvo J., Bennett C., Rodkey J., Fitzpatrick S. Pure brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor is a potent angiogenic vascular endothelial cell mitogen with sequence homology to interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., Kawahara Y., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Induction of protein kinase C activation and Ca2+ mobilization by fibroblast growth factor in Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Dayer J. M., Wohlwend A., Belin D. Concomitant secretion of prourokinase and of a plasminogen activator-specific inhibitor by cultured human monocytes-macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1653–1668. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Hamilton J., Reich E. Macrophage plasminogen activator: induction by concanavalin A and phorbol myristate acetate. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):695–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B. Current concepts and controversies in chemical carcinogenesis. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;17(2):99–120. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.380170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetter B. R. Migration of capillary endothelial cells is stimulated by tumour-derived factors. Nature. 1980 May 1;285(5759):41–43. doi: 10.1038/285041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]