Abstract
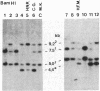
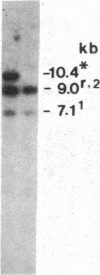
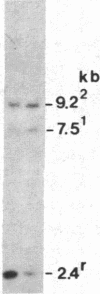
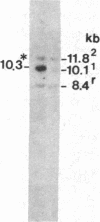
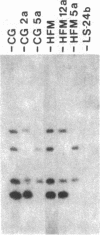
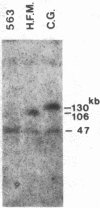
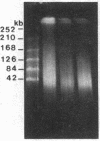
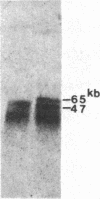
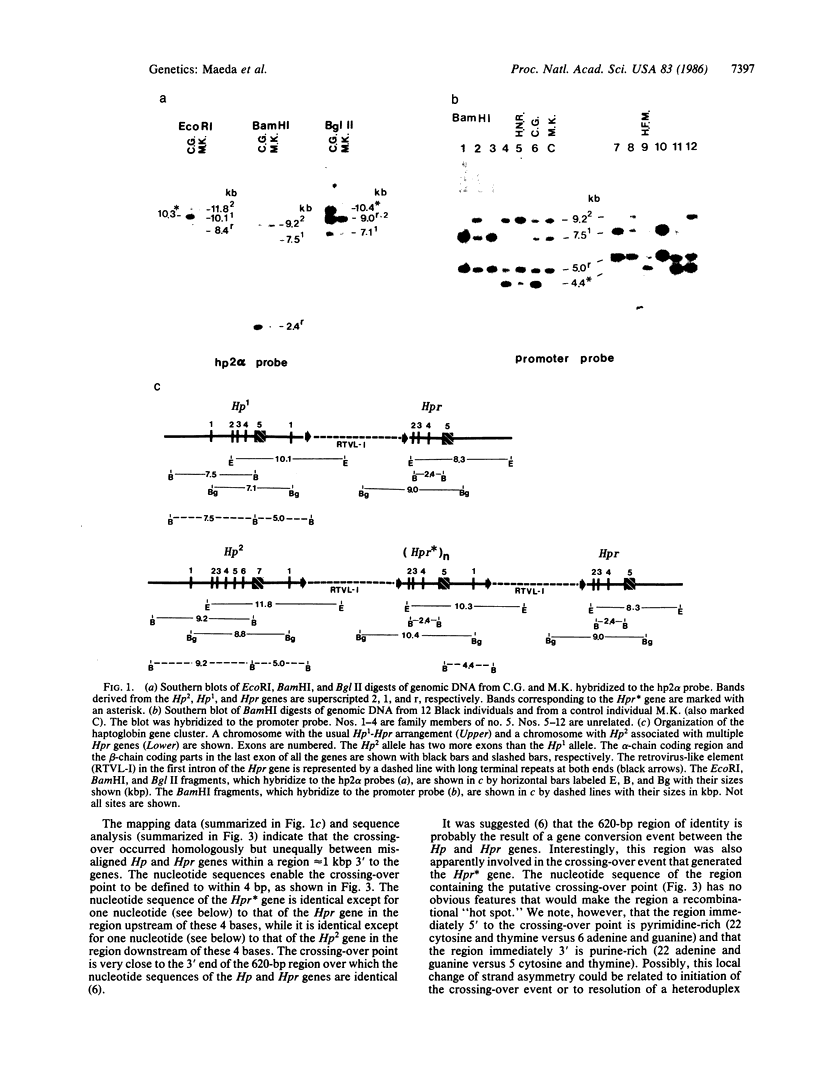
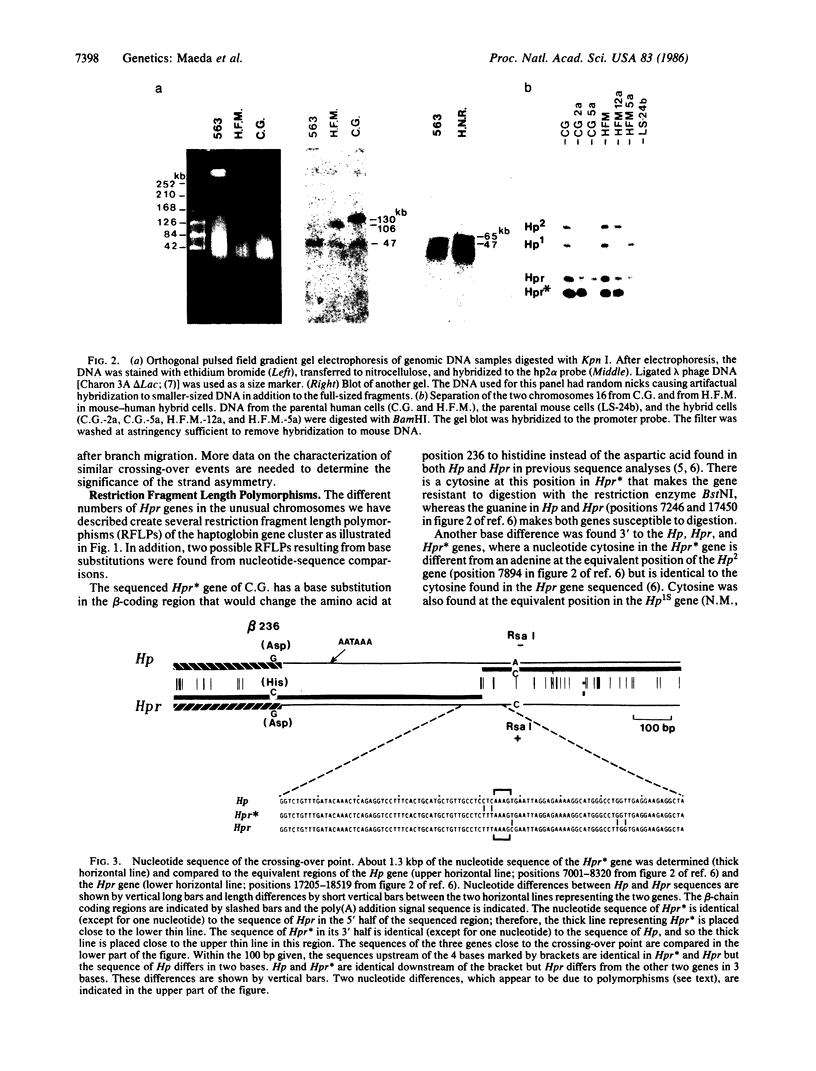
We have found polymorphisms for the number of tandemly arranged haptoglobin-related (Hpr) genes in the haptoglobin gene cluster of Blacks. Genomic mapping and nucleotide sequence analysis indicate that two copies of the Hpr gene first resulted from unequal but homologous crossing-over in a region 3' to the haptoglobin (Hp) and the haptoglobin-related genes. Subsequent increases in the number of Hpr loci have occurred in some chromosomes. Among 25 American Blacks studied (15 were unrelated), 2 related individuals have one extra copy of the Hpr gene and 5 unrelated individuals have more than two extra Hpr genes. None of 26 Whites and one Oriental studied have extra copies. In one of the Blacks, six tandemly arranged Hpr genes were demonstrated in one chromosome by pulsed field gradient electrophoresis. His other chromosome had one Hpr gene. The tandem Hpr genes were found in individuals with the haptoglobin genotypes Hp2/Hp2 (3 of 3 tested) and Hp2/Hp1 (4 of 11 tested), but none were found in the Hp1/Hp1 individuals (11 tested). Fibroblast cell cultures from two Hp2/Hp1 heterozygotes were fused to mouse cells to obtain cell lines retaining a human chromosome 16 on which the haptoglobin gene cluster is located. DNA analysis of the hybrid cells showed that in both individuals the tandemly arranged Hpr genes are linked to the Hp2 allele. These results suggest that the multiple copies are associated with the Hp2 gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensi G., Raugei G., Klefenz H., Cortese R. Structure and expression of the human haptoglobin locus. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):119–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. A general method for preparing intact nuclear DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Gerald P. S. Improved techniques for the induction of mammalian cell hybridization by polyethylene glycol. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01542629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V., Bowden D. K., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Chromosomes with one, two, three, and four fetal globin genes: molecular and hematologic analysis. Blood. 1986 Jun;67(6):1611–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Bliska J. B., Smithies O. Recombination and balanced chromosome polymorphism suggested by DNA sequences 5' to the human delta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5012–5016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N. Nucleotide sequence of the haptoglobin and haptoglobin-related gene pair. The haptoglobin-related gene contains a retrovirus-like element. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6698–6709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Smithies O. The evolution of multigene families: human haptoglobin genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:81–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Yang F., Barnett D. R., Bowman B. H., Smithies O. Duplication within the haptoglobin Hp2 gene. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):131–135. doi: 10.1038/309131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuji T., Carver J., Wilson J. B., Lam H., Reese A. L., Nagle S., Miwa S., Huisman T. H. alpha Chain and gamma chain abnormal hemoglobins in newborn babies: structural and genetic aspects. Am J Hematol. 1983 Apr;14(2):121–132. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830140204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Harpel B., Mory Y., Schwartz E., Surrey S. Construction of human gene libraries from small amounts of peripheral blood: analysis of beta-like globin genes. Hemoglobin. 1982;6(1):27–36. doi: 10.3109/03630268208996930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers P. A., Altay C., Huisman T. H., Smithies O. Two novel arrangements of the human fetal globin genes: G gamma-G gamma and A gamma-A gamma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7023–7034. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raugei G., Bensi G., Colantuoni V., Romano V., Santoro C., Costanzo F., Cortese R. Sequence of human haptoglobin cDNA: evidence that the alpha and beta subunits are coded by the same mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5811–5819. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimasaki S., Iuchi I. Diversity of human gamma-globin gene loci including a quadruplicated arrangement. Blood. 1986 Mar;67(3):784–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Trill J. J., Lee Y. I., Coy K., Taylor M. W. Genetic instability at the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus in mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):250–257. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Brune J. L., Baldwin W. D., Barnett D. R., Bowman B. H. Identification and characterization of human haptoglobin cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5875–5879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vander Straten A., Herzog A., Jacobs P., Cabezón T., Bollen A. Molecular cloning of human haptoglobin cDNA: evidence for a single mRNA coding for alpha 2 and beta chains. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):1003–1007. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]