Abstract
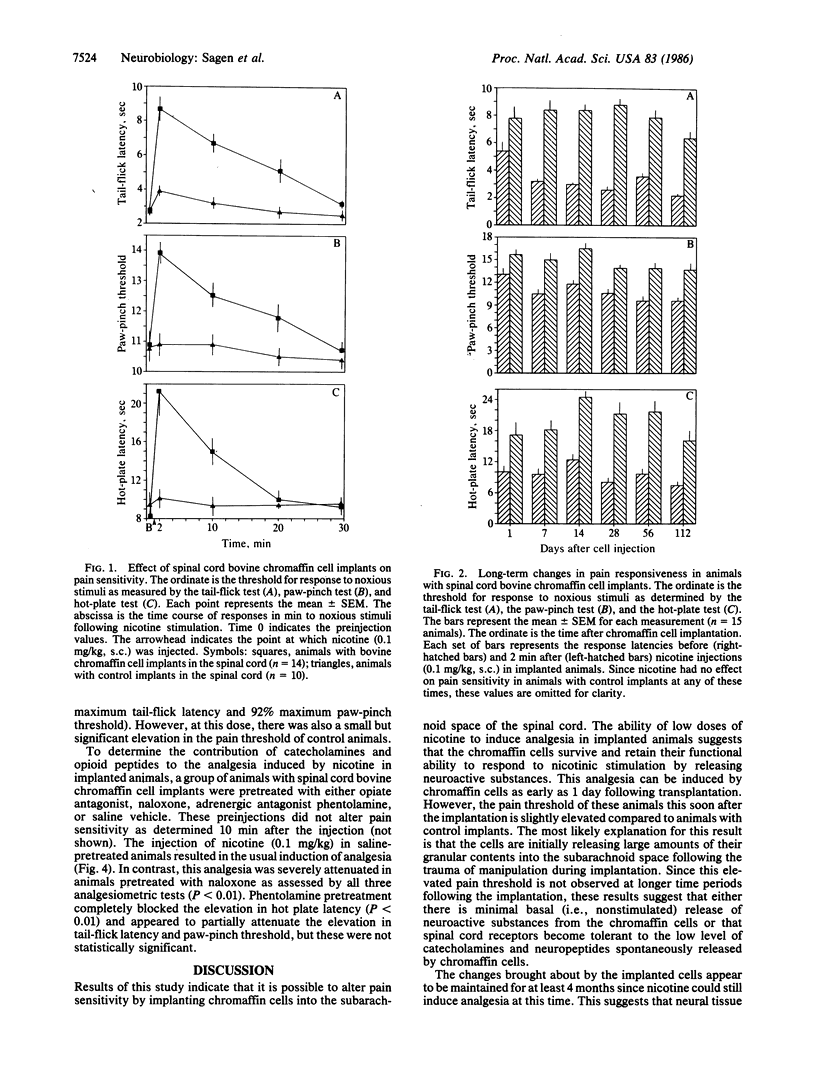
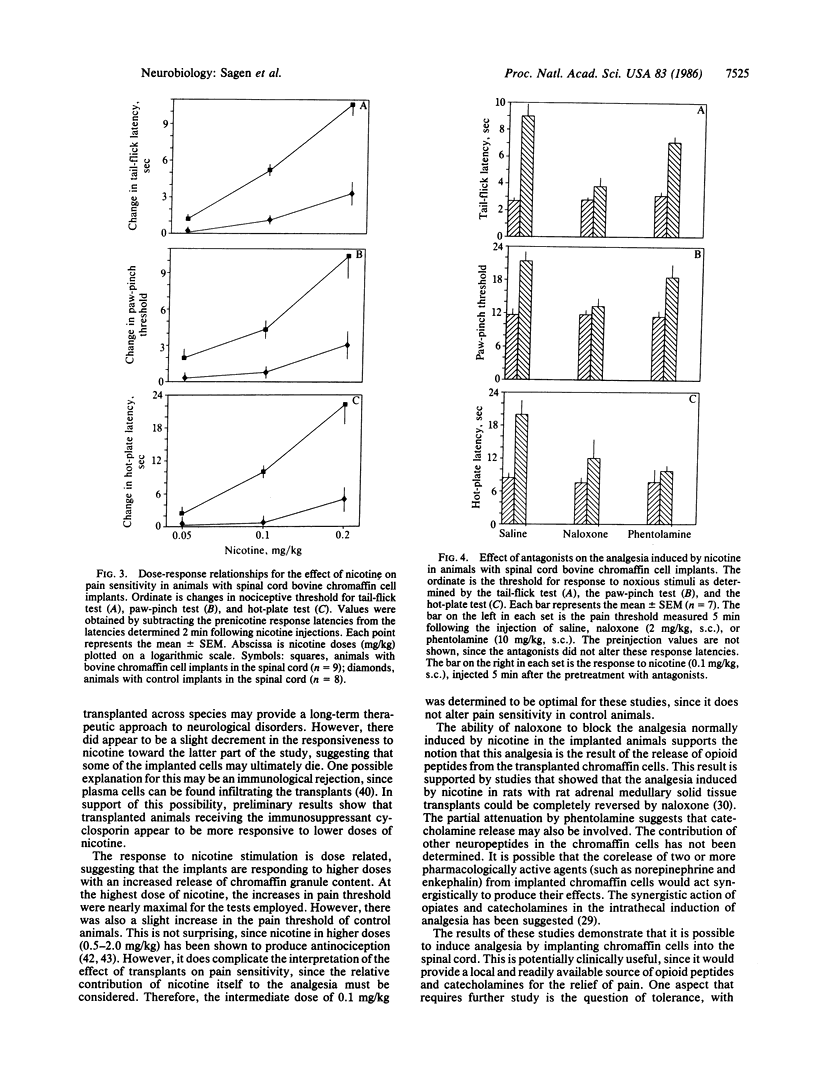
Chromaffin cells synthesize and secrete several neuroactive substances, including catecholamines and opioid peptides, that, when injected into the spinal cord, induce analgesia. Moreover, the release of these substances from the cells can be stimulated by nicotine. Since chromaffin cells from one species have been shown to survive when transplanted to the central nervous system of another species, these cells are ideal candidates for transplantation to alter pain sensitivity. Bovine chromaffin cells were implanted into the subarachnoid space of the lumbar spinal region in adult rats. Pain sensitivity and response to nicotine stimulation was determined at various intervals following cell implantation. Low doses of nicotine were able to induce potent analgesia in implanted animals as early as one day following their introduction into the host spinal cord. This response could be elicited at least through the 4 months the animals were tested. The induction of analgesia by nicotine in implanted animals was dose related. This analgesia was blocked by the opiate antagonist naloxone and partially attenuated by the adrenergic antagonist phentolamine. These results suggest that the analgesia is due to the stimulated release of opioid peptides and catecholamines from the implanted bovine chromaffin cells and may provide a new therapeutic approach for the relief of pain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBRINK W. S., GREENE H. S. N. The transplantation of tissues between zoological classes. Cancer Res. 1953 Jan;13(1):64–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Distribution and physiological significance of opioid receptors in the brain. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):47–52. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backlund E. O., Granberg P. O., Hamberger B., Knutsson E., Mårtensson A., Sedvall G., Seiger A., Olson L. Transplantation of adrenal medullary tissue to striatum in parkinsonism. First clinical trials. J Neurosurg. 1985 Feb;62(2):169–173. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.2.0169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G. D., Hallas B. H., Das K. G. Transplantation of neural tissues in the brains of laboratory mammals: technical details and comments. Experientia. 1979 Feb 15;35(2):143–153. doi: 10.1007/BF01920580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Giraud P., Dave J. R., Hotchkiss A. J., Affolter H. U. Nicotinic receptor stimulation activates enkephalin release and biosynthesis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):661–663. doi: 10.1038/312661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed W. J., Morihisa J. M., Spoor E., Hoffer B. J., Olson L., Seiger A., Wyatt R. J. Transplanted adrenal chromaffin cells in rat brain reduce lesion-induced rotational behaviour. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):351–352. doi: 10.1038/292351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer E. J., Basbaum A. I. Immunohistochemical localization of leucine-enkephalin in the spinal cord of the cat: enkephalin-containing marginal neurons and pain modulation. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Mar 1;196(3):377–389. doi: 10.1002/cne.901960303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Terenius L., Elde R., Nilsson G. Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H. Immunohistochemical analysis of the localization of neuropeptides in the adrenal gland. Arch Histol Jpn. 1985 Dec;48(5):453–481. doi: 10.1679/aohc.48.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte C., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in primate spinal cord: distribution and changes after dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light A. R., Trevino D. L., Perl E. R. Morphological features of functionally defined neurons in the marginal zone and substantia gelatinosa of the spinal dorsal horn. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jul 15;186(2):151–171. doi: 10.1002/cne.901860204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Dean D. M., Whelan L. G., Udenfriend S., Rossier J. Co-release of enkephalin and catecholamines from cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):317–319. doi: 10.1038/289317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlow M. J., Kumakura K., Guidotti A. Prolonged survival of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells in rat cerebral ventricles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5278–5281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Pazoles C. J., Creutz C. E., Scott J. H., Zinder O., Hotchkiss A. An osmotic mechanism for exocytosis from dissociated chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1114–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfit H. K., Hammond D. L. Alterations in nociceptive threshold and morphine-induced analgesia produced by intrathecally administered amine antagonists. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 10;218(1-2):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston H. J., 3rd, Ralston D. D. The distribution of dorsal root axons in laminae I, II and III of the macaque spinal cord: a quantitative electron microscope study. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Apr 15;184(4):643–684. doi: 10.1002/cne.901840404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S. V., Maderdrut J. L., Yaksh T. L. Spinal cord pharmacology of adrenergic agonist-mediated antinociception. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jun;213(3):525–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagen J., Proudfit H. K. Effect of intrathecally administered noradrenergic antagonists on nociception in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 24;310(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagen J., Winker M. A., Proudfit H. K. Hypoalgesia induced by the local injection of phentolamine in the nucleus raphe magnus: blockade by depletion of spinal cord monoamines. Pain. 1983 Jul;16(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(83)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahley T. L., Berntson G. G. Antinociceptive effects of central and systemic administrations of nicotine in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Nov;65(3):279–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00492216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine S. M., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Release of enkephalin-like immunoreactive material from isolated bovine chromaffin cells. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Jul;19(7):683–685. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan L., Yu P. H. Biosynthesis of enkephalins by chromaffin cells of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1901–1908. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenghi G., Polak J. M., Varndell I. M., Lee Y. C., Wharton J., Bloom S. R. Neurotensin-like immunoreactivity in a subpopulation of noradrenaline-containing cells of the cat adrenal gland. Endocrinology. 1983 Jan;112(1):226–233. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-1-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi H. L., Martin B. R., Aceto M. D. Nicotine-induced antinociception in rats and mice: correlation with nicotine brain levels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Apr;221(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlund K. N., Bowker R. M., Ziegler M. G., Coulter J. D. Noradrenergic projections to the spinal cord of the rat. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 14;263(1):15–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L. Pharmacology of spinal adrenergic systems which modulate spinal nociceptive processing. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):845–858. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Reddy S. V. Studies in the primate on the analgetic effects associated with intrathecal actions of opiates, alpha-adrenergic agonists and baclofen. Anesthesiology. 1981 Jun;54(6):451–467. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198106000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976 Dec;17(6):1031–1036. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(76)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



