Abstract
The parathyroid hormone (PTH) analog, [Tyr34]bovine PTH-(7-34)-amide, can inhibit the PTH-mediated elevation of plasma calcium in thyroparathyroidectomized rats in vivo. The analog is devoid of PTH-like agonist activity in this system. Repeated doses of analog inhibit the animal's calcemic response to PTH. The elevation in serum calcium levels mediated by PTH in this assay reflects PTH action (calcium mobilization) on bone. Earlier studies demonstrated antagonist properties of the analog in a renal-based assay; PTH-stimulated increases in urinary phosphate and cyclic AMP excretion were completely inhibited by the synthetic analog. Along with previous studies, this report indicates that [Tyr34]bovine PTH-(7-34)-amide is an effective in vivo antagonist for several major parameters of PTH action in both kidney and bone.
Full text
PDF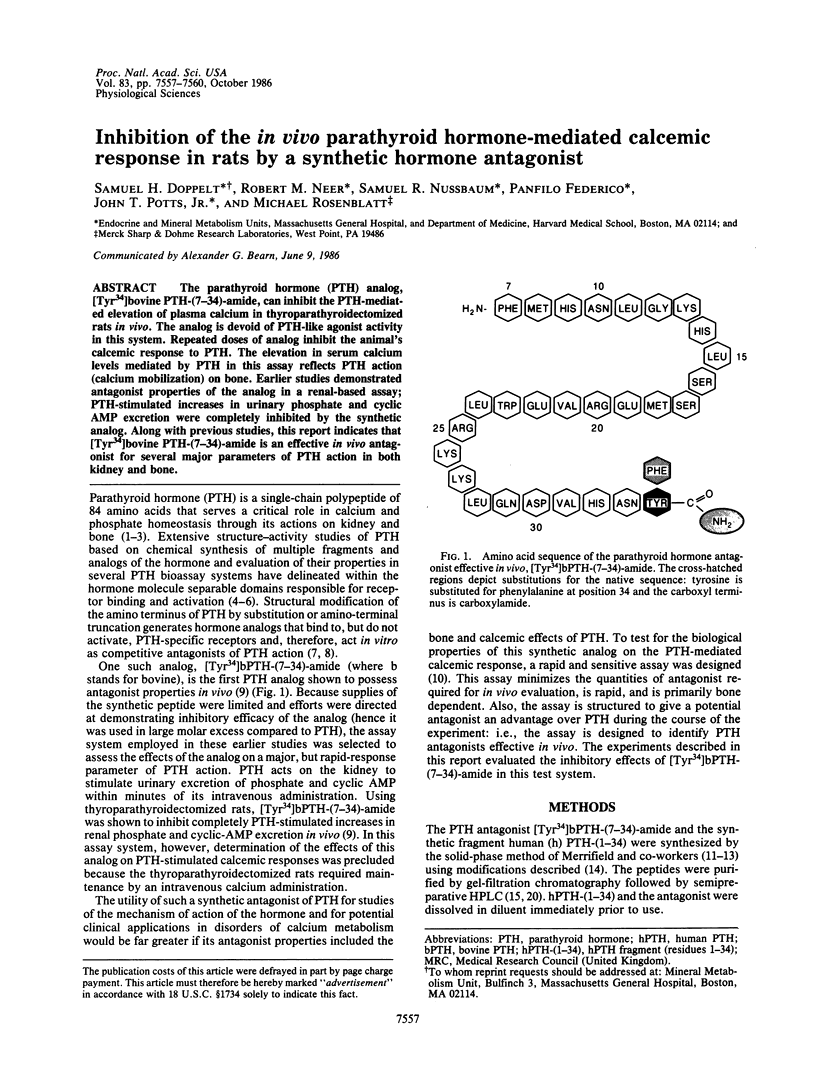

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doppelt S. H., Neer R. M., Potts J. T., Jr Human parathyroid hormone 1-34-mediated hypercalcemia in a rat model, and its inhibition by dichloromethane diphosphonate. Calcif Tissue Int. 1981;33(6):649–654. doi: 10.1007/BF02409503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring S. R., Mahaffey J. E., Rosenblatt M., Dayer J. M., Potts J. T., Jr, Krane S. M. Parathyroid hormone inhibitors: comparison of biological activity in bone- and skin-derived tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Apr;48(4):655–659. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-4-655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring S. R., Roelke M. S., Bringhurst F. R., Rosenblatt M. Differential effects of parathyroid hormone responsive cultured human cells on biological activity of parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone inhibitory analogues. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):513–518. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goltzman D., Goltzmann D., Peytremann A., Callahan E., Tregear G. W., Potts J. T., Jr Analysis of the requirements for parathyroid hormone action in renal membranes with the use of inhibiting analogues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3199–3203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi N., Holick M. F., Potts J. T., Jr, Rosenblatt M. A parathyroid hormone inhibitor in vivo: design and biological evaluation of a hormone analog. Science. 1983 Jun 3;220(4601):1053–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.6302844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:221–296. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum S. R., Rosenblatt M., Potts J. T., Jr Parathyroid hormone . renal receptor interactions. Demonstration of two receptor-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10183–10187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. A., Reit B., Robinson C. J. A chick bioassay for parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1973 Feb;92(2):454–462. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-2-454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. T., Jr, Kronenberg H. M., Rosenblatt M. Parathyroid hormone: chemistry, biosynthesis, and mode of action. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:323–396. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60471-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt M., Goltzman D., Keutmann H. T., Tregear G. W., Potts J. T., Jr Chemical and biological properties of synthetic, sulfur-free analogues of parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt M., Segre G. V., Tyler G. A., Shepard G. L., Nussbaum S. R., Potts J. T., Jr Identification of a receptor-binding region in parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):545–550. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear G. W., Van Rietschoten J., Greene E., Keutmann H. T., Niall H. D., Reit B., Parsons J. A., Potts J. T., Jr Bovine parathyroid hormone: minimum chain length of synthetic peptide required for biological activity. Endocrinology. 1973 Dec;93(6):1349–1353. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-6-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear G. W., van Rietschoten J., Sauer R., Niall H. D., Keutmann H. T., Potts J. T., Jr Synthesis, purification, and chemical characterization of the amino-terminal 1-34 fragment of bovine parathyroid hormone synthesized by the solid-phase procedure. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2817–2823. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler G. A., Rosenblatt M. Semi-preparative high-performance liquid chromatographic purification of a 28-amino acid synthetic parathyroid hormone antagonist. J Chromatogr. 1983 Aug 26;266:313–318. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanelli J. M., Lane E., Kimura T., Sakakibara S. Biological activities of synthetic human parathyroid hormone (PTH) 1-84 relative to natural bovine 1-84 PTH in two different in vivo bioassay systems. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):1962–1967. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-1962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


