Abstract
Drug development from natural sources is an important and fast developing area. Natural sources (plants) have been used to cure a range of diseases for Thousands of years. Different online medicinal plant databases provide information about classifications, activities, phytochemicals and structure of phytochemicals in different formats. These databases do not cover all aspects of medicinal plants. MAPS (Medicinal plant Activities, Phytochemicals & structural database) has been constructed with uniqueness that it combines all information in one web resource and additionally provides test targets on which particular plant found to be effective with reference to the original paper as well. MAPS database is user friendly information resource, including the data of > 500 medicinal plants. This database includes phytochemical constituents, their structure in mol format, different activities possessed by the medicinal plant with the targets reported in literature.
Availability
Keywords: Medicinal activity, medicinal plants, phytochemicals, phytochemical structures, activities with target, drug designing
Background
Medicinal Plants possess naturally occurring valuable phytochemicals [1]. Plant uses these chemicals to defend them, but recent research demonstrated that they can protect humans and animals against different diseases [2]. Medicinal plants contain various phytochemicals such as organosulfur compounds, limonoids, lignans, furyl compounds, alkaloids, polyines, thiophenes, proteins, peptides, flavonoids, terpenoids, polyphenolics, coumarins and saponins etc. These phytochemicals display curative functions due to scavenging, antioxidant activities, hampering viral entry, DNA and RNA replication against diverse range of viruses i.e antibacterial, antifungal, cancer prevention, enzyme stimulation, hormonal action, and many more. Researchers are evaluating drugs resulting from natural sources due to belief that these medicines are safe as compared to expensive synthetic drugs which are always related with adverse effects. The adverse effects of synthetic drugs necessitate for finding new harmless therapeutic agents from natural sources [3, 4].
Different online medicinal plant databases provide information about geographical distribution, classification, activities (i.e. antidiabetic, antitumor, antimicrobial), some provides phytochemical information and structures in different formats. There is no single database that combines all aspects of medicinal plants under one forum. To fulfill this gap and to provide researchers all information under one forum MAPS database is constructed.
The MAPS (Medicinal plants Activities, Phytochemicals and Structural) database provides useful information about not only included in different databases/literature but also Pakistan's medicinal plants missed in them, helping researchers working on drug discovery from natural resources. It facilitates the user to search (selecting plant name/activity/target/all information), download structures and submit information.
Design & Methods
Screening for Medicinal Plants Activities, Phytochemicals and their Structures:
Plants activities, phytochemicals and their structures were searched using PubMed [5], Pubmed Central [6], Pubchem [7], NPACT [8], Drug Bank [9] and PhytAmp [10] with different keyword i.e. plants name (scientific and common) with activities i.e (antibacterial, antimicrobial, antiviral, antifungal, antidiabetic, lavacidal, etc), structures in .mol format, phytochemicals, targets (i.e Bacillus cereus, Candida albicans, Escherichia coli and Hepatitis virus etc ).
MAPS database construction:
MAPS database is constructed using MS Access. (a)Each activity based record was stored with plant name, activity, target and literature reference; (b)Each phytochemical record was stored with medicinal plant name (scientific), phytochemical constituent with literature reference (PMID, other paper titles not found in PubMed); (c)Each Structural record includes MAPS_ID, constituent name, phytochemical class (i.e. flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, aromatic compounds, tannins), PubChem-Id, and Hyperlinks to PubChem-Id (if available), structure image and .mol format downloadable file; (d) Each Literature record was stored as PubMed ID, title, abstract, authors and PubMed Central Id (if available) and for the non-pubmed references paper title, journal name, abstract and author's information is used.
MAPS Web Interface:
MAPS database is made freely accessible on http://www.mapsdatabase.com using HTML, PHP, CSS, Aspx.Net, MySQL and MS Access (Figure 1). MAPS Database web interface includes pages for home page, activity, phytochemical, structures, literature (PMID & Other Journal) and search page. Web Interface also allows users to submit phytochemicals, activities with target, and structures only with reference to authentic source of information that will be updated by MAPS admins after reviewing.
Figure 1.
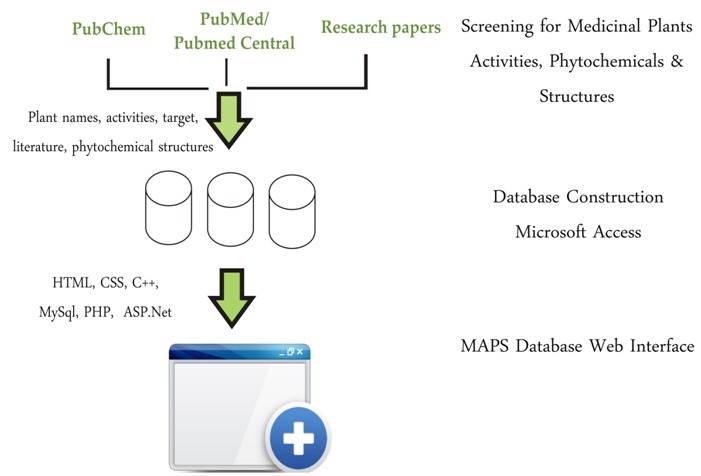
Steps followed for creating MAPS database.
Utility
Currently MAPS includes more than 500 medicinal plants, >1000 records for medicinal plants activities including test targets (i.e Vibrio cholera, Staphylococcus spp., Shigella., Salmonella spp., Influenza virus, HIV, Enterococcus spp., Dengue virus, Enterobacter spp., Candida spp., Bacillus spp., Aspergillus spp., A. aegypti larvae, Acinetobacter spp., Microsporum spp., Mycobacterium spp., Penicillium spp., Plasmodium spp., Proteus spp., Pseudomonas spp.) and activities (i.e antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, antidiabetic, antiprotozoal, anti-inflammatory, larvacidal, urease inhibitory, gastroprotective, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, thrombolytic, Antidiarrhoeal). More than 2200 phytochemicals, >1200 phytochemical structures in .mol format and >450 literature references are stored in MAPS database used for medicinal plant activtities, phytochemicals and structural search. This database can be helpful for researchers looking for plants as a source of drug designing by providing information that a specific plant contains what type of phytochemicals, on which targets it found to be effective in previous research studies, phytochemical structures & activities it possess.
Future Development
We plan to search more information and update MAPS database and to facilitate users to download complete information, search phytochemicals via PubChem Id, names or source (plant). MAPS will include user login system to store their query results.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Government College & University, Faisalabad and AzizSoft for providing facilities and funding to online MAPS Database
Footnotes
Citation:Ashfaq et al, Bioinformation 9(19): 993-995 (2013)
References
- 1.Calixto JB. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2000;33:2. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2000000200004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kubmarawa D, et al. J Med Plants Res. 2008;2:12. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Venkataswamy R, et al. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2010;72:2. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.65020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rupasinghe HP, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2003;51:20. doi: 10.1021/jf0343736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed.
- 6. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/
- 7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pccompound.
- 8. http://crdd.osdd.net/raghava/npact/
- 9. http://www.drugbank.ca/
- 10. http://phytamp.pfba-lab-tun.org/main.php.


