Abstract
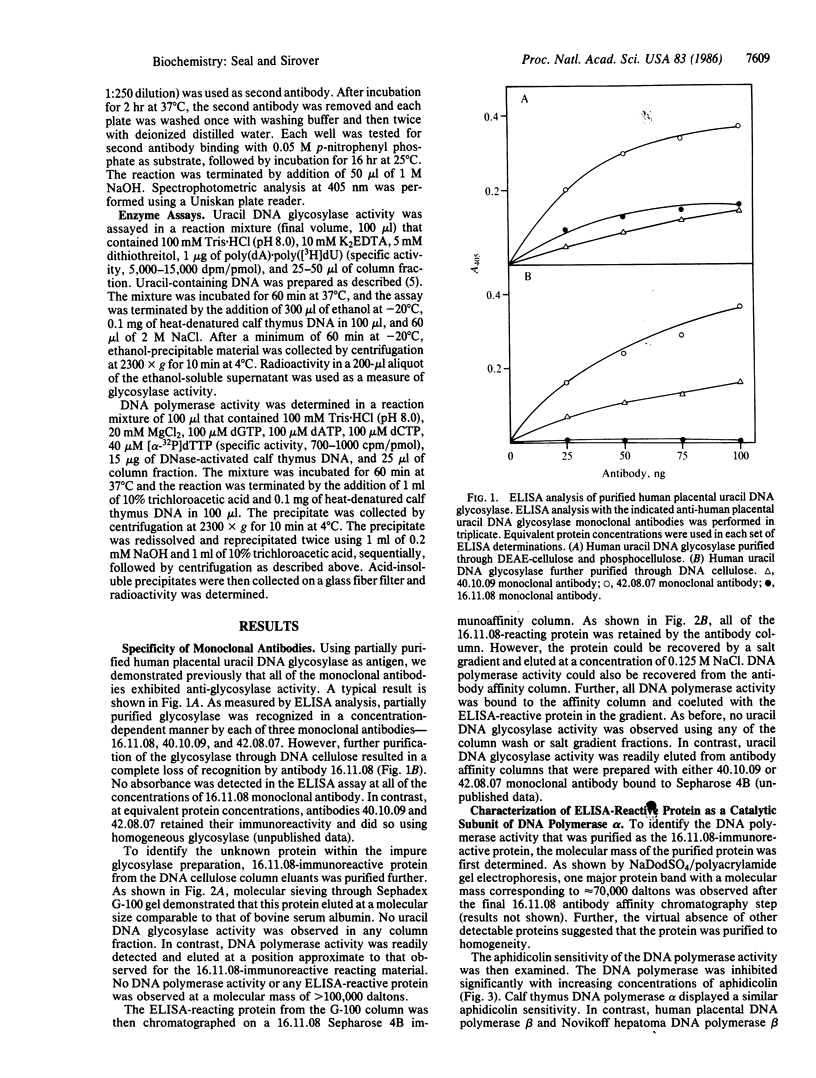
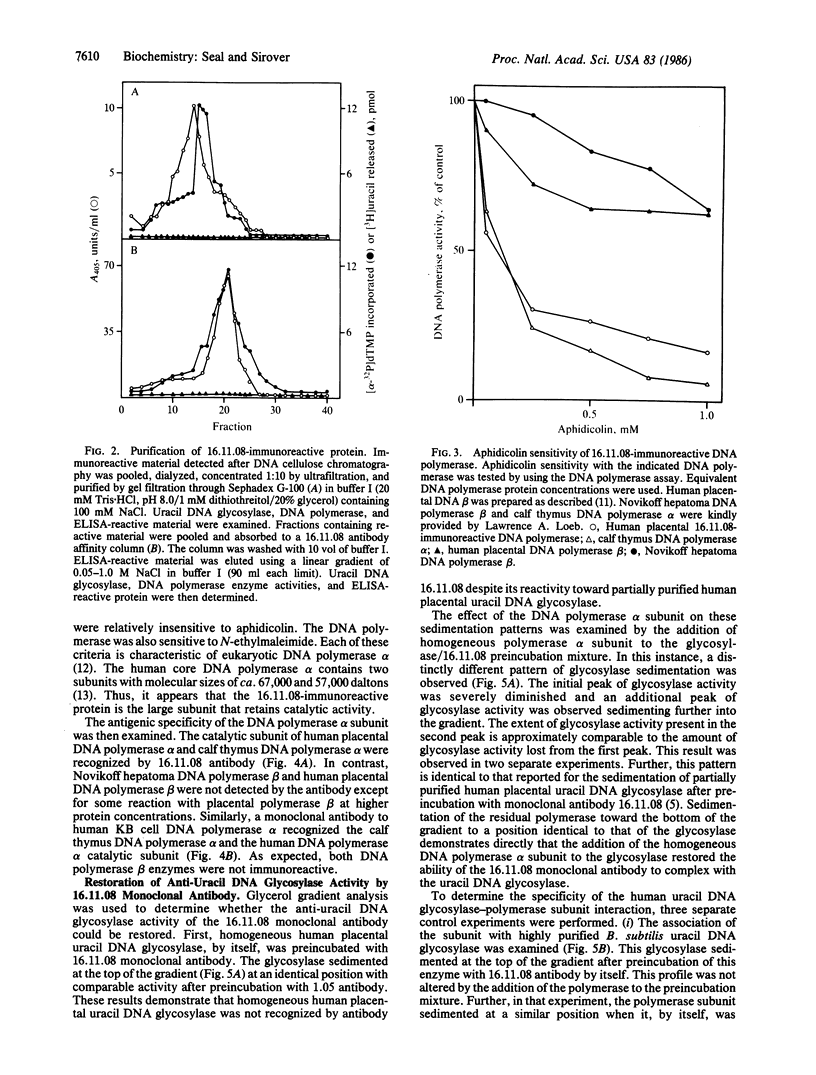
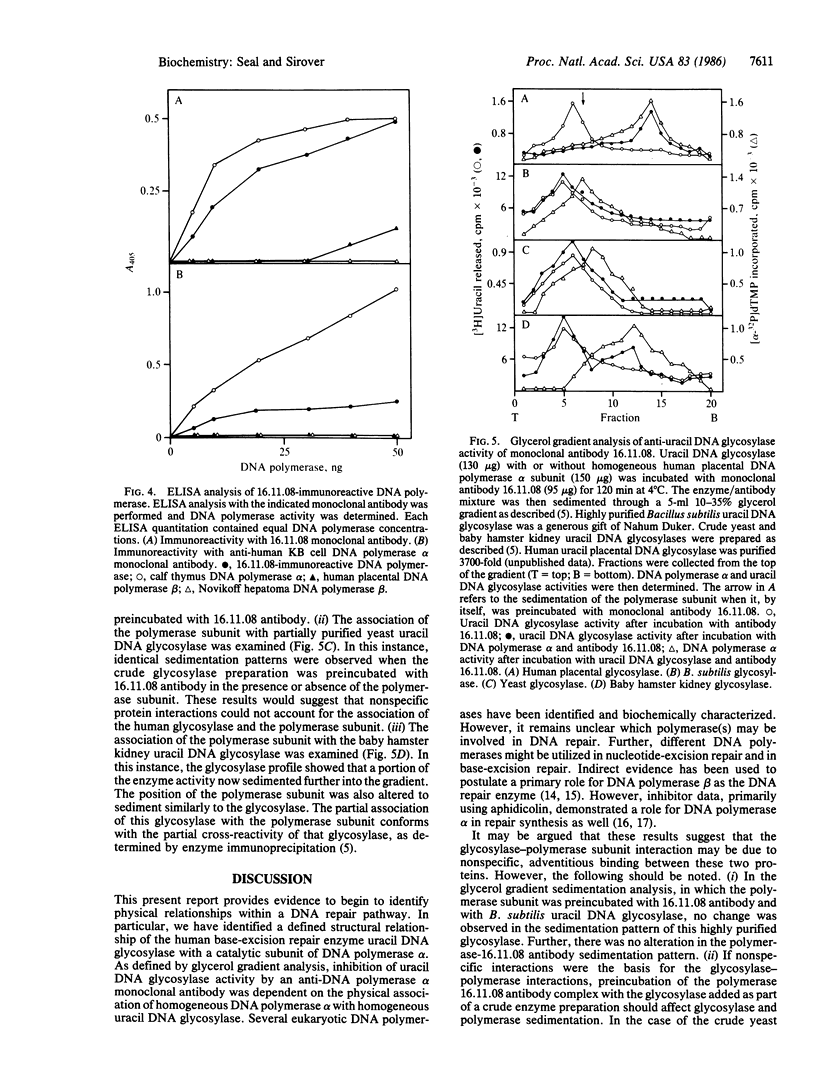
A monoclonal antibody prepared against a partially purified human uracil DNA glycosylase was found, on further purification of the enzyme, to be inactive against the glycosylase. However, immunoreactivity was observed in other protein fractions that contained DNA polymerase activity. The immunoreactive protein was purified to homogeneity and identified as a catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase alpha by molecular mass, by aphidicolin sensitivity, and by recognition by a monoclonal antibody against human KB cell DNA polymerase alpha. Our monoclonal antibody had no effect on homogeneous human uracil DNA glycosylase activity but severely inhibited the activity of the homogeneous human DNA polymerase alpha catalytic subunit. The suspicion that the two proteins were physically associated was confirmed by finding that, on mixing the DNA polymerase alpha subunit with the glycosylase, the latter was strongly inhibited by our monoclonal antibody. These results demonstrate that this monoclonal antibody recognizes not only the DNA polymerase alpha subunit but also the uracil DNA glycosylase when it is physically attached to the polymerase subunit. These results contribute to the definition of relationships between those proteins that may comprise the human base-excision repair multienzyme complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenaz P., Sirover M. A. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against the DNA repair enzyme uracil DNA glycosylase from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5822–5826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessman M. J., Lehman I. R., Adler J., Zimmerman S. B., Simms E. S., Kornberg A. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. III. THE INCORPORATION OF PYRIMIDINE AND PURINE ANALOGUES INTO DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Jul 15;44(7):633–640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.7.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron P. R., Kushner S. R., Grossman L. Involvement of helicase II (uvrD gene product) and DNA polymerase I in excision mediated by the uvrABC protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4925–4929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Brown M., Bollum F. J. Induction of DNA polymerase in mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 15;74(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filpula D., Fisher P. A., Korn D. DNA polymerase-alpha. Common polypeptide core structure of three enzyme forms from human KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2029–2040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Cooper P. K., Ganesan A. K., Smith C. A. DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayatsu H. Co-operative mutagenic actions of bisulfite and nitrogen nucleophiles. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep;115(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Shearman C. W., Loeb L. A. Mutagenesis in vitro by depurination of phiX174 dna. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):349–351. doi: 10.1038/291349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. K., Chang C. C., Trosko J. E., Dube D. K., Martin G. M., Loeb L. A. Mammalian mutator mutant with an aphidicolin-resistant DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):797–801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Apurinic sites as mutagenic intermediates. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prem veer Reddy G., Pardee A. B. Multienzyme complex for metabolic channeling in mammalian DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Kunkel T. A., Loeb L. A. Infidelity of DNA synthesis associated with bypass of apurinic sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):487–491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal G., Shearman C. W., Loeb L. A. On the fidelity of DNA replication. Studies with human placenta DNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5229–5237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Klein R. S. The deamination of cytidine and cytosine by acidic buffer solutions. Mutagenic implications. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2358–2362. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss B. S. Cellular aspects of DNA repair. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;45:45–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teebor G. W., Frenkel K. The initiation of DNA excision-repair. Adv Cancer Res. 1983;38:23–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K., Nyman P. O., Lehman I. R., Hochhauser S., Weiss B. Transient accumulation of Okazaki fragments as a result of uracil incorporation into nascent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):154–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



