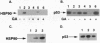Abstract
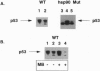
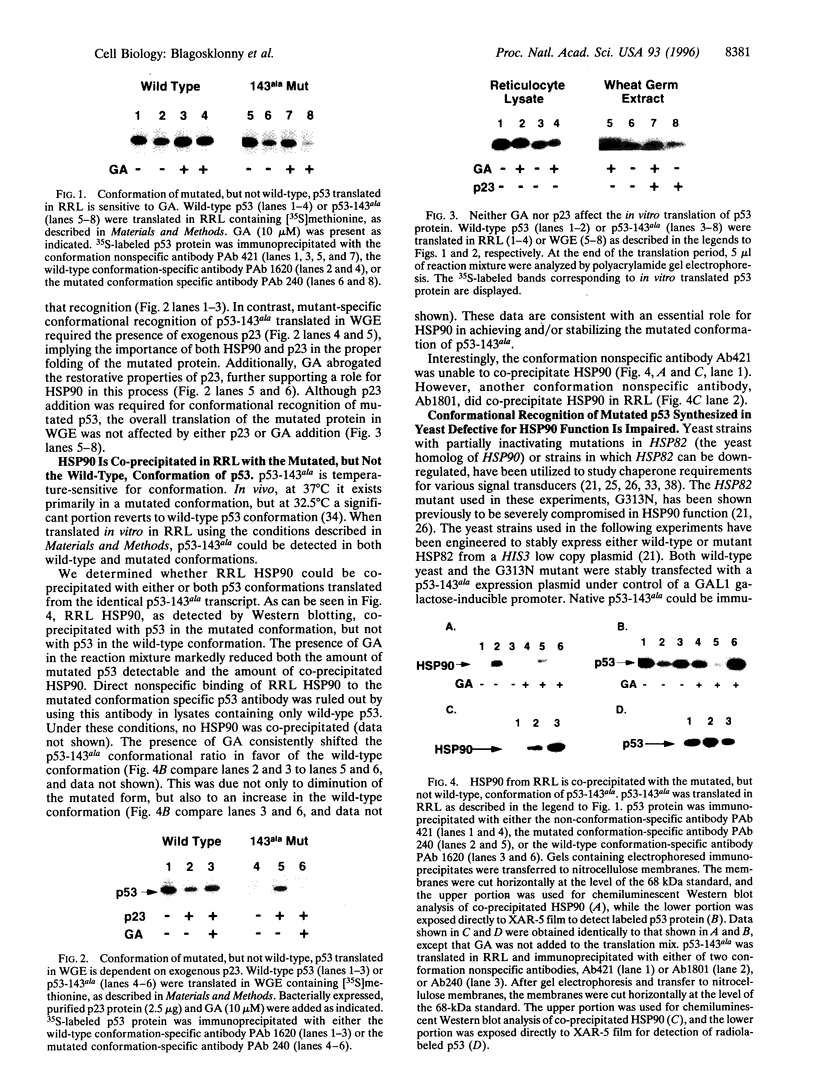
The p53 mutant, 143ala, was translated in vitro in either rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) or wheat germ extract (WGE). In RRL, p53-143ala protein of both mutant and wild-type conformation, as detected immunologically with conformation-specific antibodies, was translated. The chaperone protein HSP90, present in RRL, was found to coprecipitate only with the mutated conformation of p53. Geldanamycin, shown previously to bind to HSP90 and destabilize its association with other proteins, decreased the amount of immunologically detectable mutated p53 and increased the amount of detectable wild-type protein, without affecting the total translation of p53. When translated in WGE, known to contain functionally deficient HSP90, p53-143ala produced p53 protein, which was not recognized by a mutated conformation-specific antibody. In contrast, the synthesis of conformationally detectable wild-type p53 in this system was not compromised. Reconstitution of HSP90 function in WGE permitted synthesis of conformationally detectable mutated p53, and this was abrogated by geldanamycin. Finally, when p53-143ala was stably tansfected into yeast engineered to be defective for HSP90 function, conformational recognition of mutated p53 was impaired. When stable transfectants of p53-143ala were prepared in yeast expressing wild-type HSP90, conformational recognition of mutated p53 was antagonized by macbecin I, a geldanamycin analog also known to bind HSP90. Taken together, these data demonstrate a role for HSP90 in the achievement and/or stabilization of the mutated conformation of p53-143ala. Furthermore, we show that the mutated conformation of p53 can be pharmacologically antagonized by drugs targeting HSP90.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonsson C., Whitelaw M. L., McGuire J., Gustafsson J. A., Poellinger L. Distinct roles of the molecular chaperone hsp90 in modulating dioxin receptor function via the basic helix-loop-helix and PAS domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):756–765. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartek J., Iggo R., Gannon J., Lane D. P. Genetic and immunochemical analysis of mutant p53 in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):893–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blagosklonny M. V., Toretsky J., Neckers L. Geldanamycin selectively destabilizes and conformationally alters mutated p53. Oncogene. 1995 Sep 7;11(5):933–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohen S. P. Hsp90 mutants disrupt glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding and destabilize aporeceptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 8;270(49):29433–29438. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohen S. P., Yamamoto K. R. Isolation of Hsp90 mutants by screening for decreased steroid receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11424–11428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver L. A., Jackiw V., Bradfield C. A. The 90-kDa heat shock protein is essential for Ah receptor signaling in a yeast expression system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30109–30112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmer D., Pati S., Zambetti G., Chu S., Teresky A. K., Moore M., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Gain of function mutations in p53. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):42–46. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Bradley A. The tumor suppressor p53. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Aug 23;1155(2):181–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt M. S., Bennett W. P., Hollstein M., Harris C. C. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 15;54(18):4855–4878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Butcher S., Milner J. Temperature sensitivity for conformation is an intrinsic property of wild-type p53. Br J Cancer. 1995 Feb;71(2):227–231. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Milner J. Interaction of heat-shock protein 70 with p53 translated in vitro: evidence for interaction with dimeric p53 and for a role in the regulation of p53 conformation. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3513–3520. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A role for Hsp90 in retinoid receptor signal transduction. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Dec;6(12):1833–1842. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.12.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao M., Low J., Dorn E., Ku D., Pattengale P., Yeargin J., Haas M. Gain-of-function mutations of the p53 gene induce lymphohematopoietic metastatic potential and tissue invasiveness. Am J Pathol. 1994 Sep;145(3):702–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. A., Stancato L. F., Owens-Grillo J. K., Johnson J. L., Krishna P., Toft D. O., Pratt W. B. The 23-kDa acidic protein in reticulocyte lysate is the weakly bound component of the hsp foldosome that is required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a functional heterocomplex with hsp90. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18841–18847. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Toft D. O. A novel chaperone complex for steroid receptors involving heat shock proteins, immunophilins, and p23. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24989–24993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Toft D. O. Binding of p23 and hsp90 during assembly with the progesterone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Jun;9(6):670–678. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.6.8592513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. A conformation hypothesis for the suppressor and promoter functions of p53 in cell growth control and in cancer. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Aug 22;245(1313):139–145. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Cook A., Sheldon M. A new anti-p53 monoclonal antibody, previously reported to be directed against the large T antigen of simian virus 40. Oncogene. 1987;1(4):453–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. Flexibility: the key to p53 function? Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Feb;20(2):49–51. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88954-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. Forms and functions of p53. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994 Jun;5(3):211–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Watson J. V. Addition of fresh medium induces cell cycle and conformation changes in p53, a tumour suppressor protein. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1683–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimnaugh E. G., Worland P. J., Whitesell L., Neckers L. M. Possible role for serine/threonine phosphorylation in the regulation of the heteroprotein complex between the hsp90 stress protein and the pp60v-src tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 1;270(48):28654–28659. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.48.28654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Khursheed B., Garabedian M. J., Fortin M. G., Lindquist S., Yamamoto K. R. Reduced levels of hsp90 compromise steroid receptor action in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):166–168. doi: 10.1038/348166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Tokino T., Thiagalingam S., el-Deiry W. S., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Sequence-specific transcriptional activation is essential for growth suppression by p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. J., Clarke M. F. Alteration of p53 conformation and induction of apoptosis in a murine erythroleukemia cell line by dimethylsulfoxide. Leuk Res. 1994 Aug;18(8):617–621. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaknovich R., Shue G., Kohtz D. S. Conformational activation of a basic helix-loop-helix protein (MyoD1) by the C-terminal region of murine HSP90 (HSP84). Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5059–5068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shue G., Kohtz D. S. Structural and functional aspects of basic helix-loop-helix protein folding by heat-shock protein 90. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2707–2711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Whitesell L., Nair S. C., Chen S., Prapapanich V., Rimerman R. A. Progesterone receptor structure and function altered by geldanamycin, an hsp90-binding agent. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6804–6812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Addison C., Jenkins J. R. Characterization of mutant p53-hsp72/73 protein-protein complexes by transient expression in monkey COS cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3740–3747. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Chumakov P., Welch W. J., Jenkins J. R. Mutant p53 proteins bind hsp 72/73 cellular heat shock-related proteins in SV40-transformed monkey cells. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):201–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan W. P., Toft D. O. Mutational analysis of hsp90 binding to the progesterone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20373–20379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw M. L., McGuire J., Picard D., Gustafsson J. A., Poellinger L. Heat shock protein hsp90 regulates dioxin receptor function in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4437–4441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell L., Mimnaugh E. G., De Costa B., Myers C. E., Neckers L. M. Inhibition of heat shock protein HSP90-pp60v-src heteroprotein complex formation by benzoquinone ansamycins: essential role for stress proteins in oncogenic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8324–8328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Lindquist S. Heat-shock protein hsp90 governs the activity of pp60v-src kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7074–7078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Guo X. Y., Hu G. Y., Liu W. B., Shay J. W., Deisseroth A. B. A temperature-sensitive mutant of human p53. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2535–2544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Hu G., Estey E., Hester J., Deisseroth A. Altered conformation of the p53 protein in myeloid leukemia cells and mitogen-stimulated normal blood cells. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1645–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]