Abstract
A conserved residue at the dihydrofolate binding site of dihydrofolate reductase (EC 1.5.1.3), leucine-54, was replaced with glycine to ascertain the role of this hydrophobic amino acid. The effect of the mutation is both to increase the dissociation rate of dihydrofolate and decrease the rate of hydride transfer thus changing the rate-limiting step in catalysis from product loss (leucine-54) to hydride transfer (glycine-54). The total stabilization by leucine-54 of the transition state for hydride transfer is ca. 10(4)-fold (delta delta G approximately 5.4 kcal/mol) at subsaturating dihydrofolate levels relative to free enzyme despite its location some 10 A from the site of chemical reaction.
Full text
PDF
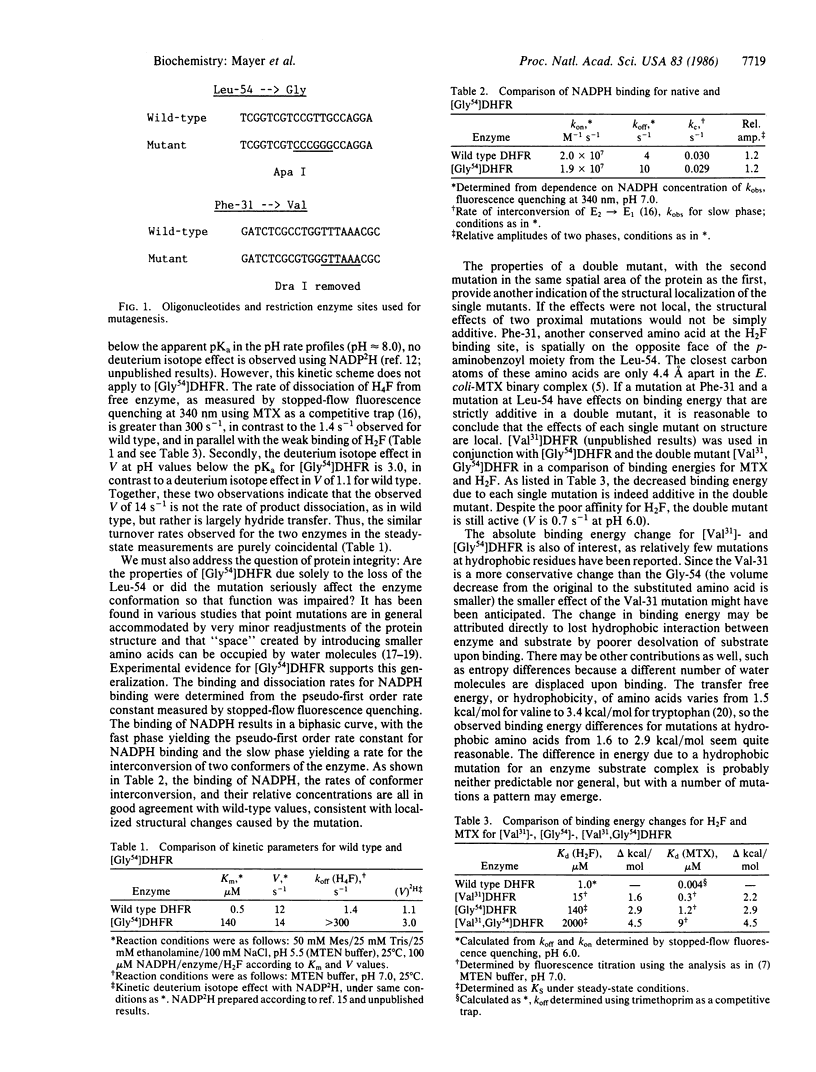

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolin J. T., Filman D. J., Matthews D. A., Hamlin R. C., Kraut J. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 A resolution. I. General features and binding of methotrexate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13650–13662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley P. J., Dunn S. M., King R. W. Kinetics of substrate, coenzyme, and inhibitor binding to Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):874–879. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. T., Mayer R. J., Fierke C. A., Benkovic S. J. Site-specific mutagenesis of dihydrofolate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(2):73–82. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Helix movements and the reconstruction of the haem pocket during the evolution of the cytochrome c family. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Largman C., Fletcher T., Roczniak S., Barr P. J., Fletterick R., Rutter W. J. Redesigning trypsin: alteration of substrate specificity. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):291–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3838593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbadie-McFarland G., Cohen L. W., Riggs A. D., Morin C., Itakura K., Richards J. H. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis as a general and powerful method for studies of protein function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbadie-McFarland G., Neitzel J. J., Richards J. H. Active-site mutants of beta-lactamase: use of an inactive double mutant to study requirements for catalysis. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):332–338. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. M., Batchelor J. G., King R. W. Kinetics of ligand binding to dihydrofolate reductase: binary complex formation with NADPH and coenzyme analogues. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2356–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filman D. J., Bolin J. T., Matthews D. A., Kraut J. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 A resolution. II. Environment of bound NADPH and implications for catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13663–13672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. S., Bock S. C., Rokita S. E., Kaiser E. T. Modification of the active site of alkaline phosphatase by site-directed mutagenesis. Science. 1986 Jan 10;231(4734):145–148. doi: 10.1126/science.3510454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell E. E., Villafranca J. E., Warren M. S., Oatley S. J., Kraut J. Functional role of aspartic acid-27 in dihydrofolate reductase revealed by mutagenesis. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1123–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.3511529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman B. T. Methotrexate-agarose in the purification of dihydrofolate reductase. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:272–281. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leatherbarrow R. J., Fersht A. R., Winter G. Transition-state stabilization in the mechanism of tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase revealed by protein engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7840–7844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. Establishment of a hydrophobicity scale. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2211–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter M. E., Johnson K. A. Transient state kinetic analysis of the ATP-induced dissociation of the dynein-microtubule complex. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6582–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Morrison J. F. Catalytic mechanism of the dihydrofolate reductase reaction as determined by pH studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2753–2758. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Morrison J. F. Kinetic mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by dihydrofolate reductase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3757–3765. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Morrison J. F. The pH-dependence of the binding of dihydrofolate and substrate analogues to dihydrofolate reductase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 29;745(3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D., Raines R., Kawashima E., Knowles J. R., Gilbert W. Active site of triosephosphate isomerase: in vitro mutagenesis and characterization of an altered enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2272–2276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



