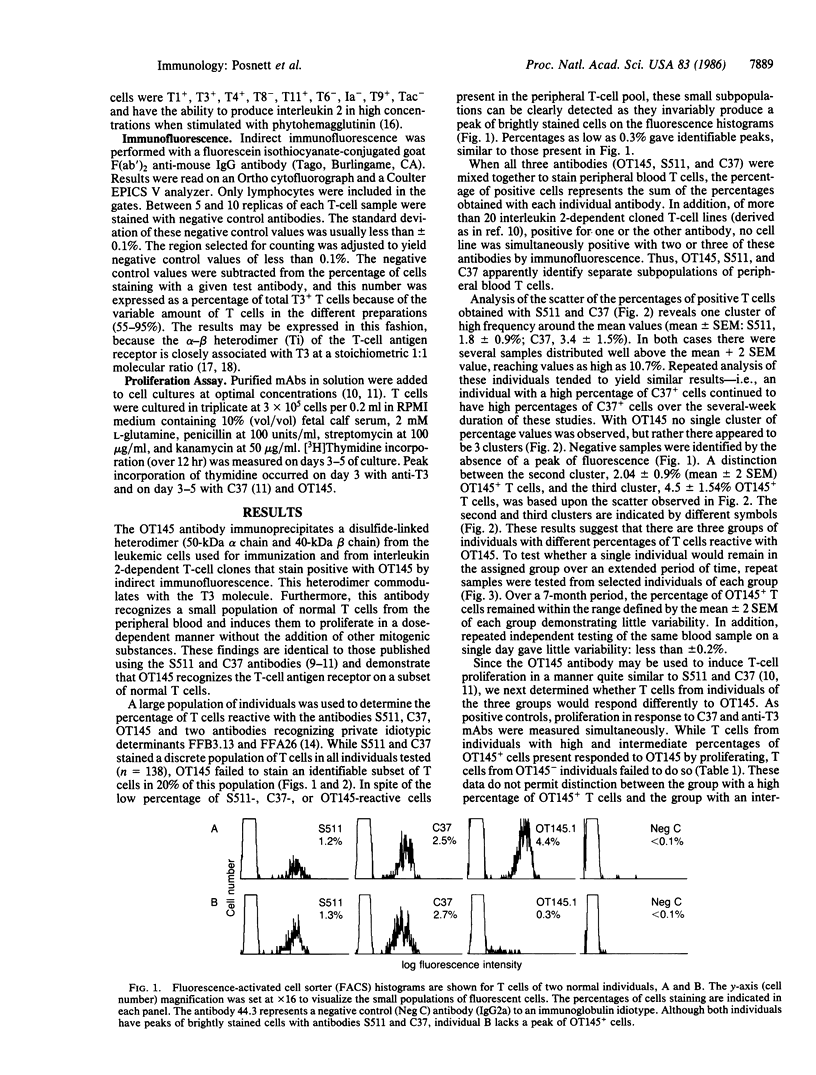
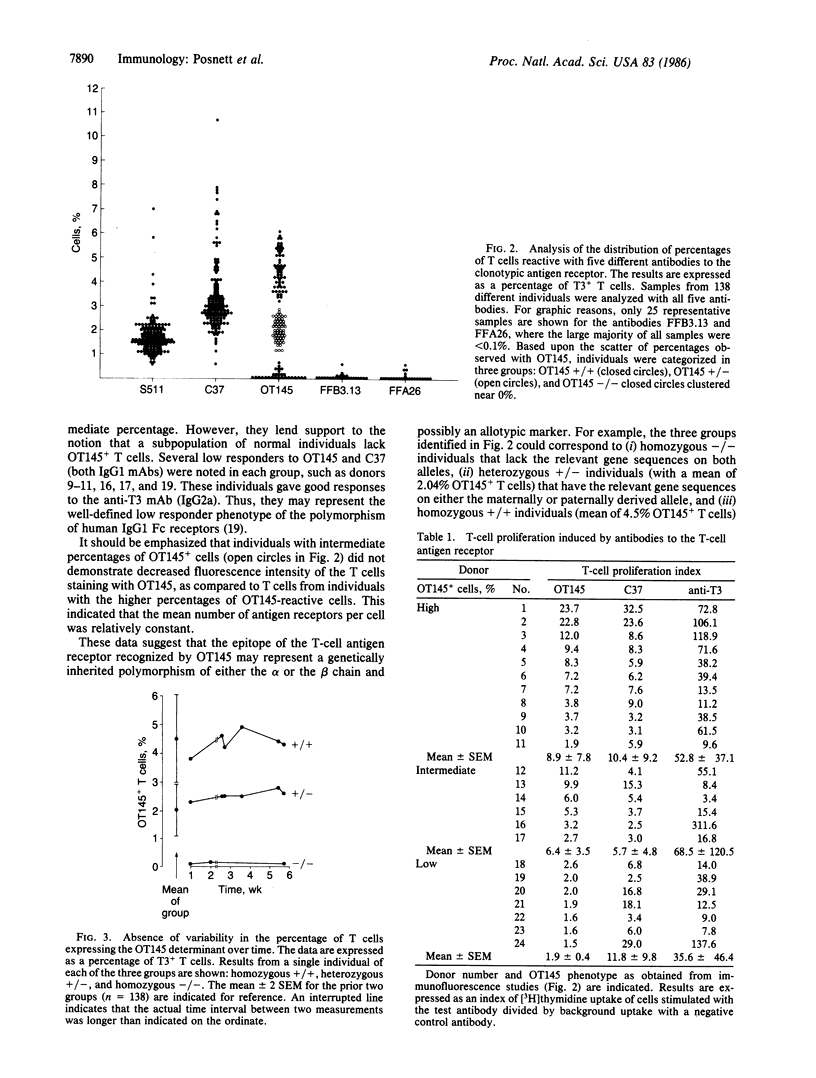
Abstract
Three different murine monoclonal antibodies to the human clonotypic T-cell antigen receptor immunoprecipitate the alpha-beta chain heterodimer; induce comodulation of the clonotypic molecule with the T3 molecular complex; stain small populations of normal polyclonal T cells, suggesting that they react with variable or joining region determinants of the clonotypic receptor; and induce proliferation of resting T cells. While two of these antibodies detect the clonotypic receptor in all individuals studied, the third antibody (OT145), described herein, does not detect the T-cell antigen receptor on T cells of all individuals. By indirect immunofluorescence, three groups can be distinguished within a population of individuals (n = 138) by OT145. Individuals lacking T cells reactive with OT145 have a homozygous OT145-phenotype. T cells from such individuals fail to proliferate in the presence of OT145 in contrast to T cells from OT145+ individuals. Individuals with a relatively large percentage of OT145+ T cells, 4.5 +/- 1.54% (mean +/- 2 SEM) are homozygous OT145+, while those with an intermediate percentage, 2.04 +/- 0.9%, have a heterozygous phenotype. Family studies suggest autosomal codominant inheritance of the OT145 phenotype. The distribution of the three OT145-defined phenotypes varies considerably in populations of different ethnic background. Taken together these data suggest that the polymorphism detected by OT145 may represent a variable or joining region allotypic system of the human T-cell antigen receptor. In addition, our results indicate that allelic exclusion governs the expression of the clonotypic receptor by human T cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acuto O., Campen T. J., Royer H. D., Hussey R. E., Poole C. B., Reinherz E. L. Molecular analysis of T cell receptor (Ti) variable region (V) gene expression. Evidence that a single Ti beta V gene family can be used in formation of V domains on phenotypically and functionally diverse T cell populations. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1326–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behlke M. A., Chou H. S., Huppi K., Loh D. Y. Murine T-cell receptor mutants with deletions of beta-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):767–771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler R. D., Fisher D. E., Wang C. Y., Rinnooy Kan E. A., Kunkel H. G. Idiotype-like molecules on cells of a human T cell leukemia. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):1000–1005. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler R. D., Posnett D. N., Chiorazzi N. Stimulation of a subset of normal resting T lymphocytes by a monoclonal antibody to a crossreactive determinant of the human T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1450–1463. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. New genetic model for allelism at histocompatibility and other complex loci: polymorphism for control of gene expression. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1471–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylston A. W., Cosford P. Growth of normal human T lymphocytes induced by monoclonal antibody to the T cell antigen receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jul;15(7):738–742. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., Trowbridge I. S., Strominger J. L. Cross-linking of human T cell receptor proteins: association between the T cell idiotype beta subunit and the T3 glycoprotein heavy subunit. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Zabriskie J. B., Kunkel H. G. Oligoclonal immunoglobulins in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and multiple sclerosis: a study of idiotypic determinants. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jan;35(1):67–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Thompson G., Halper J. P., Knowles D. M. OT-CLL: a human T cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia that produces IL 2 in high titer. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):935–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUBB R. Agglutination of erythrocytes coated with incomplete anti-Rh by certain rheumatoid arthritic sera and some other sera; the existence of human serum groups. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(3):195–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., Hannum C., White J., Roehm N., Kubo R., Kappler J., Marrack P. The antigen-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted receptor on T cells. VI. An antibody to a receptor allotype. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):452–471. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Kronenberg M., Hunkapiller T. T cell antigen receptors and the immunoglobulin supergene family. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover M. L., Marks J., Chipman J., Palmer E., Stastny P., Capra J. D. Restriction fragment length polymorphism of the gene encoding the alpha chain of the human T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1087–1092. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Dreesman G. R. Common idiotypic determinant associated with human antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):385–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J. Rabbit immunoglobulin allotypes: structure, immunology, and genetics. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:35–86. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60218-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Agnello V., Joslin F. G., Winchester R. J., Capra J. D. Cross-idiotypic specificity among monoclonal IgM proteins with anti- -globulin activity. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):331–342. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Bernstein K. E., McCartney-Francis N., Alexander C. B., Young-Cooper G. O., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H. The structural and genetic basis for expression of normal and latent VHa allotypes of the rabbit. Mol Immunol. 1984 Nov;21(11):1067–1081. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Fukumori J., Tanaka H. Evidence of unique idiotypic determinants and similar idiotypic determinants on human antithyroglobulin antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):381–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Acuto O., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Evidence for the T3-associated 90K heterodimer as the T-cell antigen receptor. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):808–810. doi: 10.1038/303808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUDIN J. L'allotypie de certains antigènes protéidiques du sérum. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1956 May 23;242(21):2606–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Chiappino G., Kelus A. S., Gell P. G. Cellular localization of immunoglobulins with different allotypic specificities in rabbit lymphoid tissues. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):853–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posnett D. N., Bigler R. D., Bushkin Y., Fisher D. E., Wang C. Y., Mayer L. F., Chiorazzi N., Kunkel H. G. T cell antiidiotypic antibodies reveal differences between two human leukemias. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):494–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posnett D. N., Wisniewolski R., Pernis B., Kunkel H. G. Dissection of the human antigammaglobulin idiotype system with monoclonal antibodies. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Feb;23(2):169–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. A., Kindt T. J. Segregation of polymorphic T-cell receptor genes in human families. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3804–3808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehm N. W., Carbone A., Kushnir E., Taylor B. A., Riblet R. J., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen receptor on T cells: the genetics of expression of an allotype. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2176–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A., Rauch J., Madaio M. P., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Idiotypic cross-reactions of monoclonal human lupus autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):718–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Gefter M. L., Brodeur P., Riblet R., Marshak-Rothstein A. The genetic basis of antibody production: the dominant anti-arsonate idiotype response of the strain A mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):1023–1032. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim G. K., Augustin A. A. V beta gene polymorphism and a major polyclonal T cell receptor idiotype. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):89–92. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon G., Schiffenbauer J., Keiser H. D., Diamond B. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify shared idiotypes on human antibodies to native DNA from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):850–854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D., Hamers-Casterman C., Van der Loo W., Hamers R. A rabbit with the allotypic phenotype: ala2a3 b4b5b6. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1313–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., Willems H. W., Reekers P. P., Capel P. J., Koene R. A. Polymorphism in mitogenic effect of IgG1 monoclonal antibodies against T3 antigen on human T cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):445–447. doi: 10.1038/304445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor-Kobrin C., Manser T., Moran T. M., Imanishi-Kari T., Gefter M., Bona C. A. Shared idiotopes among antibodies encoded by heavy-chain variable region (VH) gene members of the J558 VH family as basis for cross-reactive regulation of clones with different antigen specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7696–7700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A. Idiotype restriction in myasthenia gravis antibodies. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):293–294. doi: 10.1038/290293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler E. Differential activity of allelic gamma-globulin genes in antibody-producing cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1765–1772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willims R. C., Jr, Kunkel H. G., Capra J. D. Antigenic specificities related to the cold agglutinin activity of gamma M globulins. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):379–381. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



