Abstract
Revivals of quantum correlations in composite open quantum systems are a useful dynamical feature against detrimental effects of the environment. Their occurrence is attributed to flows of quantum information back and forth from systems to quantum environments. However, revivals also show up in models where the environment is classical, thus unable to store quantum correlations, and forbids system-environment back-action. This phenomenon opens basic issues about its interpretation involving the role of classical environments, memory effects, collective effects and system-environment correlations. Moreover, an experimental realization of back-action-free quantum revivals has applicative relevance as it leads to recover quantum resources without resorting to more demanding structured environments and correction procedures. Here we introduce a simple two-qubit model suitable to address these issues. We then report an all-optical experiment which simulates the model and permits us to recover and control, against decoherence, quantum correlations without back-action. We finally give an interpretation of the phenomenon by establishing the roles of the involved parties.
 In quantum systems, information can flow back and forth between the system and its environment, leading to revivals of quantum correlations. Using a simple model, Xu et al. experimentally show how revivals can occur with a classical environment despite the absence of back-action from the environment.
In quantum systems, information can flow back and forth between the system and its environment, leading to revivals of quantum correlations. Using a simple model, Xu et al. experimentally show how revivals can occur with a classical environment despite the absence of back-action from the environment.
In a multipartite quantum system one can identify different kinds of quantum correlations (such as entanglement and genuine quantum correlations), each with characteristics useful as resources for quantum information processing1,2. The exploitation of these quantum correlation resources is however jeopardized by the detrimental effects of the environment surrounding the quantum system. Quantum correlations between noninteracting qubits in independent environments have been shown to decay asymptotically2,3 or even to disappear at a finite time4,5 under the action of Markovian noise. Non-Markovian noise, like that arising from structured environments or from strong couplings, has instead been shown to lead, during the evolution, to revivals of quantum correlations4,6,7, permitting their partial recovery and thus an extension of their exploitation.
Revivals of quantum correlations, initially present in a quantum system, have been explained in terms of repeated correlation exchanges between the qubits and their non-Markovian quantum environments because of the back-action from the environments to the qubits4,6,8,9,10,11. Recently, it has been shown that revivals of quantum correlations may also occur when the environment is classical2,12,13,14,15,16 and it does not back react on the quantum system. Moreover, in such a case, the environment cannot either store or share the quantum correlations initially present in the quantum system. It thus appears that for revivals to occur it is not essential to have a non-Markovian quantum environment with back-action. This fact however leads to basic issues about the interpretation of back-action-free quantum revivals. In particular, it is essential to establish: (1) the role of the classical environment in reviving both entanglement and purely quantum correlations, for instance if it may act as a control system for what operation is applied to the qubits; (2) the role of collective effects of the environment on the qubits; (3) the role of the memory effects; (4) the role of possible system–environment correlations.
In order to address these issues and explain the mechanisms underlying the revivals without back-action, we consider a simple model that excludes the presence of collective effects of the environment on the qubits and also takes into account decoherence on the qubit evolution, so to be in a realistic scenario. We also require that the model present a system dynamics where the correlations are analytically measurable by known quantifiers, and moreover, it is realizable by a neat experimental setup that avoids any side effects that can affect the expected system dynamics and complicate the interpretation. Here we introduce a model of two noninteracting qubits, initially entangled, where only one qubit is subject to a random external classical field with inhomogeneous broadening in its amplitude. This model satisfies the above requirements. We then report the results of an all-optical experiment that simulates this model, with a random classical field mimicked by quantum degrees of freedom, and allows us to observe and control revivals of two-qubit quantum correlations without system-environment back-action. Moreover, we show a direct connection between the occurrence of the revivals and the intrinsic non-Markovianity (not due to a quantum environment) of the system evolution. Finally, we give an interpretation of the phenomenon showing the role of the classical environment in reviving quantum correlations.
Results
Theoretical model
We consider a system of two noninteracting initially entangled qubits, namely a and b, where the qubit a is isolated while the qubit b resonantly interacts with a random external classical field, whose phase is either ϕ+=+π/2 or ϕ−=−π/2 with equal probability 1/2 and whose amplitude has a Gaussian distribution. This model is illustrated in Fig. 1a. The interaction Hamiltonian between the qubit b and a classical field E with phase ϕ, in the rotating frame at the qubit-field frequency, is H=iħ(Ω/2)(σ+e−iϕ−σ−eiϕ) where the coupling constant (Rabi frequency) Ω is proportional to the field amplitude and σ± are the raising and lowering operators in the basis {|0〉,|1〉}. The time evolution operator U(t)=e−iHt/ħ has the matrix form15
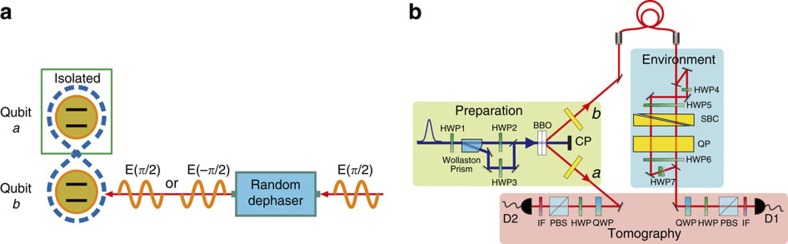
Figure 1. Model and experimental setup.
(a) Illustration of the model of a random external classical field acting only on the qubit b, whereas qubit a is isolated. The random dephaser shifts of π, with probability 1/2, the phase (π/2) of the input field. (b), Experimental setup simulating the physical model of panel a. The state preparation process is started by separating the ultraviolet pulses into two paths with the Wollaston prism. The relative amplitude between the two paths can be controlled by a HWP1. HWP2 and HWP3, with angles set to 22.5°, are used to control the polarization of the pump light by rotating |H〉 and |V〉 to 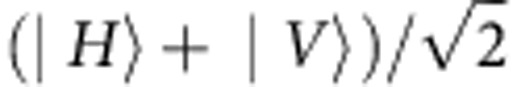 and
and 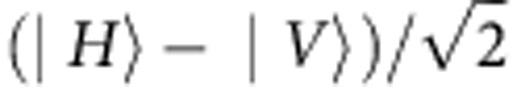 , respectively. Photon pairs are emitted into modes a and b. The birefringence in the beta-barium-borate crystals is compensated by the quartz plates (CP). The photon in mode b is then coupled by a single-mode fiber and directed to the environment part. The Soleil-Babinet compensator (SBC) and quartz plates (QPs) add a relative phase
, respectively. Photon pairs are emitted into modes a and b. The birefringence in the beta-barium-borate crystals is compensated by the quartz plates (CP). The photon in mode b is then coupled by a single-mode fiber and directed to the environment part. The Soleil-Babinet compensator (SBC) and quartz plates (QPs) add a relative phase 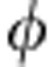 , proportional to their length, between |H〉 and |V〉. HWP4 and HWP7, with angles set to 0° introduce a relative π phase between horizontal and vertical polarizations. The angles of HWP5 and HWP6 are set to be 22.5°, which rotates |H〉 and |V〉 to
, proportional to their length, between |H〉 and |V〉. HWP4 and HWP7, with angles set to 0° introduce a relative π phase between horizontal and vertical polarizations. The angles of HWP5 and HWP6 are set to be 22.5°, which rotates |H〉 and |V〉 to 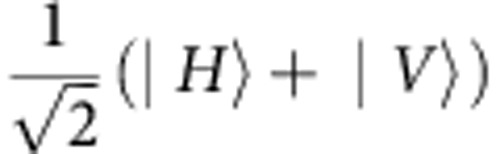 and
and 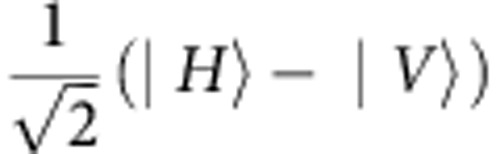 , respectively. Quantum state tomography is implemented with the polarizations of the final states analysed by a quarter-wave plate (QWP), a HWP and a polarization beam splitter (PBS) in each arm. The photons are detected by single photon avalanche detectors (D1 and D2) with 3 nm interference filters (IFs) in front of them.
, respectively. Quantum state tomography is implemented with the polarizations of the final states analysed by a quarter-wave plate (QWP), a HWP and a polarization beam splitter (PBS) in each arm. The photons are detected by single photon avalanche detectors (D1 and D2) with 3 nm interference filters (IFs) in front of them.
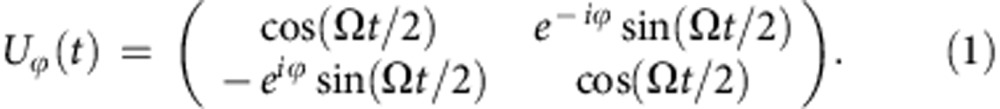 |
Due to the randomness of the field phase acting on the qubit b and being the qubit a isolated, the global dynamical map of the model of Fig. 1a is 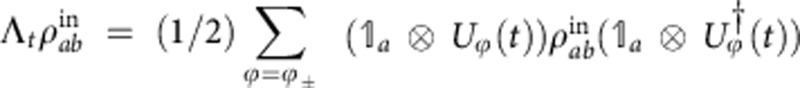 , where
, where 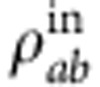 is the initial two-qubit state. A relevant property of this map is that it moves inside the class of Bell-diagonal states (that is, mixtures of the four Bell states), for which analytic expressions of the most used quantifiers of correlations are known2,17,18. Therefore, we shall choose special Bell-diagonal states as initial states of the system. At this stage the evolution is cyclic and does not exhibit decoherence. In order to introduce decoherence in the system evolution, we consider the field suffering a noise source due to signal inhomogeneous broadening whose effect is to induce a Gaussian distribution in the field amplitude and thus in the Rabi oscillation frequency Ω of the qubit evolution, that is
is the initial two-qubit state. A relevant property of this map is that it moves inside the class of Bell-diagonal states (that is, mixtures of the four Bell states), for which analytic expressions of the most used quantifiers of correlations are known2,17,18. Therefore, we shall choose special Bell-diagonal states as initial states of the system. At this stage the evolution is cyclic and does not exhibit decoherence. In order to introduce decoherence in the system evolution, we consider the field suffering a noise source due to signal inhomogeneous broadening whose effect is to induce a Gaussian distribution in the field amplitude and thus in the Rabi oscillation frequency Ω of the qubit evolution, that is 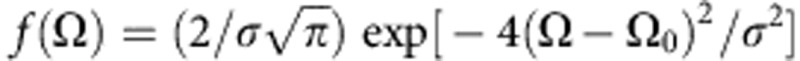 where Ω0 and σ are the central Rabi frequency and the Rabi frequency width, respectively. The effect of noise is therefore transferred to the intrinsic evolution of the quantum system. The final evolved state
where Ω0 and σ are the central Rabi frequency and the Rabi frequency width, respectively. The effect of noise is therefore transferred to the intrinsic evolution of the quantum system. The final evolved state 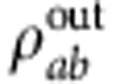 is obtained by tracing out the Rabi frequency degree of freedom from
is obtained by tracing out the Rabi frequency degree of freedom from 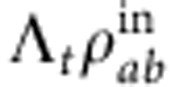 .
.
Experimental setup
The experimental setup simulating the model introduced above is displayed in Fig. 1b. The quantum system is given by two polarized photons, each one being a qubit with basis states |H〉 (horizontal polarization) and |V〉 (vertical polarization). The preparation part of the setup is able to generate polarization-entangled photon pairs in a given Bell-diagonal state 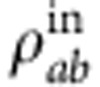 . The photon in mode a is directly sent to the state tomography part whereas the photon in mode b is directed to the environment part and successively to the state tomography part.
. The photon in mode a is directly sent to the state tomography part whereas the photon in mode b is directed to the environment part and successively to the state tomography part.
The environment is given both by the two photon paths separated by a beam-splitter, the reflected path p+ and the transmitted path p−, and by the measurement process that traces over the time difference between the two paths themselves, creating a statistical mixture of them with equal probabilities (1/2). The effect of the two paths is to make the photon basis states |H〉, |V〉 undergo, apart from an unimportant global phase factor, the unitary transformations (see second section of Methods)
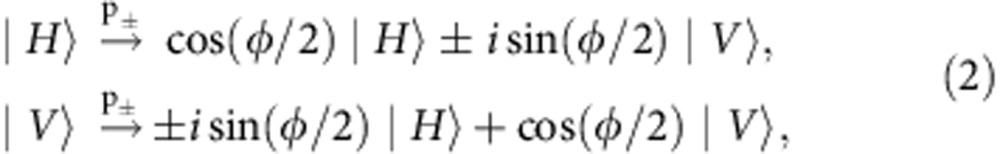 |
where 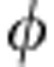 =ωτ is the phase difference between |H〉 and |V〉 introduced by the Soleil-Babinet compensator (SBC) and the quartz plates (QPs). ω is the photon frequency and τ ≡ LΔn/c is the time difference to cross the optical element (SBC or QP), with L being the thickness of the optical element, c the vacuum speed of light, Δn the difference between the indices of refraction of the horizontal and vertical polarizations. The action of each path in equation (2) corresponds to a rotation Up±(
=ωτ is the phase difference between |H〉 and |V〉 introduced by the Soleil-Babinet compensator (SBC) and the quartz plates (QPs). ω is the photon frequency and τ ≡ LΔn/c is the time difference to cross the optical element (SBC or QP), with L being the thickness of the optical element, c the vacuum speed of light, Δn the difference between the indices of refraction of the horizontal and vertical polarizations. The action of each path in equation (2) corresponds to a rotation Up±(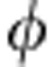 ) of the basis states {|H〉,|V〉} of b. The two paths p± of equation (2) act on the photon b exactly as the two time evolution operators
) of the basis states {|H〉,|V〉} of b. The two paths p± of equation (2) act on the photon b exactly as the two time evolution operators 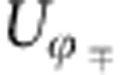 (t) of equation (1), respectively, with the correspondences |0〉 ↔ |H〉, |1〉 ↔ |V〉 and
(t) of equation (1), respectively, with the correspondences |0〉 ↔ |H〉, |1〉 ↔ |V〉 and 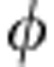 =ωτ ↔ Ωt (which implies Ω ↔ ω). The environment part of the setup simulates the random phase of the field acting on qubit b (random dephaser) by the action of the beam-splitter that separates the two photon paths, corresponding to the effect of the field with either phase, plus the measurement process that does not distinguish the two paths p±. This mimics the random external field acting on qubit b, giving the overall output state
=ωτ ↔ Ωt (which implies Ω ↔ ω). The environment part of the setup simulates the random phase of the field acting on qubit b (random dephaser) by the action of the beam-splitter that separates the two photon paths, corresponding to the effect of the field with either phase, plus the measurement process that does not distinguish the two paths p±. This mimics the random external field acting on qubit b, giving the overall output state 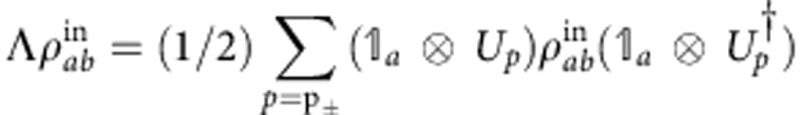 . Up to now we have considered a photon with frequency ω. In fact, in our experiment the photon has an intrinsic Gaussian frequency distribution
. Up to now we have considered a photon with frequency ω. In fact, in our experiment the photon has an intrinsic Gaussian frequency distribution 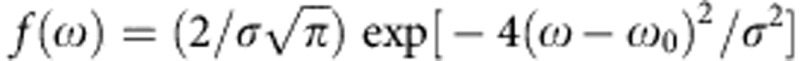 (ref. 19), where ω0 is the center frequency and σ the frequency width. This frequency degree of freedom introduces decoherence by a decoherence parameter κ=∫f(ω)cos[
(ref. 19), where ω0 is the center frequency and σ the frequency width. This frequency degree of freedom introduces decoherence by a decoherence parameter κ=∫f(ω)cos[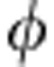 (ω)]dω=cos(ω0τ)exp(−σ2τ2/16) (ref. 3). This decoherence source is of the same kind as that due to the Rabi frequency distribution in the model introduced above. The effective evolved state
(ω)]dω=cos(ω0τ)exp(−σ2τ2/16) (ref. 3). This decoherence source is of the same kind as that due to the Rabi frequency distribution in the model introduced above. The effective evolved state 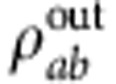 is then obtained by tracing out the photon frequency degree of freedom from
is then obtained by tracing out the photon frequency degree of freedom from 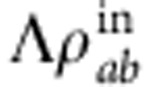 .
.
We prepare initial Bell diagonal states of the form (see first section of Methods)
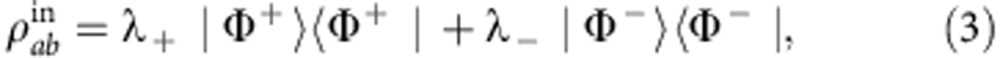 |
where λ++λ−=1 and 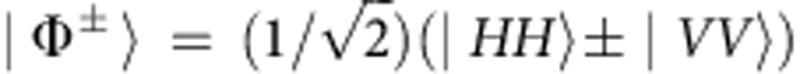 . λ+ is arbitrarily determined by the relative power between the two pump paths created by the Wollaston prism. As a consequence, the two-photon output state is the Bell-diagonal state (see second section of Methods)
. λ+ is arbitrarily determined by the relative power between the two pump paths created by the Wollaston prism. As a consequence, the two-photon output state is the Bell-diagonal state (see second section of Methods)
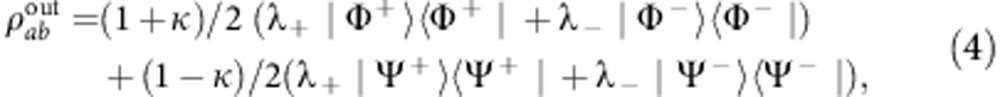 |
where 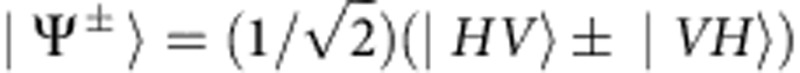 . When L is small so that
. When L is small so that  (exp(−σ2τ2/16) ≈1), the decoherence parameter becomes κ≈ cos(
(exp(−σ2τ2/16) ≈1), the decoherence parameter becomes κ≈ cos( =ω0τ) and we have a cyclic and thus coherent evolution: this is the case when only the SBC, that allows us to adjust small lengths, is used. When the QPs are used the decoherent evolution comes out.
=ω0τ) and we have a cyclic and thus coherent evolution: this is the case when only the SBC, that allows us to adjust small lengths, is used. When the QPs are used the decoherent evolution comes out.
Experimental dynamics of correlations
We investigate the dynamics of the various kinds of correlations present in the two-qubit system. We quantify the total correlations by the quantum mutual information2
 and the entanglement by concurrence1
and the entanglement by concurrence1
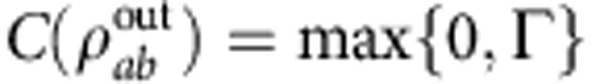 , where Γ is a function of
, where Γ is a function of 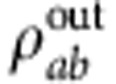 . Quantum correlations are instead quantified by the quantum discord2
. Quantum correlations are instead quantified by the quantum discord2
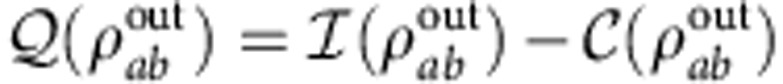 , where
, where 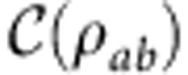 indicates the classical correlations (see third section of Methods).
indicates the classical correlations (see third section of Methods).
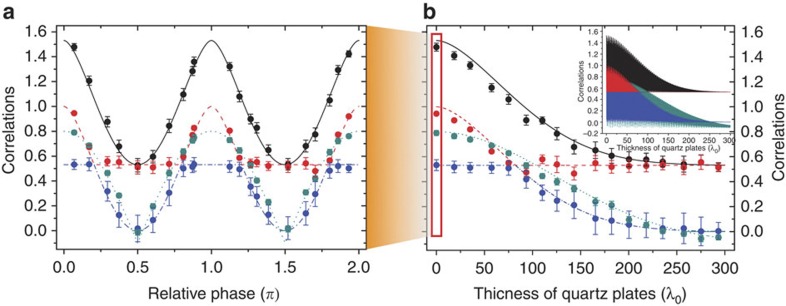
The results for the coherent evolution, realized by the SBC device with the QPs removed, are plotted as a function of the relative phase 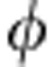 =ω0τ in Fig. 2a, starting from
=ω0τ in Fig. 2a, starting from 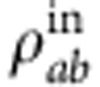 with λ+=0.9. Total correlations oscillate with period π. Plateaus and sudden changes in the dynamics of classical and quantum correlations occur several times, showing their robustness against variations of the relative phase. Quantum correlations revive after vanishing at about π/2 and 3π/2 (in a 2π period). Entanglement exhibits dark periods around the same points and then revives.
with λ+=0.9. Total correlations oscillate with period π. Plateaus and sudden changes in the dynamics of classical and quantum correlations occur several times, showing their robustness against variations of the relative phase. Quantum correlations revive after vanishing at about π/2 and 3π/2 (in a 2π period). Entanglement exhibits dark periods around the same points and then revives.
Figure 2. Dynamics of correlations in the absence of system-environment back-action.
The initial input state ρabin has λ+=0.9. The black solid line, dashed red line, dot-dashed blue line and dotted dark cyan line represent, respectively, the theoretical predictions of total , classical , quantum correlations and concurrence C (the value is set to 0 when Γ<0, which is represented by the solid dark cyan line). The black, red, blue and dark cyan dots represent the corresponding experimental results. (a) The dynamics of correlations in the coherent evolution. Only the SBC is used in the experimental setup and the relative phase (in units of π) is 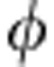 =ω0τ. Revivals of entanglement and of quantum correlations are clearly noticed. (b) The maximum of the correlations is plotted as a function of the QP length L (in units of λ0=800 nm, that is the center photon wavelength). The coherent evolution, including oscillations and revivals, in a is a part of the decoherent evolution in b, which is denoted by the red box in b. The inset of b shows the theoretical dynamics of the various kinds of correlations with a calculation precision set to 0.1λ0. Error bars are due to the counting statistics.
=ω0τ. Revivals of entanglement and of quantum correlations are clearly noticed. (b) The maximum of the correlations is plotted as a function of the QP length L (in units of λ0=800 nm, that is the center photon wavelength). The coherent evolution, including oscillations and revivals, in a is a part of the decoherent evolution in b, which is denoted by the red box in b. The inset of b shows the theoretical dynamics of the various kinds of correlations with a calculation precision set to 0.1λ0. Error bars are due to the counting statistics.
In Fig. 2b, we further show the experimental results for the decoherent evolution, where both SBC and QPs are used. We plot the envelope dynamics of correlations as a function of the QP length L for the same initial state 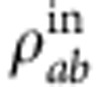 with λ+=0.9, by measuring the maximum amplitudes of revival of the quantifiers. A sudden change in behaviour in the dynamics of the maximum values of classical and quantum correlations is found when L≈82λ0 (λ0=800 nm is the center photon wavelength). The maximum of entanglement revivals decreases monotonously and completely vanishes at L≈258λ0. The theoretical curves exhibiting these decaying revivals are displayed in the inset of Fig. 2b. The coherent evolution in Fig. 2a is part of the decoherent evolution in Fig. 2b, which is denoted by the red box in Fig. 2b. Although the decay behavior of the maximum values of correlations is similar to that in ref. 3, the internal noise mechanism is completely different. There are no revivals of correlations in the Markovian evolution of ref. 3, whereas here the correlations exhibit collapses and revivals during the evolution in absence of system-environment back-action.
with λ+=0.9, by measuring the maximum amplitudes of revival of the quantifiers. A sudden change in behaviour in the dynamics of the maximum values of classical and quantum correlations is found when L≈82λ0 (λ0=800 nm is the center photon wavelength). The maximum of entanglement revivals decreases monotonously and completely vanishes at L≈258λ0. The theoretical curves exhibiting these decaying revivals are displayed in the inset of Fig. 2b. The coherent evolution in Fig. 2a is part of the decoherent evolution in Fig. 2b, which is denoted by the red box in Fig. 2b. Although the decay behavior of the maximum values of correlations is similar to that in ref. 3, the internal noise mechanism is completely different. There are no revivals of correlations in the Markovian evolution of ref. 3, whereas here the correlations exhibit collapses and revivals during the evolution in absence of system-environment back-action.
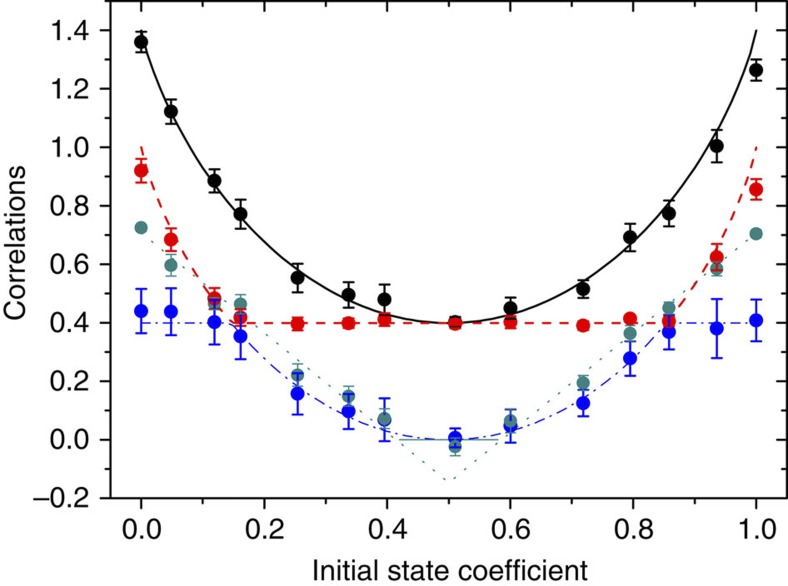
Our experimental setup controls λ+ and thus the revival amplitude. Figure 3 shows the results for the coherent evolution at a relative phase 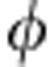 =π/4 (also applicable at
=π/4 (also applicable at 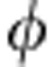 =3π/4 in the region of first revival). It is seen that all correlations are symmetric to the point λ+=0.5, which represents a classical initial state (zero quantum correlations). Interestingly, there is a range of values of λ+ (
=3π/4 in the region of first revival). It is seen that all correlations are symmetric to the point λ+=0.5, which represents a classical initial state (zero quantum correlations). Interestingly, there is a range of values of λ+ ( and
and 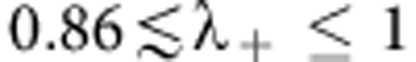 ) where quantum correlations remain unchanged at their maximum value, implying that at
) where quantum correlations remain unchanged at their maximum value, implying that at 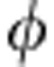 =3π/4 they cannot take a value larger than that observed in Fig. 2a, for λ+=0.9. This is connected to a peculiar behaviour of the sudden change points of Q. In contrast, the degree of entanglement revival at
=3π/4 they cannot take a value larger than that observed in Fig. 2a, for λ+=0.9. This is connected to a peculiar behaviour of the sudden change points of Q. In contrast, the degree of entanglement revival at 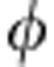 =3π/4 can be increased with respect to that of Fig. 2a, for example, by increasing λ+.
=3π/4 can be increased with respect to that of Fig. 2a, for example, by increasing λ+.
Figure 3. Control of the amount of correlations.
Different kinds of correlations as a function of λ+ (initial state coefficient) in the case of coherent evolution, at a fixed value of relative phase 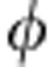 =ω0τ set to π/4. Due to the periodic behaviour of the correlations as a function of
=ω0τ set to π/4. Due to the periodic behaviour of the correlations as a function of 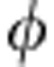 observed in Fig. 2a, the results are immediately applicable, for example, at the point
observed in Fig. 2a, the results are immediately applicable, for example, at the point 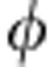 =3π/4 that is in the region of first revival. The black solid line, dashed red line, dot-dashed blue line and dotted dark cyan line represent, respectively, the theoretical predictions of total , classical , quantum correlations and concurrence C (the value is set to 0 when Γ<0, which is represented by the solid dark cyan line). Black, red, blue and dark cyan dots represent the corresponding experimental results. Error bars are due to the counting statistics. There is a good agreement among theoretical curves and experimental points.
=3π/4 that is in the region of first revival. The black solid line, dashed red line, dot-dashed blue line and dotted dark cyan line represent, respectively, the theoretical predictions of total , classical , quantum correlations and concurrence C (the value is set to 0 when Γ<0, which is represented by the solid dark cyan line). Black, red, blue and dark cyan dots represent the corresponding experimental results. Error bars are due to the counting statistics. There is a good agreement among theoretical curves and experimental points.
Connection to non-Markovianity
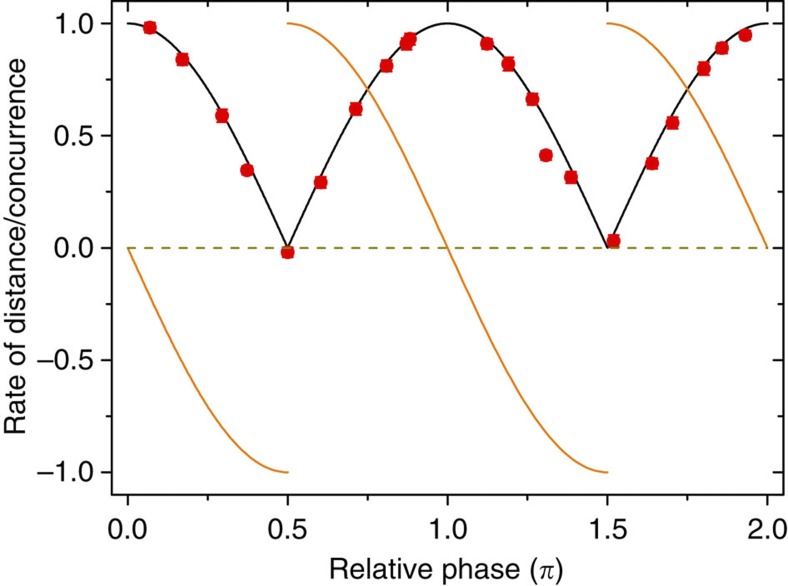
The observation of the revivals without back-action in our setup can be connected to the intrinsic non-Markovianity of the system evolution. In our system, photon b experiences the noisy environment and photon a can be treated as an isolated ancilla. Non-Markovianity then immediately follows from the non-monotonous behaviour of entanglement evolution obtained starting from the input Bell state 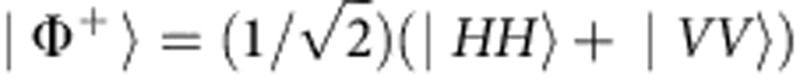 (ref. 20), displayed in Fig. 4 for the coherent case. This aspect is emphasized if we consider the non-Markovianity measure based on the trace distance D(t)8. Any temporary increase of D(t) is a signature of non-Markovianity that can be identified by the regions where the rate of change σ(t)=dD(t)/dt is positive. For our local map of random external fields, within the coherent case where
(ref. 20), displayed in Fig. 4 for the coherent case. This aspect is emphasized if we consider the non-Markovianity measure based on the trace distance D(t)8. Any temporary increase of D(t) is a signature of non-Markovianity that can be identified by the regions where the rate of change σ(t)=dD(t)/dt is positive. For our local map of random external fields, within the coherent case where 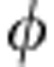 =ω0τ is the dimensionless time variable, we have21
σ(
=ω0τ is the dimensionless time variable, we have21
σ(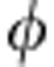 )=−sgn(cos
)=−sgn(cos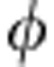 )sin
)sin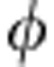 where sgn(x) is the sign function (see last section of Methods). We find σ(
where sgn(x) is the sign function (see last section of Methods). We find σ(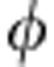 )>0 just when entanglement revivals occur, as displayed in Fig. 4. Interestingly, we also notice that the larger entangling rates of the system correspond to the larger signatures of memory effects (larger values of σ(
)>0 just when entanglement revivals occur, as displayed in Fig. 4. Interestingly, we also notice that the larger entangling rates of the system correspond to the larger signatures of memory effects (larger values of σ(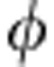 )).
)).
Figure 4. Revivals and non-Markovianity.
The entanglement evolution, quantified by the concurrence C, of the initial maximally entangled state 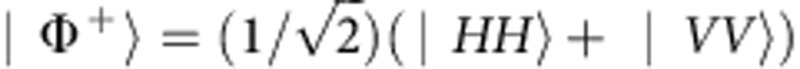 for the coherent case as a function of the relative phase
for the coherent case as a function of the relative phase 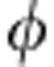 =ω0τ (in units of π). Red dots represent the experimental results of C and the black solid line represents the corresponding theoretical prediction C=|cos
=ω0τ (in units of π). Red dots represent the experimental results of C and the black solid line represents the corresponding theoretical prediction C=|cos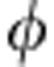 |. The orange solid line represents the evolution of the trace distance rate of change σ(
|. The orange solid line represents the evolution of the trace distance rate of change σ(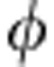 ) that is positive (signature of non-Markovianity) just when the entanglement revivals occur. The dashed dark yellow line represents the boundary 0.
) that is positive (signature of non-Markovianity) just when the entanglement revivals occur. The dashed dark yellow line represents the boundary 0.
The trace-distance measure indicates the presence of non-Markovianity when the distinguishability of the pair of states increases with time: this can be simply interpreted as a flow of information from the environment back to the system which enhances the possibility of distinguishing the two states. We however remark that this back-flow of information does not necessarily imply back-action and correlation exchange. The presence of system-environment back-action means that the system affects its dynamics via the environment. When the environment dynamics is unaffected by the system this back-action on the system cannot occur. This is the case considered in our model and in the corresponding experimental setup.
Interpretation
The connection between the revivals and the intrinsic non-Markovianity of the system evolution does not by itself provide an explanation of the observed phenomenon but only gives a necessary condition for it to occur. A possible interpretation of the phenomenon of quantum correlation recovery in absence of system-environment back-action can be provided when one describes the initial global system-environment state 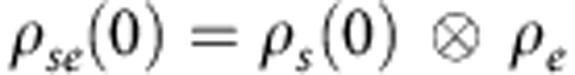 of our setup as a quantum-classical state15, where the quantum part is the two-photon system
of our setup as a quantum-classical state15, where the quantum part is the two-photon system 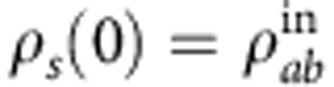 and the classical part is the environment e acting locally on the photon b. The environment can only be in a separable mixture of its basis states that in our setup can be expressed as
and the classical part is the environment e acting locally on the photon b. The environment can only be in a separable mixture of its basis states that in our setup can be expressed as 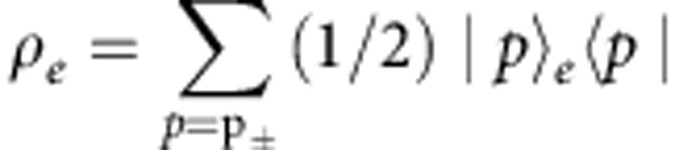 , where |p±〉e are the basis states corresponding to the two random paths (field phases in the theoretical model) of equation (2). By this formalism, we are able to quantify the correlations present in the global quantum-classical system a-b-e. We also show that the environment e and the photon b never become correlated during the evolution and that this aspect however does not jeopardize the role of the classical environment in reviving the quantum correlations initially present in the quantum system.
, where |p±〉e are the basis states corresponding to the two random paths (field phases in the theoretical model) of equation (2). By this formalism, we are able to quantify the correlations present in the global quantum-classical system a-b-e. We also show that the environment e and the photon b never become correlated during the evolution and that this aspect however does not jeopardize the role of the classical environment in reviving the quantum correlations initially present in the quantum system.
For the sake of simplicity let us consider the case when decoherence is negligible (analogous argumentations hold even if decoherence is present). The two-qubit output state 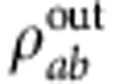 is obtained by tracing the overall evolved state ρse(
is obtained by tracing the overall evolved state ρse( ) over the environment e, where
) over the environment e, where 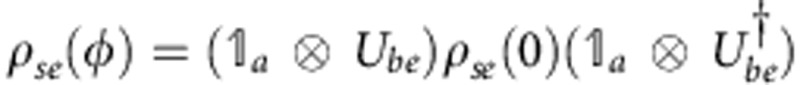 and
and 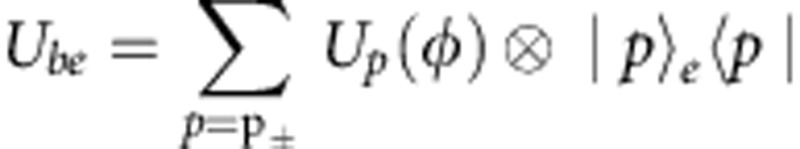 is the unitary operation acting on qubit b and its environment e. This way, the same dynamics observed above for a-b correlations exhibiting the revivals is retrieved. During the time evolution, due to
is the unitary operation acting on qubit b and its environment e. This way, the same dynamics observed above for a-b correlations exhibiting the revivals is retrieved. During the time evolution, due to  , the states of the classical environment are invariant, the qubit b does not affect the environment and the back-action by the environment on the qubit is absent. Moreover, a classical environment cannot store any quantum correlations on its own. One could then think that the presence of revivals is due to some correlation established between b and e. The subsystem b-e evolves under the local unitary operation Ube so that the correlations between b-e are invariant. If one traces ρse(
, the states of the classical environment are invariant, the qubit b does not affect the environment and the back-action by the environment on the qubit is absent. Moreover, a classical environment cannot store any quantum correlations on its own. One could then think that the presence of revivals is due to some correlation established between b and e. The subsystem b-e evolves under the local unitary operation Ube so that the correlations between b-e are invariant. If one traces ρse(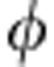 ) over the isolated qubit a, it is straightforward to show that the qubit b and its environment e never become quantum correlated. For example, for an initial Bell-diagonal state between a–b like that of equation (3), it results that the reduced state of b–e during the evolution is the uncorrelated state
) over the isolated qubit a, it is straightforward to show that the qubit b and its environment e never become quantum correlated. For example, for an initial Bell-diagonal state between a–b like that of equation (3), it results that the reduced state of b–e during the evolution is the uncorrelated state  . Therefore, the qubit–environment correlations do not have any role in the occurrence of the phenomenon under investigation.
. Therefore, the qubit–environment correlations do not have any role in the occurrence of the phenomenon under investigation.
From the structure of Ube it is clear that the environment only has the role of a control system for what unitary operation is applied to the qubit b. By memory effects, the environment e keeps a classical record of what unitary operation has been applied to the qubit b and this happens even without back-action. It is the lack of this classical information that makes quantum correlations disappear at a given time and it is the recovery of this information that makes quantum correlations then revive. The information the environment holds about a system is therefore due to what action the environment performs on the system. To better clarify this aspect, let us consider the evolution in Fig. 4. When quantum correlations are zero, for example at 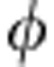 =π/2, there is a complete lack of classical information about what unitary operation the environment is applying to the qubit (statistical mixing of the two different unitary operations Up±); successively, when the initial quantum correlations are recovered at
=π/2, there is a complete lack of classical information about what unitary operation the environment is applying to the qubit (statistical mixing of the two different unitary operations Up±); successively, when the initial quantum correlations are recovered at 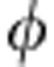 =π, this information becomes known because the two unitaries both act as a σx ‘bit-flip’ operation (they are just the same operation).
=π, this information becomes known because the two unitaries both act as a σx ‘bit-flip’ operation (they are just the same operation).
Discussion
In this article we have introduced a simple two-qubit model particularly suitable to investigate the issue of the occurrence of revivals of quantum correlations despite the absence of back-action. In this model only one qubit of the pair locally interacts with a classical environment, in the form of a random external field with inhomogeneous broadening. The model forbids any mechanism both of system-environment back-action and of quantum correlation storage. Moreover, this model presents an overall decoherent evolution where any collective effect of external fields on the two-qubit system is excluded. We have then reported the results of a novel all-optical experimental setup that simulates the introduced model and permits us to observe revivals of quantum correlations (entanglement, quantum discord), with a decreasing revival amplitude in time. The amplitude of revivals can be controlled by adjusting the parameter of the initially prepared state.
We have also experimentally and theoretically shown, as a necessary condition for revivals of quantum correlations to occur, the link between the revivals themselves and the intrinsic non-Markovian feature of the system evolution. We have provided a possible interpretation of the phenomenon in terms of quantum-classical system, showing the role had by the classical environment as a control system for what action it has on the quantum system and then in reviving quantum correlations. The introduced model and the corresponding experimental setup have thus permitted us to identify an interpretation of the phenomenon and to exclude side effects. Our findings clearly reveal that the revivals of quantum correlations are a dynamical feature of composite open systems independent of the nature (classical or quantum) of the environment.
Finally, our results introduce the possibility to recover and control, against decoherence, quantum correlation resources even in absence of back-action, without resorting to quantum structured environments22,23,24 or correction procedures4,25,26,27 and moreover open the way to further studies on the issue of quantum correlation revivals in classical environments15,28.
Methods
State preparation process
As depicted in Fig. 1b, ultraviolet pulses are frequency doubled from a mode-locked Ti:sapphire laser centered at 800 nm with 130 fs pulse width and 76 MHz repetition rate, and pass through a half-wave plate (HWP)1 and a Wollaston prism to be separated into two optical pump paths. The HWP1 rotates the polarization of the ultraviolet pulses which are separated by the Wollaston prism into two paths. The Wollaston prism transmits horizontal polarization |H〉 and reflects vertical polarization |V〉. Therefore, the relative amplitude between the two pump paths can be controlled by the HWP1. The HWP2 and HWP3 are used to control the polarization of the corresponding pump light. The two pump pulses are then combined by a polarization-independent beam-splitter and pump two identically cut type-I beta-barium-borate crystals, with their optic axes aligned in mutually perpendicular planes29, to generate entangled photon pairs. After compensating the birefringence effect between |H〉 and |V〉 in beta-barium-borate crystals with quartz plates (CP), maximally entangled photon pairs are generated in the state 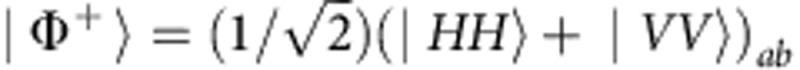 by the transmitted pump pulses and in the state
by the transmitted pump pulses and in the state 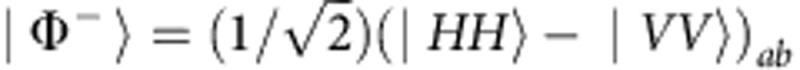 by the reflected pump pulses. In our experiment, the time difference between the two pump paths is larger than the coherence length of the pump light so that the path information is traced out at the end of measurement3. The prepared state is then the Bell-diagonal state
by the reflected pump pulses. In our experiment, the time difference between the two pump paths is larger than the coherence length of the pump light so that the path information is traced out at the end of measurement3. The prepared state is then the Bell-diagonal state 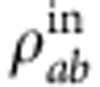 of equation (3).
of equation (3).
Action of the environment part of the setup and output state
If the photon b is in the horizontal polarization |H〉 and enters the environment part of the setup (see Fig. 1b), it undergoes all the transformations due to each optical component in the transmitted path (p−) and reflected part (p+) that give, respectively, 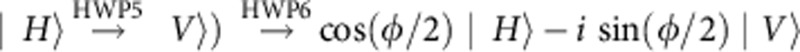 and
and 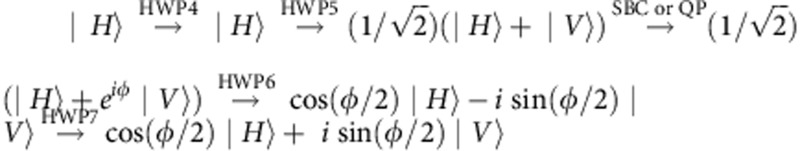 , where we have omitted the unimportant global phase factor ei
, where we have omitted the unimportant global phase factor ei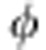 /2. These are the two unitary transformations for |H〉 given in equation (2), with
/2. These are the two unitary transformations for |H〉 given in equation (2), with 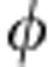 =ωτ. Analogously, one obtains those for the polarization |V〉. In particular, we find that the transmitted path transformation is
=ωτ. Analogously, one obtains those for the polarization |V〉. In particular, we find that the transmitted path transformation is 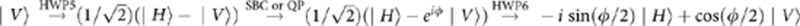 , whereas the reflected path transformation is
, whereas the reflected path transformation is 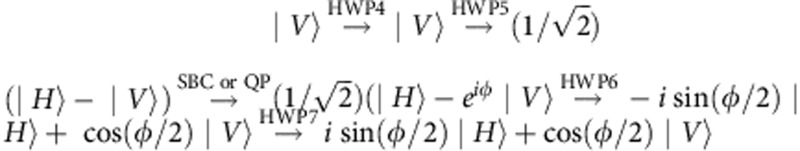 . These are the two unitary transformations for |V〉 displayed in equation (2).
. These are the two unitary transformations for |V〉 displayed in equation (2).
We now consider the evolution of the two-photon state 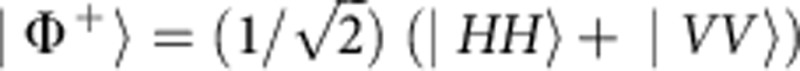 with a single frequency ω. The state at the end of the transmitted part and of the reflected part is obtained by applying the transformations of equation (2) only on the second qubit b and it reads, respectively,
with a single frequency ω. The state at the end of the transmitted part and of the reflected part is obtained by applying the transformations of equation (2) only on the second qubit b and it reads, respectively,
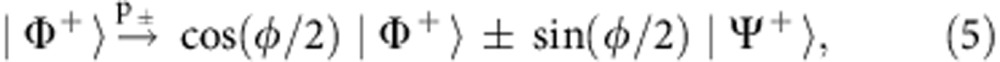 |
where 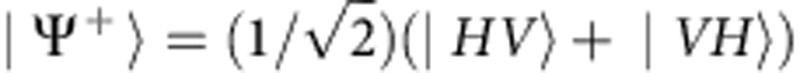 . After tracing out the path information (the detection in our experiment traces over the time difference between the two paths), the input state |Φ+〉 then becomes the output mixed state.
. After tracing out the path information (the detection in our experiment traces over the time difference between the two paths), the input state |Φ+〉 then becomes the output mixed state.
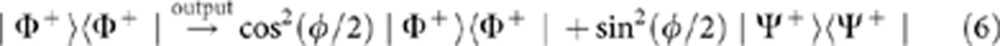 |
Similarly, when the input state is |Φ−〉 the output state becomes
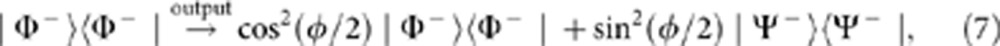 |
where 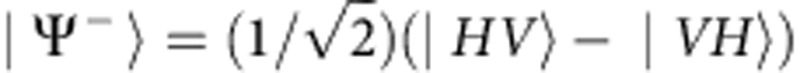 . Therefore, starting from the effectively prepared state
. Therefore, starting from the effectively prepared state 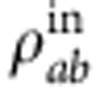 of equation (3), the two-photon output state is
of equation (3), the two-photon output state is
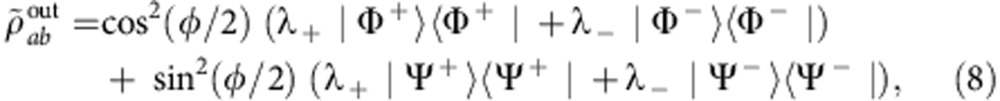 |
The previous output state corresponds to the case of coherent evolution, where only the SBC is used (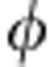 =ω0τ). Considering the Gaussian distribution f(ω) of the frequency ω, the decoherence parameter κ=∫f(ω)cos
=ω0τ). Considering the Gaussian distribution f(ω) of the frequency ω, the decoherence parameter κ=∫f(ω)cos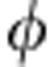 (ω)dω arises by tracing out the photon frequency degrees of freedom. As
(ω)dω arises by tracing out the photon frequency degrees of freedom. As 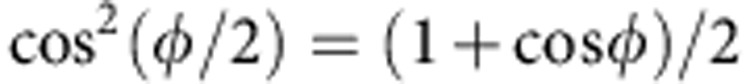 and
and 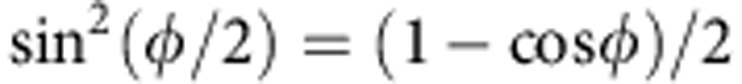 , the introduction of the decoherence parameter κ turns the previous state
, the introduction of the decoherence parameter κ turns the previous state 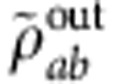 into the output state
into the output state 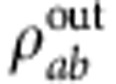 given in equation (4).
given in equation (4).
Correlation quantifiers
Total correlations are calculated by the quantum mutual information 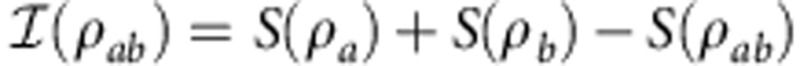 , where ρa and ρb are the reduced density matrices of ρab whereas
, where ρa and ρb are the reduced density matrices of ρab whereas 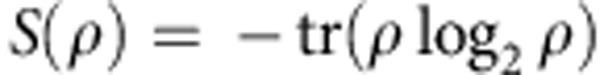 is the von Neumann entropy2. Classical correlations are defined as the maximal information gained about ρab by a measurement on one of the qubits, that is2
is the von Neumann entropy2. Classical correlations are defined as the maximal information gained about ρab by a measurement on one of the qubits, that is2
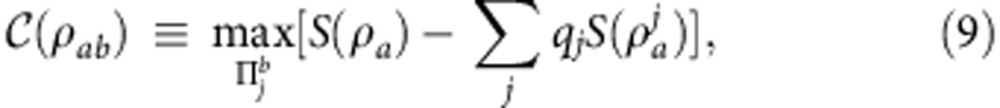 |
where 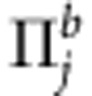 is the set of projective measurements performed on qubit b,
is the set of projective measurements performed on qubit b, 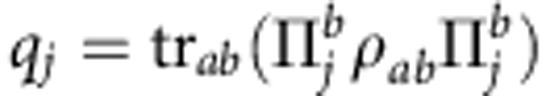 and
and 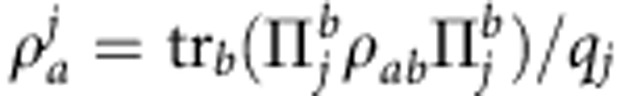 is the post-measurement state of a after obtaining the outcome j on b. Quantum correlations (quantum discord) are then given by2
is the post-measurement state of a after obtaining the outcome j on b. Quantum correlations (quantum discord) are then given by2
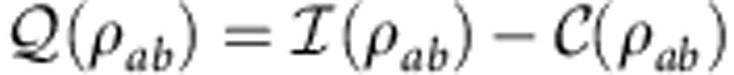 . Two-qubit entanglement is quantified by concurrence1
C(ρab)=max{0,Γ}, where
. Two-qubit entanglement is quantified by concurrence1
C(ρab)=max{0,Γ}, where 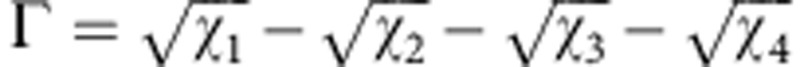 , and χj are the eigenvalues in decreasing order of the matrix
, and χj are the eigenvalues in decreasing order of the matrix 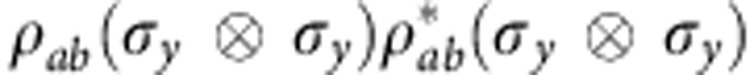 with σy denoting the second Pauli matrix and
with σy denoting the second Pauli matrix and 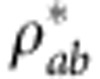 corresponding to the complex conjugate of ρab in the canonical basis {|HH〉,|HV〉,|VH〉,|VV〉}. The theoretical dynamics of the correlation quantifiers is found by using their known analytical expressions for Bell-diagonal states2,17. The experimental results are acquired from the reconstructed output density matrices (by state tomography). Total correlations and concurrence are directly calculated for the output states. For obtaining classical and quantum correlations the maximization of equation (9) is required, performed by scanning the projective operators
corresponding to the complex conjugate of ρab in the canonical basis {|HH〉,|HV〉,|VH〉,|VV〉}. The theoretical dynamics of the correlation quantifiers is found by using their known analytical expressions for Bell-diagonal states2,17. The experimental results are acquired from the reconstructed output density matrices (by state tomography). Total correlations and concurrence are directly calculated for the output states. For obtaining classical and quantum correlations the maximization of equation (9) is required, performed by scanning the projective operators 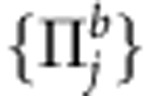 represented by {cosα|H〉+eiθsinα|V〉, e−iθsinα|H〉−cosα|V〉} on photon b. The scan precision of α and θ is set to π/100.
represented by {cosα|H〉+eiθsinα|V〉, e−iθsinα|H〉−cosα|V〉} on photon b. The scan precision of α and θ is set to π/100.
Quantifier of non-Markovianity
We consider a maximally entangled input state 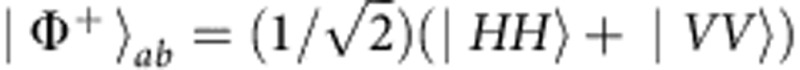 , with the photon b subject to the environment and photon a isolated. The output state, in the coherent evolution case (
, with the photon b subject to the environment and photon a isolated. The output state, in the coherent evolution case (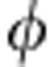 =ω0τ is the dimensionless time variable), becomes
=ω0τ is the dimensionless time variable), becomes 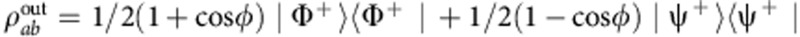 . The entanglement of the final state is quantified by the concurrence C=2 max[1/2(1+cos
. The entanglement of the final state is quantified by the concurrence C=2 max[1/2(1+cos ), 1/2(1−cos
), 1/2(1−cos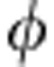 )]−1, that is C(
)]−1, that is C(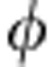 )=|cos
)=|cos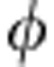 |.
|.
We quantify the memory effects present in the evolution of a system using the criterion of non-Markovianity based on the distinguishability of two evolving quantum states, as measured by the trace distance D(ρ1(t),ρ2(t))=(1/2)|ρ1(t)−ρ2(t)|, where 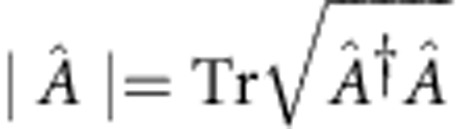 , ρi(t)=Λtρi(0) (i=1,2) and Λt is a dynamical map of the open system8. The rate of change of the trace distance is
, ρi(t)=Λtρi(0) (i=1,2) and Λt is a dynamical map of the open system8. The rate of change of the trace distance is
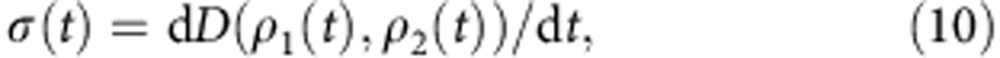 |
Given two initial states of the system, any temporary increase of the trace distance (σ(t)>0) is a signature of memory effects (non-Markovianity of the dynamical map of the system). In order to obtain the degree of non-Markovianity one then takes the maximum of σ(t) over the possible initial states ρ1,2(0) and calculates8
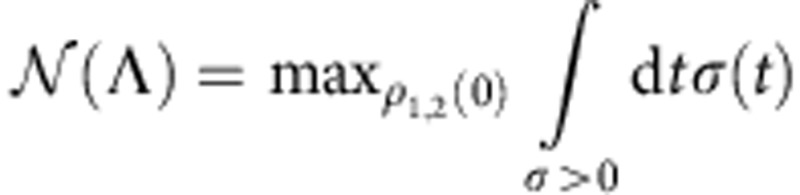 .
.
Let us now consider the dynamical map of random external fields acting on a qubit in the coherent case (small lengths of the QPs, SBC compensator) 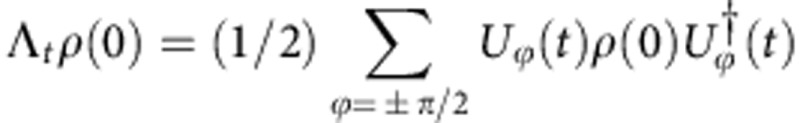 , where Uϕ is defined in equation (1) and Ωt ≡ ω0τ=
, where Uϕ is defined in equation (1) and Ωt ≡ ω0τ= . For two arbitrary initial states, ρk(0) (k=1,2) in the basis {|0〉 ≡ |H〉,|1〉 ≡ |V〉}
. For two arbitrary initial states, ρk(0) (k=1,2) in the basis {|0〉 ≡ |H〉,|1〉 ≡ |V〉}
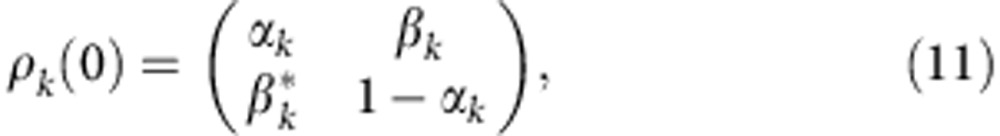 |
the trace distance evolves as 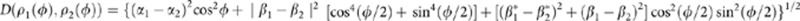 . It follows that the maximum of the rate of change is found for the initial states having α1=α2=1/2 and β1=−β2=i/2, that is the pure states
. It follows that the maximum of the rate of change is found for the initial states having α1=α2=1/2 and β1=−β2=i/2, that is the pure states 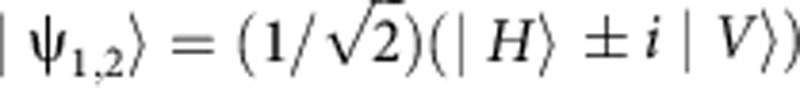 . In this case the trace distance is D(ρ1(
. In this case the trace distance is D(ρ1(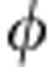 ),ρ2(
),ρ2(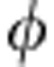 ))=|cos
))=|cos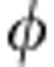 |=C(
|=C(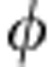 ) and the corresponding rate of change is σ(
) and the corresponding rate of change is σ(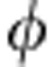 )=−sgn(cos
)=−sgn(cos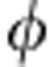 )sin
)sin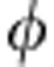 21.
21.
Author contributions
J.-S.X. designed the experiment. J.-S.X. and K.S. performed the experiment with the assistance of X.-Y.X. R.L.F., G.C. and E.A. provided the theoretical analysis. C.-F.L. and G.-C.G. supervised the project. R.L.F., G.C. and J.-S.X. wrote the manuscript. All authors read the manuscript and discussed the experimental results.
Additional information
How to cite this article: Xu, J.-S. et al. Experimental recovery of quantum correlations in absence of system-environment back-action. Nat. Commun. 4:2851 doi: 10.1038/ncomms3851 (2013).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2011CB921200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos 11004185, 11274297, 61322506, 60921091, 11274289, 11325419, 61327901), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. WK 2030020019, WK2470000011), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0508), Science foundation for the excellent PHD thesis (Grant No. 201218) and the CAS.
References
- Horodecki R., Horodecki P., Horodecki M. & Horodecki K. Quantum entanglement. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 865–942 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Modi K., Brodutch A., Cable H., Paterek T. & Vedral V. The classical-quantum boundary for correlations: discord and related measures. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 1655–1707 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Xu J.-S. et al. Experimental investigation of classical and quantum correlations under decoherence. Nat. Commun. 1, 7 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu T. & Eberly J. H. Sudden death of entanglement. Science 323, 598–601 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida M. P. et al. Environment-induced sudden death of entanglement. Science 316, 579–582 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo Franco R., Bellomo B., Maniscalco S. & Compagno G. Dynamics of quantum correlations in two-qubit systems within non-Markovian environments. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 27, 1345053 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Xu J.-S. et al. Experimental demonstration of photonic entanglement collapse and revival. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 100502 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B.-H. et al. Experimental control of the transition from Markovian to non-Markovian dynamics of open quantum systems. Nat. Phys. 7, 931–934 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo B., Lo Franco R. & Compagno G. Non-Markovian effects on the dynamics of entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 160502 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López C. E., Romero G. & Retamal J. C. Dynamics of entanglement transfer through multipartite dissipative systems. Phys. Rev. A 81, 062114 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Chiuri A., Greganti C., Mazzola L., Paternostro M. & Mataloni P. Linear optics simulation of non-Markovian quantum dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2, 968 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Lang A. & Joynt R. Disentanglement and decoherence from classical non-Markovian noise: random telegraph noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 9, 727–747 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Lo Franco R., D’Arrigo A., Falci G., Compagno G. & Paladino E. Entanglement dynamics in superconducting qubits affected by local bistable impurities. Phys. Scr. T147, 014019 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Bordone P., Buscemi F. & Benedetti C. Effect of Markov and non-Markov classical noise on entanglement dynamics. Fluct. Noise Lett. 11, 1242003 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Lo Franco R., Bellomo B., Andersson E. & Compagno G. Revival of quantum correlations without system-environment back-action. Phys. Rev. A 85, 032318 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Altintas F., Kurt A. & Eryigit R. Classical memoryless noise-induced maximally discordant mixed separable steady states. Phys. Lett. A 377, 53–59 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo B., Lo Franco R. & Compagno G. Dynamics of geometric and entropic quantifiers of correlations in open quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 86, 012312 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson B., Lo Franco R. & Adesso G. Comparative investigation of the freezing phenomena for quantum correlations under nondissipative decoherence. Phys. Rev. A 88, 012120 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Xu J.-S. et al. Experimental characterization of entanglement dynamics in noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 240502 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas Á., Huelga S. F. & Plenio M. B. Entanglement and non-Markovianity of quantum evolutions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 050403 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannone M., Lo Franco R. & Compagno G. Comparison of non-Markovianity criteria in a qubit system under random external fields. Phys. Scr. T153, 014047 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo B., Lo Franco R., Maniscalco S. & Compagno G. Entanglement trapping in structured environments. Phys. Rev. A 78, 060302(R) (2008). [Google Scholar]
- Barreiro J. T. et al. Experimental multiparticle entanglement dynamics induced by decoherence. Nat. Phys. 6, 943–946 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. et al. Quantum memory for entangled continuous-variable states. Nat. Phys. 7, 13–16 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- Dong R. et al. Experimental entanglement distillation of mesoscopic quantum states. Nat. Phys. 4, 919–923 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman H. M. & Milburn G. J. Quantum Measurement and Control Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, NY, USA, (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Bylander J. et al. Noise spectroscopy through dynamical decoupling with a superconducting flux qubit. Nat. Phys. 7, 565–570 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- D’Arrigo A. et al. Recovering entanglement by local operations. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/1207.3294 (2012).
- Kwiat P. G., Waks E., White A. G., Appelbaum I. & Eberhard P. H. Ultrabright source of polarization-entangled photons. Phys. Rev. A 60, R773–R776 (1999). [Google Scholar]