Abstract
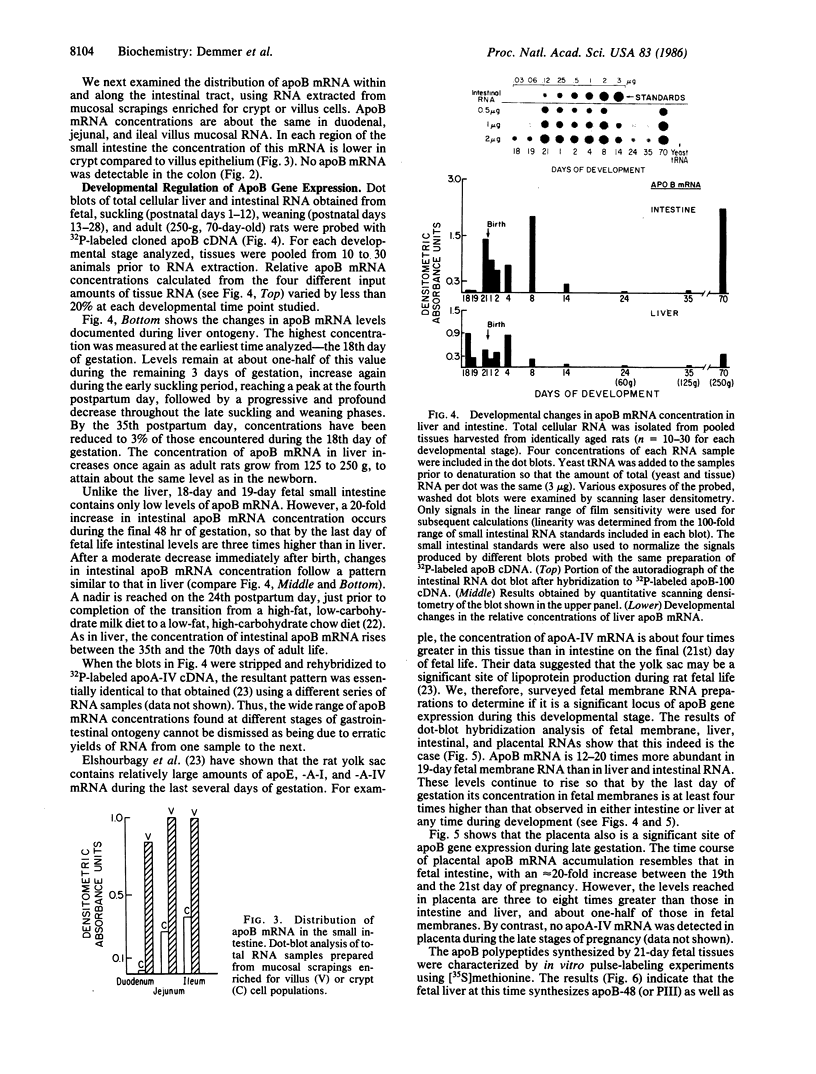
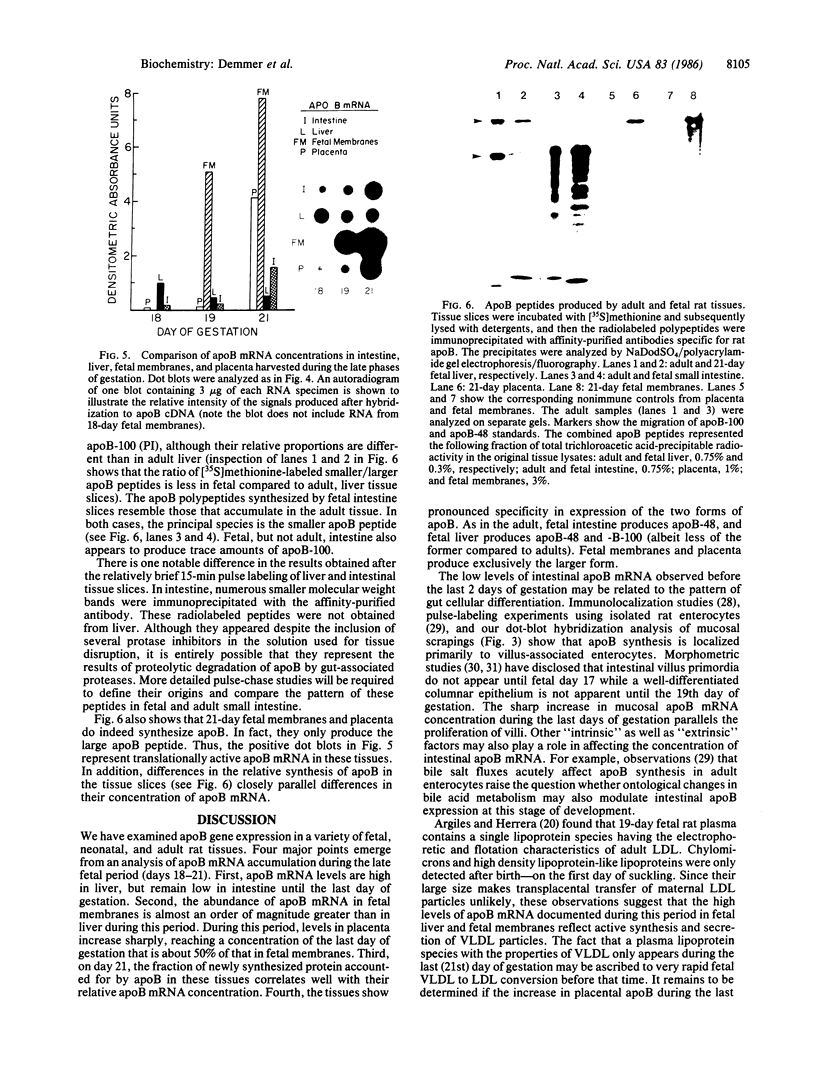
Expression of the apolipoprotein B (apoB) gene was examined in a variety of fetal, neonatal, and adult rat tissues by probing RNA blots with a cloned rat apoB cDNA. Among 10 adult male tissues surveyed, small intestine had the highest concentration of apoB mRNA. Its abundance in liver and adrenal gland was 40% and 0.5%, respectively, of that in small bowel, while none was detected in colon, kidney, testes, spleen, lung, heart, or brain. ApoB mRNA is as abundant in 18-day fetal liver as at any subsequent period of hepatic development. In contrast, the concentration of apoB mRNA remains low in fetal intestine until the last (21st) day of gestation, when it increases sharply to levels that are several-fold higher than in the liver. ApoB mRNA levels in fetal membranes harvested during this late gestational period were 10 times greater than in fetal liver. Since the major lipoprotein species in 19-day fetal plasma is low density lipoprotein, these observations suggest that fetal liver, and particularly its functional homologue, the yolk sac, are the principal sites of fetal lipoprotein synthesis at this stage of development. A 20-fold increase in placental apoB mRNA concentrations during the last 48 hr of pregnancy (to a level that is 50% of that encountered in fetal membrane RNA) suggests a specific role for this organ in maternal-fetal lipid transport immediately prior to parturition. Pulse-labeling experiments using 21-day fetal tissue slices showed that the liver synthesizes both apoB-100 (B-PI) and apoB-48 (B-PIII) albeit in somewhat different ratios than the adult organ. Fetal intestine produces almost exclusively the smaller apoB species, while fetal membranes and placenta synthesize only the larger peptide. The postnatal pattern of apoB mRNA accumulation is similar in liver and intestine. Profound decreases were observed during the late suckling and weaning periods, followed by an increase to adult levels. These final concentrations were similar to those encountered at birth. Analysis of these developmental changes offers an opportunity to generate testable hypotheses about the factors that modulate apoB synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argiles J., Herrera E. Lipids and lipoproteins in maternal and fetus plasma in the rat. Biol Neonate. 1981;39(1-2):37–44. doi: 10.1159/000241390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Quint J., Forte T., Graham P. Synthesis of two forms of apolipoprotein B by cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Mar 31;99(2):700–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91800-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gordon J. I. Developmental regulation of a gene that encodes a cysteine-rich intestinal protein and maps near the murine immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2516–2520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Olofsson S. O., Bondjers G., Darnfors C., Wiklund O., Bjursell G. Molecular cloning of human apolipoprotein B cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8813–8826. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Rubin C. E., Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. Ultrastructural immunolocalization of apolipoprotein B within human jejunal absorptive cells. J Lipid Res. 1983 Sep;24(9):1229–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Kollmer M. E., Glickman R. M. Apolipoprotein B synthesis in rat small intestine: regulation by dietary triglyceride and biliary lipid. J Lipid Res. 1986 Jan;27(1):30–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb S. S., Disteche C., Motulsky A. G., Lebo R. V., Kan Y. W. Chromosomal localization of the human apolipoprotein B gene and detection of homologous RNA in monkey intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):419–422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb S. S., Motulsky A. G., Albers J. J. A partial cDNA clone for human apolipoprotein B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4983–4986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Huang Y. O., Baker N., Kannan R. Apolipoprotein B is structurally and metabolically heterogeneous in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):157–161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Jacobs J. C., Schumaker V. N., Puppione D. L. Molecular weights of apoprotein B obtained from human low-density lipoprotein (apoprotein B-PI) and from rat very low density lipoprotein (apoprotein B-PIII). Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1569–1578. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Boguski M. S., Liao W. S., Jefferson L. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Expression of rat apolipoprotein A-IV and A-I genes: mRNA induction during development and in response to glucocorticoids and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando-Warnakulasuriya G. J., Eckerson M. L., Clark W. A., Wells M. A. Lipoprotein metabolism in the suckling rat: characterization of plasma and lymphatic lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1983 Dec;24(12):1626–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost S. C., Clark W. A., Wells M. A. Studies on fat digestion, absorption, and transport in the suckling rat. IV. In vivo rates of triacylglycerol secretion by intestine and liver. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jul;24(7):899–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. L. Investigation of cell lineage and differentiation in the extraembryonic endoderm of the mouse embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1982 Apr;68:175–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning S. J. Postnatal development: coordination of feeding, digestion, and metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):G199–G214. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.3.G199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst J. J., Sunshine P. Postnatal development of the small intestine of the rat. Changes in mucosal morphology at weaning. Pediatr Res. 1969 Jan;3(1):27–33. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196901000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. S., Bock S. C., Feinstein S. I., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein B cDNA clone isolation and demonstration that liver apolipoprotein B mRNA is 22 kilobases in length. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6825–6829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi K., Lu Y. F., Sugano M. Secretion of apolipoproteins in the suckling rat. Absence of low-molecular-weight apolipoprotein B of hepatic origin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. Apolipoprotein B: structural and metabolic heterogeneity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:637–650. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Rall S. C., Jr, Innerarity T. L., Jacobson S. F., Urdea M. S., Levy-Wilson B., Powell L. M., Pease R. J., Eddy R., Nakai H. Human apolipoprotein B: structure of carboxyl-terminal domains, sites of gene expression, and chromosomal localization. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):37–43. doi: 10.1126/science.2994225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Lackner K. J., Hospattankar A. V., Anchors J. M., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human apolipoprotein B-100: cloning, analysis of liver mRNA, and assignment of the gene to chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8340–8344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., West R., Mehrabian M., Reuben M. A., LeBoeuf R. C., Kaptein J. S., Johnson D. F., Schumaker V. N., Yuhasz M. P., Schotz M. C. Cloning and expression of apolipoprotein B, the major protein of low and very low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian M., Schumaker V. N., Fareed G. C., West R., Johnson D. F., Kirchgessner T., Lin H. C., Wang X. B., Ma Y. H., Mendiaz E. Human apolipoprotein B: identification of cDNA clones and characterization of mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6937–6953. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian M., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Klisak I. J., Schumaker V. N., Heinzmann C., Zollman S., Ma Y. H., Lusis A. J. Human apolipoprotein B: chromosomal mapping and DNA polymorphisms of hepatic and intestinal species. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 May;12(3):245–254. doi: 10.1007/BF01570783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne R. W., Theolis R., Jr, Verdery R. B., Marcel Y. L. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):23–30. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. I., Little J. M., Lester R. Development of the bile acid pool in rats from neonatal life through puberty to maturity. Digestion. 1983;28(4):216–224. doi: 10.1159/000198991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protter A. A., Hardman D. A., Schilling J. W., Miller J., Appleby V., Chen G. C., Kirsher S. W., McEnroe G., Kane J. P. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding the amino-terminal region of human apolipoprotein B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1467–1471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W. K., Heath J. K. Apolipoprotein expression by murine visceral yolk sac endoderm. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Jun;81:143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W. K., Hopkins B., Thompson S., Heath J. K., Luke B. M., Graham C. F. Synthesis of apolipoproteins, alphafoetoprotein, albumin, and transferrin by the human foetal yolk sack and other foetal organs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Feb;85:191–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Myant N. B., Sidoli A., Rodriguez J. C., Cortese C., Baralle F. E., Cortese R. Molecular cloning of human LDL apolipoprotein B cDNA. Evidence for more than one gene per haploid genome. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Dec;58(1-3):277–289. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Marsh J. B. Metabolic heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trier J. S., Moxey P. C. Morphogenesis of the small intestine during fetal development. Ciba Found Symp. 1979 Jan 16;(70):3–29. doi: 10.1002/9780470720530.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. B., Szczepanik P., Gould J. B., Klein P., Lester R. Bile salt metabolism in the human premature infant. Preliminary observations of pool size and synthesis rate following prenatal administration of dexamethasone and phenobarbital. Gastroenterology. 1975 Sep;69(3):706–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. F., Chen S. H., Yang C. Y., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W., Li W. H., Sparrow J. T., Gotto A. M., Jr, Chan L. Molecular cloning and expression of partial cDNAs and deduced amino acid sequence of a carboxyl-terminal fragment of human apolipoprotein B-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7265–7269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Variant forms of plasma apolipoprotein B. Hepatic and intestinal biosynthesis and heterogeneous metabolism in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3615–3618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]