Abstract
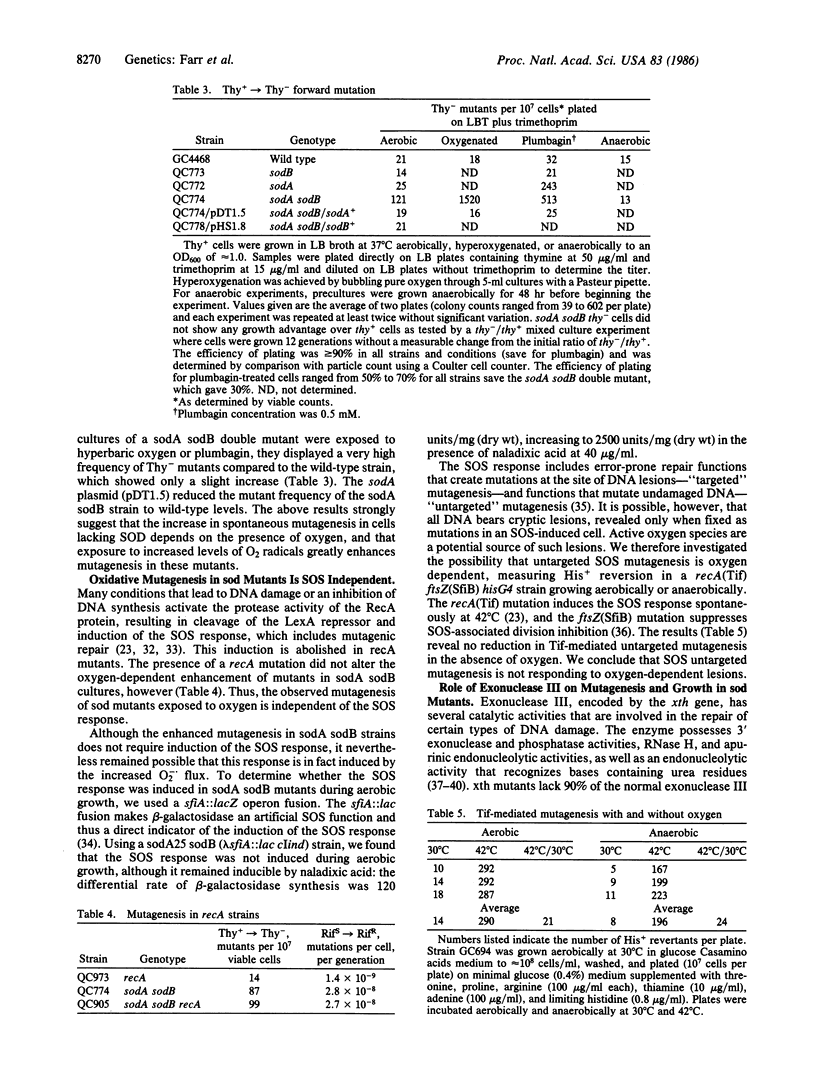
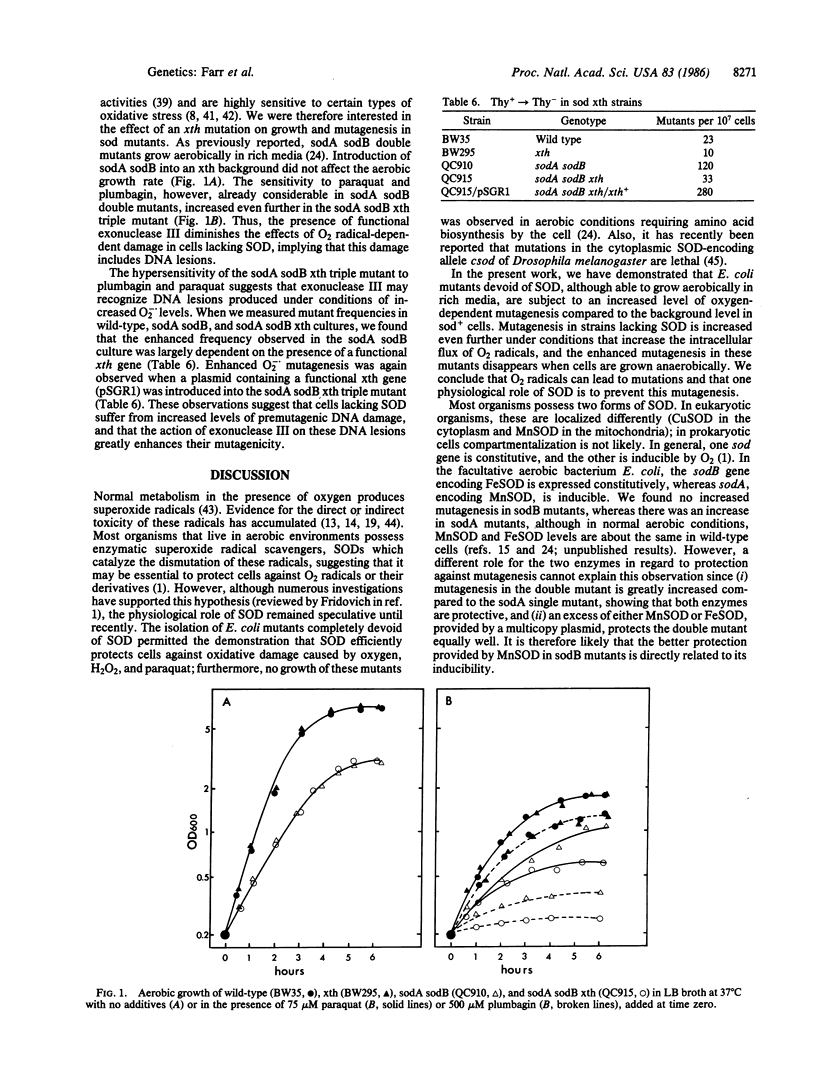
Escherichia coli double mutants (sodA sodB) completely lacking superoxide dismutase (SOD) have greatly enhanced mutation rates during aerobic growth. Single mutants lacking manganese SOD (MnSOD) but possessing iron SOD (FeSOD) have a smaller increase, and single mutants lacking FeSOD but possessing MnSOD do not show such an increase. The enhancement of mutagenesis is completely dependent on the presence of oxygen, and treatments that increase the flux of superoxide radicals produce even higher levels of mutagenesis. The presence of a plasmid overproducing either form of SOD reduces the level of mutagenesis to that of wild type, showing that the O2-dependent enhancement results from a lack of SOD. The enhancement of mutagenesis is RecA-independent, and a complete lack of SOD does not induce the SOS response during aerobic growth. However, the enhanced mutagenesis in aerobically grown sodA sodB mutants is largely dependent on functional exonuclease III, suggesting that the increased flux of superoxide radicals results in DNA lesions that can be acted on by this enzyme, leading to mutations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N. Dietary carcinogens and anticarcinogens. Oxygen radicals and degenerative diseases. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1256–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.6351251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Lee P. C., Wilson S. W., Cutler C. W., Ames B. N. AppppA and related adenylylated nucleotides are synthesized as a consequence of oxidation stress. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawn K., Fridovich I. DNA strand scission by enzymically generated oxygen radicals. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Feb;206(2):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawn M. K., Fridovich I. Increased superoxide radical production evokes inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):922–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Rotilio G. Biochemistry of oxygen radical species. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:22–35. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruyninckx W. J., Mason H. S., Morse S. A. Are physiological oxygen concentrations mutagenic? Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):606–607. doi: 10.1038/274606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillet-Fauquet P., Defais M., Radman M. Molecular mechanisms of induced mutagenesis. Replication in vivo of bacteriophage phiX174 single-stranded, ultraviolet light-irradiated DNA in intact and irradiated host cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 25;117(1):95–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S. D., Hilliker A. J., Phillips J. P. Cytogenetic analysis of the cSOD microregion in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Feb;112(2):205–215. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlioz A., Touati D. Isolation of superoxide dismutase mutants in Escherichia coli: is superoxide dismutase necessary for aerobic life? EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):623–630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaregola S., D'Ari R., Huisman O. Role of DNA replication in the induction and turn-off of the SOS response in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):440–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00334136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Sies H., Boveris A. Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):527–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesis P. L., Levin D. E., Smith M. T., Ernster L., Ames B. N. Mutagenicity of quinones: pathways of metabolic activation and detoxification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1696–1700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Clark A. J. Construction of an Hfr strain useful for transferring recA mutations between Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):529–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.529-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J., Linn S. Escherichia coli xth mutants are hypersensitive to hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1079–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1079-1082.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Linn S. 5,6-Saturated thymine lesions in DNA: production by ultraviolet light or hydrogen peroxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3781–3789. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing D. Synergistic damage from H2O2 and OH radicals in irradiated cells. Radiat Res. 1983 Apr;94(1):171–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr S. B., Natvig D. O., Kogoma T. Toxicity and mutagenicity of plumbagin and the induction of a possible new DNA repair pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1309–1316. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1309-1316.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases: regularities and irregularities. Harvey Lect. 1983 1984;79:51–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Castellazzi M., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. III. Mutations sfiA and sfiB restore division in tif and lon strains and permit the expression of mutator properties of tif. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Oct 22;140(4):309–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Intracellular production of superoxide radical and of hydrogen peroxide by redox active compounds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Sep;196(2):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Regulation of the synthesis of superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. Induction by methyl viologen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7667–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide radical and the oxygen enhancement of the toxicity of paraquat in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8143–8148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R. An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):797–799. doi: 10.1038/290797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R. Effect of suppressors of SOS-mediated filamentation on sfiA operon expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):169–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.169-175.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kow Y. W., Wallace S. S. Exonuclease III recognizes urea residues in oxidized DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8354–8358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. AppppA, heat-shock stress, and cell oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7496–7500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Hollstein M., Christman M. F., Schwiers E. A., Ames B. N. A new Salmonella tester strain (TA102) with A X T base pairs at the site of mutation detects oxidative mutagens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7445–7449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milcarek C., Weiss B. Mutants of Escherichia coli with altered deoxyribonucleases. I. Isolation and characterization of mutants for exonuclease 3. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):303–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody C. S., Hassan H. M. Mutagenicity of oxygen free radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2855–2859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munkres K. D., Furtek C. A. Assay of rate of aging of conidia of Neurospora crassa. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:263–270. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., KORNBERG A. A DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID PHOSPHATASE-EXONUCLEASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. PURIFICATION OF THE ENZYME AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:242–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto H., Touati D. Cloning of the iron superoxide dismutase gene (sodB) in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):418–420. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.418-420.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammartano L. J., Tuveson R. W. Escherichia coli xthA mutants are sensitive to inactivation by broad-spectrum near-UV (300- to 400-nm) radiation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):904–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.904-906.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati D. Cloning and mapping of the manganese superoxide dismutase gene (sodA) of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1078–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1078-1087.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. J., Hochhauser S. J., Cintron N. M., Weiss B. Genetic mapping of xthA, the structural gene for exonuclease III in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1082–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1082-1088.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



