Abstract
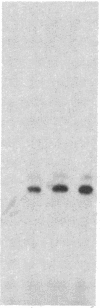
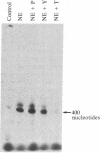
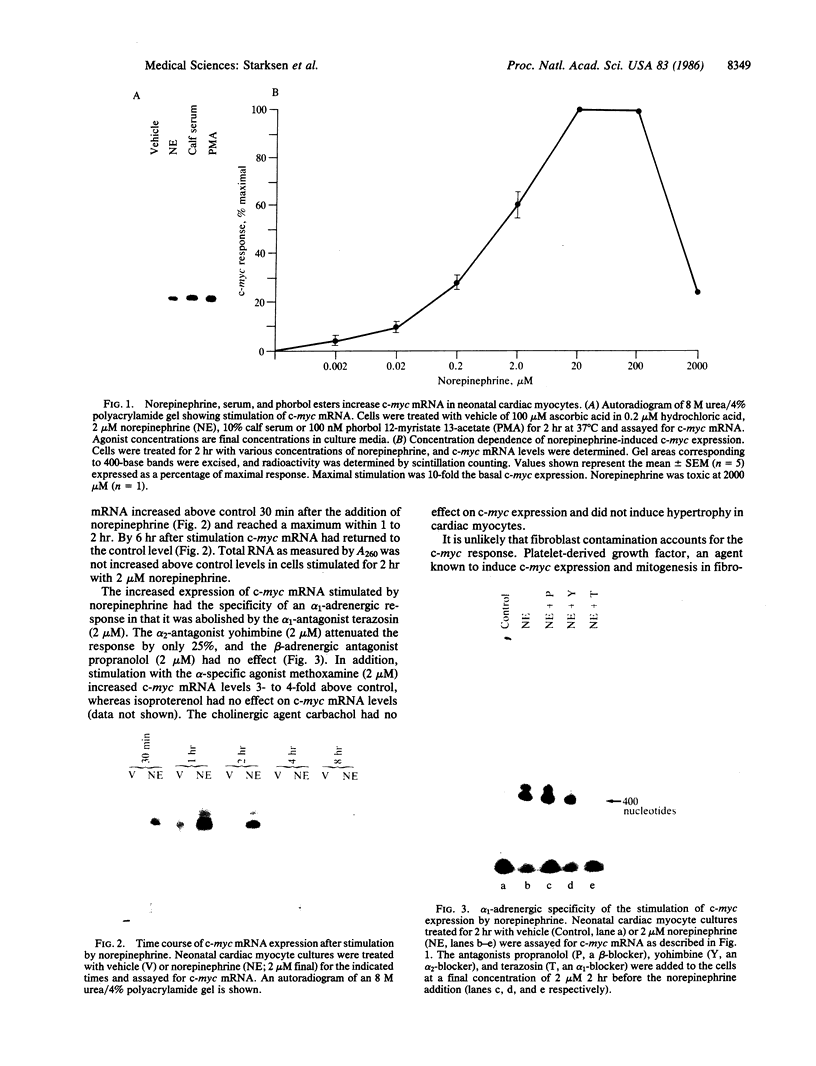
The mechanism of hormonally induced cell hypertrophy is unknown. Stimulation of cardiac myocytes by alpha 1-adrenergic agents, phorbol esters, and serum induces an increase in the cell size of nondividing cardiac myocytes in primary culture. Expression of the c-myc gene, known to be increased in growth factor-induced cell division, was studied in this model of cell hypertrophy. The alpha-adrenergic agonist norepinephrine (0.002-20 microM) increased levels of c-myc-encoded mRNA to 10-fold over control levels. This increase was detectable at 30 min, peaked at 2 hr, and returned to baseline by 6 hr after stimulation. The norepinephrine response was abolished by the alpha 1-antagonist terazosin (2 microM) but was not affected by the beta-adrenergic antagonist propranolol (2 microM) and was only slightly (25%) attenuated by the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine (2 microM). Serum and the phorbol ester tumor promoter phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate also enhanced c-myc expression in cardiac myocyte cultures. These findings show that the induction of cardiac myocyte hypertrophy is associated with enhanced expression of the c-myc gene and suggest that hormonally induced cell hypertrophy and cell division share common mechanistic pathways.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., Dani C., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Pouyssegur J., Jeanteur P. c-myc gene is transcribed at high rate in G0-arrested fibroblasts and is post-transcriptionally regulated in response to growth factors. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):443–445. doi: 10.1038/317443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Alpha 1-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 1985 Oct;57(4):532–537. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Groudine M. Amplification of endogenous myc-related DNA sequences in a human myeloid leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):679–681. doi: 10.1038/298679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Onc gene amplification in promyelocytic leukaemia cell line HL-60 and primary leukaemic cells of the same patient. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):61–63. doi: 10.1038/299061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Mechti N., Piechaczyk M., Lebleu B., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Increased rate of degradation of c-myc mRNA in interferon-treated Daudi cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4896–4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Mechanisms involved in alpha-adrenergic phenomena. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 1):E633–E647. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.6.E633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Anton E. D., Fahey D., Friedland B. K., Jonak G. J. Interferon regulates c-myc gene expression in Daudi cells at the post-transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1151–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Battey J., Lenoir G., Moulding C., Murphy W., Potter H., Stewart T., Taub R. Translocations among antibody genes in human cancer. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):765–771. doi: 10.1126/science.6356357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P., McGrath A., Savion S. Myocyte hypertrophy in neonatal rat heart cultures and its regulation by serum and by catecholamines. Circ Res. 1982 Dec;51(6):787–801. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.6.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Stimulation of hypertrophy of cultured neonatal rat heart cells through an alpha 1-adrenergic receptor and induction of beating through an alpha 1- and beta 1-adrenergic receptor interaction. Evidence for independent regulation of growth and beating. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):884–894. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Moulding C., Battey J., Murphy W., Vasicek T., Lenoir G. M., Leder P. Activation and somatic mutation of the translocated c-myc gene in burkitt lymphoma cells. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]