Abstract
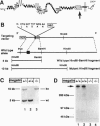
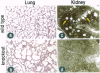
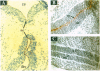
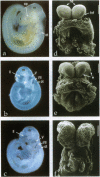
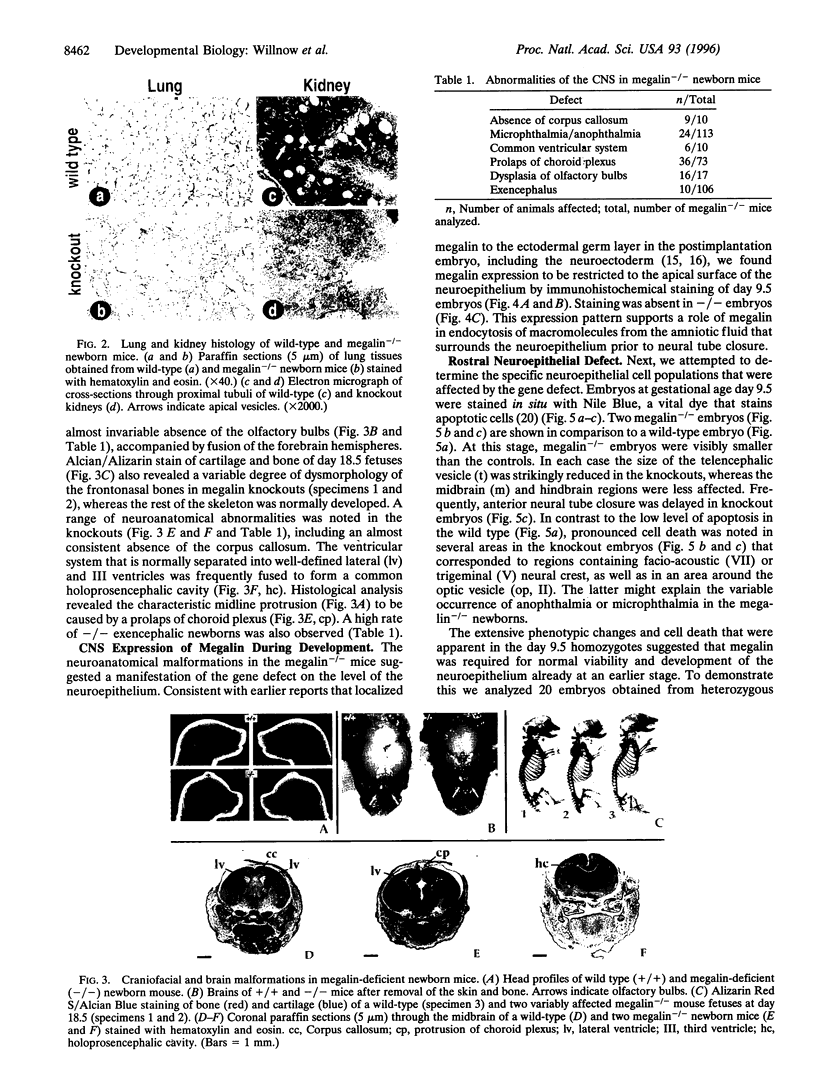
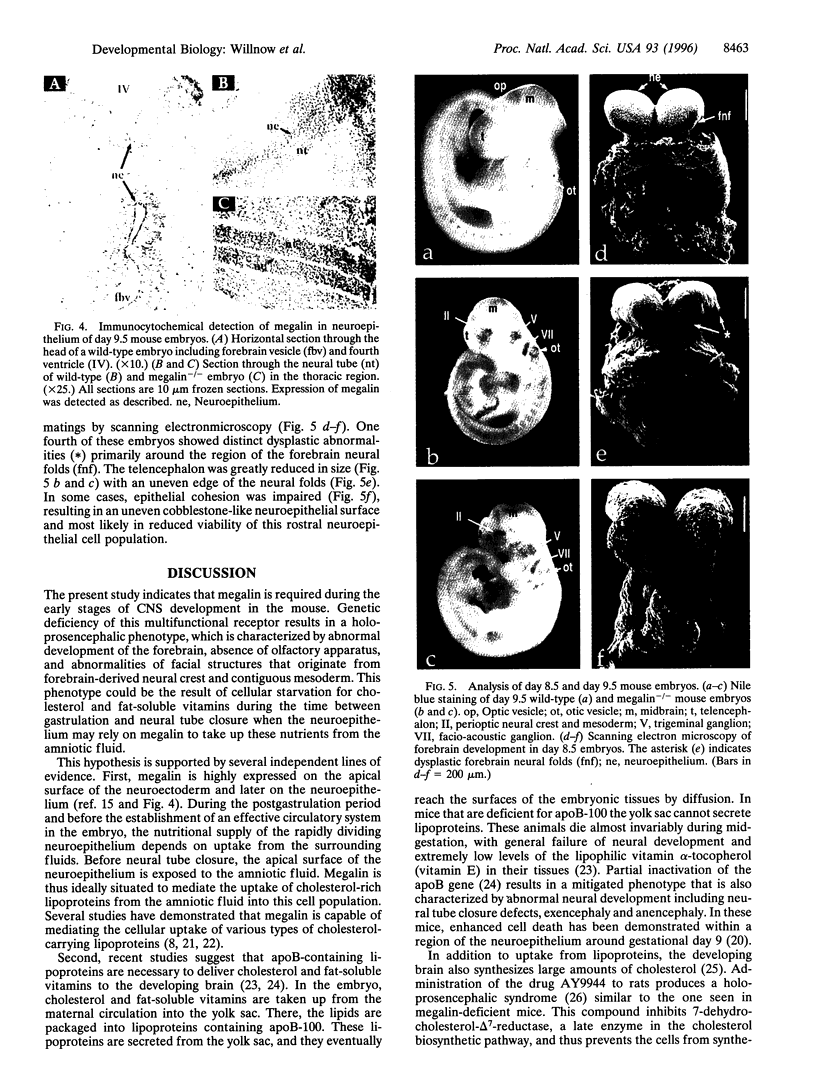
gp330/megalin, a member of the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene family, is expressed on the apical surfaces of epithelial tissues, including the neuroepithelium, where it mediates the endocytic uptake of diverse macromolecules, such as cholesterol-carrying lipoproteins, proteases, and antiproteinases. Megalin knockout mice manifest abnormalities in epithelial tissues including lung and kidney that normally express the protein and they die perinatally from respiratory insufficiency. In brain, impaired proliferation of neuroepithelium produces a holoprosencephalic syndrome, characterized by lack of olfactory bulbs, forebrain fusion, and a common ventricular system. Similar syndromes in humans and animals are caused by insufficient supply of cholesterol during development. Because megalin can bind lipoproteins, we propose that the receptor is part of the maternal-fetal lipoprotein transport system and mediates the endocytic uptake of essential nutrients in the postgastrulation stage.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biemesderfer D., Dekan G., Aronson P. S., Farquhar M. G. Assembly of distinctive coated pit and microvillar microdomains in the renal brush border. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 2):F55–F67. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.1.F55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc-Caron M. H., Condamine H., Kerjaschki D. Rat Heymann nephritis antigen is closely related to brushin, a glycoprotein present in early mouse embryo epithelia. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 Sep-Oct;138(5):707–722. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen E. I., Gliemann J., Moestrup S. K. Renal tubule gp330 is a calcium binding receptor for endocytic uptake of protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Oct;40(10):1481–1490. doi: 10.1177/40.10.1382088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Armiento J., Dalal S. S., Okada Y., Berg R. A., Chada K. Collagenase expression in the lungs of transgenic mice causes pulmonary emphysema. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):955–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90391-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Kita T., Suckling K. E., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Cholesterol synthesis in vivo and in vitro in the WHHL rabbit, an animal with defective low density lipoprotein receptors. J Lipid Res. 1983 Apr;24(4):469–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Jr, Ruland S. L., Flynn L. M., Stokowski R. P., Young S. G. Knockout of the mouse apolipoprotein B gene results in embryonic lethality in homozygotes and protection against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in heterozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1774–1778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gueth-Hallonet C., Santa-Maria A., Verroust P., Maro B. Gp330 is specifically expressed in outer cells during epithelial differentiation in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Development. 1994 Nov;120(11):3289–3299. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.11.3289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Hamann U., Rogne S., Myklebost O., Gausepohl H., Stanley K. K. Surface location and high affinity for calcium of a 500-kd liver membrane protein closely related to the LDL-receptor suggest a physiological role as lipoprotein receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4119–4127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homanics G. E., Maeda N., Traber M. G., Kayden H. J., Dehart D. B., Sulik K. K. Exencephaly and hydrocephaly in mice with targeted modification of the apolipoprotein B (Apob) gene. Teratology. 1995 Jan;51(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420510102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homanics G. E., Smith T. J., Zhang S. H., Lee D., Young S. G., Maeda N. Targeted modification of the apolipoprotein B gene results in hypobetalipoproteinemia and developmental abnormalities in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2389–2393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounnas M. Z., Chappell D. A., Strickland D. K., Argraves W. S. Glycoprotein 330, a member of the low density lipoprotein receptor family, binds lipoprotein lipase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14176–14181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounnas M. Z., Haudenschild C. C., Strickland D. K., Argraves W. S. Immunological localization of glycoprotein 330, low density lipoprotein receptor related protein and 39 kDa receptor associated protein in embryonic mouse tissues. In Vivo. 1994 May-Jun;8(3):343–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kounnas M. Z., Loukinova E. B., Stefansson S., Harmony J. A., Brewer B. H., Strickland D. K., Argraves W. S. Identification of glycoprotein 330 as an endocytic receptor for apolipoprotein J/clusterin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 2;270(22):13070–13075. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.22.13070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., Herz J. Structures and functions of multiligand lipoprotein receptors: macrophage scavenger receptors and LDL receptor-related protein (LRP). Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:601–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M. J. Differential staining of cartilage and bone in whole mouse fetuses by alcian blue and alizarin red S. Teratology. 1980 Dec;22(3):299–301. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420220306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Pallesen G. Distribution of the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Sep;269(3):375–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00353892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlando R. A., Kerjaschki D., Kurihara H., Biemesderfer D., Farquhar M. G. gp330 associates with a 44-kDa protein in the rat kidney to form the Heymann nephritis antigenic complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6698–6702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux C., Horvath C., Dupuis R. Teratogenic action and embryo lethality of AY 9944R. Prevention by a hypercholesterolemia-provoking diet. Teratology. 1979 Feb;19(1):35–38. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420190106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Pietromonaco S., Loo A. K., Farquhar M. G. Complete cloning and sequencing of rat gp330/"megalin," a distinctive member of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9725–9729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonbaum C. P., Lee S., Mahowald A. P. The Drosophila yolkless gene encodes a vitellogenin receptor belonging to the low density lipoprotein receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson S., Chappell D. A., Argraves K. M., Strickland D. K., Argraves W. S. Glycoprotein 330/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-2 mediates endocytosis of low density lipoproteins via interaction with apolipoprotein B100. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 18;270(33):19417–19421. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.33.19417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tint G. S., Irons M., Elias E. R., Batta A. K., Frieden R., Chen T. S., Salen G. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis associated with the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 13;330(2):107–113. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401133300205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willnow T. E., Goldstein J. L., Orth K., Brown M. S., Herz J. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein and gp330 bind similar ligands, including plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes and lactoferrin, an inhibitor of chylomicron remnant clearance. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26172–26180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willnow T. E., Rohlmann A., Horton J., Otani H., Braun J. R., Hammer R. E., Herz J. RAP, a specialized chaperone, prevents ligand-induced ER retention and degradation of LDL receptor-related endocytic receptors. EMBO J. 1996 Jun 3;15(11):2632–2639. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. B., Lopes M. B., VandenBerg S. R., Gonias S. L. Characterization and immunohistochemical localization of alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein) in human brain. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):37–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng G., Bachinsky D. R., Stamenkovic I., Strickland D. K., Brown D., Andres G., McCluskey R. T. Organ distribution in rats of two members of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene family, gp330 and LRP/alpha 2MR, and the receptor-associated protein (RAP). J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Apr;42(4):531–542. doi: 10.1177/42.4.7510321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]