Abstract
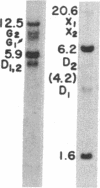
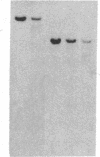
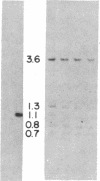
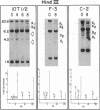
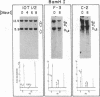
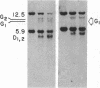
The mouse skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptor is regulated, at least in part, by transcriptional mechanisms. As a first step toward defining the cis- and trans-acting factors involved in acetylcholine receptor transcriptional regulation, we examined mouse muscle and fibroblast cells for the presence of DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the chromatin surrounding the delta-subunit gene. We detect six DNase I-hypersensitive sites in muscle DNA blots hybridized with a mouse delta-subunit cDNA. Two hypersensitive sites lie distantly 5' to the delta gene, one lies near the 5' end of the delta gene, one lies near its 3' end, and two hypersensitive sites lie distantly 3'. The pair of distantly 3' hypersensitive sites should by analogy to chicken and human genomes lie near the gamma-subunit gene. Only the distantly 5' pair of hypersensitive sites is present in fibroblasts; the remainder is muscle specific. Two hypersensitive sites, one at the 3' end of the delta gene and one distantly 3', appear only after terminal muscle differentiation and, therefore, are developmentally regulated, similarly to receptor subunit mRNAs. All four muscle-specific hypersensitive sites are excellent candidates for regulatory loci for the delta- and gamma-subunit genes of mouse acetylcholine receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Merlie J. P. Transcriptional regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes during muscle development. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11452–11455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costlow N. A., Simon J. A., Lis J. T. A hypersensitive site in hsp70 chromatin requires adjacent not internal DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):147–149. doi: 10.1038/313147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell R. B. Independent regulation by sodium butyrate of gonadotropin alpha gene expression and cell cycle progression in HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):829–839. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C., Cartwright I. L., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Selected topics in chromatin structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:485–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Boulter J., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Muscle denervation increases the levels of two mRNAs coding for the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2553–2558. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02553.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr cDNA clone analysis of six co-regulated mRNAs encoding skeletal muscle contractile proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg K. E., Mudd J., Shah V., Merlie J. P. Nucleotide sequence of the mouse muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):5111–5111. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. A., Corces V., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C. DNase I hypersensitive sites in Drosophila chromatin occur at the 5' ends of regions of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPolla R. J., Mayne K. M., Davidson N. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the complete protein coding region of the delta subunit of the mouse acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7970–7974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Isenberg K. E., Russell S. D., Sanes J. R. Denervation supersensitivity in skeletal muscle: analysis with a cloned cDNA probe. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):332–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. Concentration of acetylcholine receptor mRNA in synaptic regions of adult muscle fibres. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):66–68. doi: 10.1038/317066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Mauron A., Stalder R., Alliod C., Ballivet M. Structure linkage, and sequence of the two genes encoding the delta and gamma subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7975–7979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Glaser L., Merlie J. P., Lindstrom J. Expression of acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit mRNA during differentiation of the BC3H1 muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3330–3336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Harris A. J., Devine C. E., Heinemann S. Characterization of a unique muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):398–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebbane R., Clokey G., Merlie J. P., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Characterization of the mRNA for mouse muscle acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit by quantitative translation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3294–3303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibahara S., Kubo T., Perski H. J., Takahashi H., Noda M., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of human genomic DNA encoding gamma subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):15–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. M., Jones P. A. Multiple new phenotypes induced in 10T1/2 and 3T3 cells treated with 5-azacytidine. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):771–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Swanson L. W., Lindstrom J. Characteristics of monoclonal antibodies to denatured Torpedo and to native calf acetylcholine receptors: species, subunit and region specificity. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Jan;10(3):235–253. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., LaPolla R. J., Davidson N. Mouse muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit: cDNA sequence and gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3539–3555. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]