Abstract
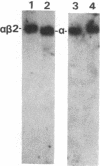
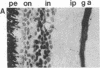
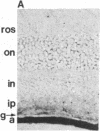
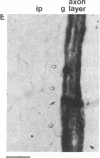
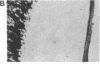
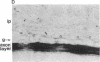
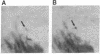
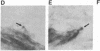
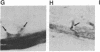
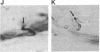
Affinity-purified antibodies against the sodium channel from rat brain were employed to localize sodium channels in the retina by immunocytochemical procedures. In rat retina, intense staining was observed in the ganglion cell axon layer and light staining was detected in fibers of the inner plexiform layer. In frog retina, only the ganglion cell axon layer was stained. Examination at higher magnification revealed that axon hillocks and initial segments of ganglion cells had a high density of immunoreactive sodium channels, whereas the cell bodies were devoid of stain. The sharply defined region of high sodium channel density at the axon hillock is likely to be responsible for the low threshold for action potential initiation in this region of vertebrate central neurons.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKI T., TERZUOLO C. A. Membrane currents in spinal motoneurons associated with the action potential and synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Nov;25:772–789. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes S., Werblin F. Gated currents generate single spike activity in amacrine cells of the tiger salamander retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1509–1512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Crill W. E. Voltage clamp of cat motoneurone somata: properties of the fast inward current. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:231–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Caldwell J. H., Campbell D. T. Na channels in skeletal muscle concentrated near the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):588–590. doi: 10.1038/313588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel P. J., Beavo J. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of catalytic subunit of skeletal muscle adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2691–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudier J. A., Berwald-Netter Y., Dellmann H. D., Boudier J. L., Couraud F., Koulakoff A., Cau P. Ultrastructural visualization of Na+-channel associated [125I]alpha-scorpion toxin binding sites on fetal mouse nerve cells in culture. Brain Res. 1985 May;352(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Localization of sodium channels in cultured neural cells. J Neurosci. 1981 Jul;1(7):777–783. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-07-00777.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Morrow C. S., Hartshorne R. P. Neurotoxin binding to receptor sites associated with voltage-sensitive sodium channels in intact, lysed, and detergent-solubilized brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11379–11387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M. R., Casnellie J. E., Catterall W. A. Selective phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7918–7921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M. R., Catterall W. A. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel in synaptic nerve ending particles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8210–8218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Levinson S. R. Immunocytochemical localization of sodium channel distributions in the excitable membranes of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6707–6711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J., FURUKAWA T. Intracellular and extracellular responses of the several regions of the Mauthner cell of the goldfish. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Nov;25:732–771. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.6.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Devreotes P. N. Newly synthesized acetylcholine receptors are located in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):237–244. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz L. C., Brockes J. P. Immunochemical properties and cytochemical localization of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from the electroplax of the eel (Electrophorus electricus). J Neurosci. 1983 Nov;3(11):2300–2309. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-11-02300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovich B., Bonilla E., Casadei J., Barchi R. Immunocytochemical localization of the mammalian voltage-dependent sodium channel using polyclonal antibodies against the purified protein. J Neurosci. 1984 Sep;4(9):2259–2268. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-09-02259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiri H., Zeitoun I., Grunhagen H. H., Lev-Ram V., Eshhar Z., Schlessinger J. Monoclonal antibodies associated with sodium channel block nerve impulse and stain nodes of Ranvier. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 17;310(1):168–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner D. J., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Separation and characterization of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10597–10604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Dacheux R. Dendritic and somatic spikes in mudpuppy amacrine cells: indentification and TTX sensitivity. Brain Res. 1976 Mar 5;104(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90657-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Strichartz G. R. A new method for labelling saxitoxin and its binding to non-myelinated fibres of the rabbit vagus, lobster walking leg, and garfish olfactory nerves. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):477–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthy P. V., Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Retrograde labeling, enrichment, and characterization of retinal ganglion cells from the neonatal rat. J Neurosci. 1983 Dec;3(12):2532–2544. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-12-02532.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Jr Sites of action potential generation in cultured vertebrate neurons. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 12;288(1-2):381–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Almers W. Photobleaching through glass micropipettes: sodium channels without lateral mobility in the sarcolemma of frog skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):946–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman S. G., Ritchie J. M. Organization of ion channels in the myelinated nerve fiber. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1502–1507. doi: 10.1126/science.2409596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S., Copenhagen D. R. Control of retinal sensitivity. 3. Lateral interactions at the inner plexiform layer. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jan;63(1):88–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S., Dowling J. E. Organization of the retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus. II. Intracellular recording. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):339–355. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollner D. A., Catterall W. A. Antigenic differences among the voltage-sensitive sodium channels in the peripheral and central nervous systems and skeletal muscle. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 1;331(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90724-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]