Abstract
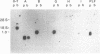
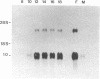
We have isolated a cDNA clone for the 23-kDa mouse placental lactogen II (mPL-II) from a phage lambda gt11 expression library containing cDNA synthesized from BALB/c placental RNA. Translation in vitro of placental mRNA selected by hybridization to the mPL-II cDNA clones yields a 26-kDa polypeptide that is the size of the expected precursor protein and that is immunoprecipitated with anti-mPL-II antiserum. The mPL-II cDNA clones hybridize to a 1.0-kilobase placental-specific mRNA. This mRNA, found in the fetal portion of the placenta, appears as early as day 10 of gestation and increases to a maximal level by day 12. The mPL-II cDNA nucleotide sequence has been determined. This sequence contains an open reading frame encoding a polypeptide of 222 amino acids with the amino-terminal 31 amino acids forming the signal sequence for secretion. The predicted secreted protein has 51% amino acid homology with mouse prolactin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colosi P., Marr G., Lopez J., Haro L., Ogren L., Talamantes F. Isolation, purification, and characterization of mouse placental lactogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):771–775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M. L., Kirk K. L., Friesen H. G. Isolation and identification of a cDNA clone of rat placental lactogen II. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10871–10878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M. L., Peden L. M., Friesen H. G. Isolation of a novel prolactin-like cDNA clone from developing rat placenta. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10879–10884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Talamantes F. Immunocytochemical localization of mouse placental lactogen in the mouse placenta. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Apr;32(4):379–382. doi: 10.1177/32.4.6368678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haro L. S., Talamantes F. J. Interaction of mouse prolactin with mouse hepatic receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Jun;41(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Lee S. J., Ogren L., Talamantes F., Nathans D. Identification of proliferin mRNA and protein in mouse placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4356–4359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. A new member of the prolactin-growth hormone gene family expressed in mouse placenta. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1419–1423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of a growth-related mRNA encoding a member of the prolactin-growth hormone family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4255–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Talamantes F. Nucleotide sequence of mouse prolactin and growth hormone mRNAs and expression of these mRNAs during pregnancy. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9574–9579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. C., Friesen H. G. Two forms of rat placental lactogen revealed by radioimmunoassay. Endocrinology. 1981 Jun;108(6):2388–2390. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-6-2388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. C., Gillespie B., Friesen H. G. Characterization of the two forms of rat placental lactogen (rPL): rPL-I and rPL-II. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1862–1866. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. J., Colosi P., Ogren L., Talamantes F. Identification and partial characterization of a lactogen from the midpregnant mouse conceptus. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1313–1317. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. J., Colosi P., Talamantes F. The development and characterization of a homologous radioimmunoassay for mouse placental lactogen. Endocrinology. 1982 Feb;110(2):668–670. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-2-668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talamantes F., Ogren L., Markoff E., Woodard S., Madrid J. Phylogenetic distribution, regulation of secretion, and prolactin-like effects of placental lactogens. Fed Proc. 1980 Jun;39(8):2582–2587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]