Abstract
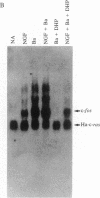
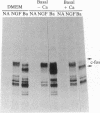
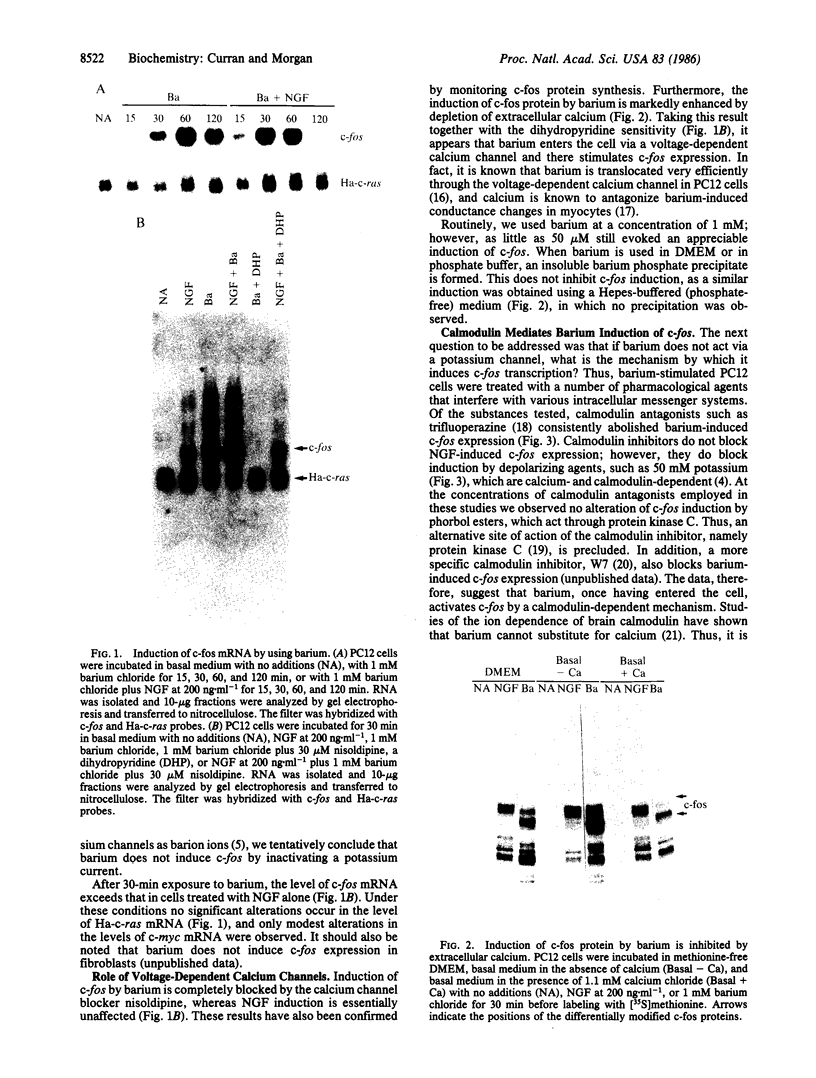
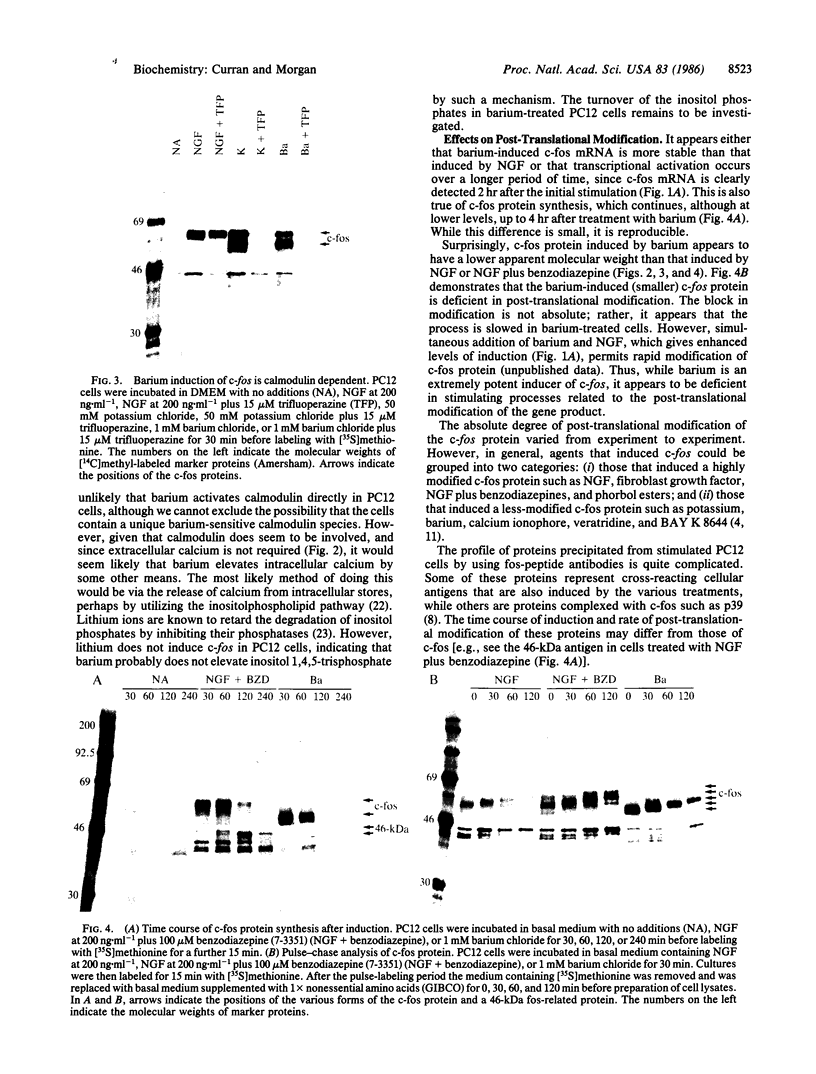
The addition of exogenous barium ions to PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells elicits a transient induction of the c-fos gene. Induction is antagonized by extracellular calcium and the dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, and it is attenuated in the presence of calmodulin inhibitors. Thus, barium appears to enter the cell through a voltage-dependent calcium channel and, either directly or indirectly, interacts with calmodulin to stimulate c-fos expression. This property of barium is not shared by a range of di- and trivalent cations examined. Agents that induce the c-fos gene in PC12 cells may be divided into two broad categories. The first comprises polypeptide growth factors and phorbol esters, which give rise to a c-fos protein that undergoes extensive post-translational modification. The second, which comprises depolarizing agents and barium ions, acts via calcium channels and yields a c-fos protein that undergoes less extensive post-translational modification. These different forms of c-fos protein can be distinguished on the basis of their apparent molecular weights on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Taylor S. R. Interaction of barium ions with potassium channels in squid giant axons. Biophys J. 1980 Jun;30(3):473–488. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85108-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aub D. L., Putney J. W., Jr Metabolism of inositol phosphates in parotid cells: implications for the pathway of the phosphoinositide effect and for the possible messenger role of inositol trisphosphate. Life Sci. 1984 Apr 2;34(14):1347–1355. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Camerer H., Kunze D. L., Lux H. D. Similarity of unitary Ca2+ currents in three different species. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):156–158. doi: 10.1038/299156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao S. H., Suzuki Y., Zysk J. R., Cheung W. Y. Activation of calmodulin by various metal cations as a function of ionic radius. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):75–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Morgan J. I. Superinduction of c-fos by nerve growth factor in the presence of peripherally active benzodiazepines. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.4035354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. L. Calcium-mediated inactivation of the calcium conductance in caesium-loaded giant neurones of Aplysia californica. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., DeFeo D., Maryak J. M., Young H. A., Shih T. Y., Chang E. H., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. Dual evolutionary origin for the rat genetic sequences of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):408–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.408-420.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Tanaka T. Naphthalenesulfonamides as calmodulin antagonists. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:185–194. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Schubert D., Verma I. M. Induction of the proto-oncogene fos by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7330–7334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Role of ion flux in the control of c-fos expression. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):552–555. doi: 10.1038/322552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Curran T., Müller D., Guilbert L. Induction of c-fos during myelomonocytic differentiation and macrophage proliferation. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):546–548. doi: 10.1038/314546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prozialeck W. C., Weiss B. Inhibition of calmodulin by phenothiazines and related drugs: structure-activity relationships. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Sep;222(3):509–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Schaber M., Kramer R., Crowl R., Curran T. The fos gene product undergoes extensive post-translational modification in eukaryotic but not in prokaryotic cells. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase: inhibition by antipsychotic drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 12;98(3):669–676. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Rozengurt E. Serum stimulates the Na+,K+ pump in quiescent fibroblasts by increasing Na+ entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynor A. E., Schubert D. Phospholipases elevate cyclic AMP levels and promote neurite extension in a clonal nerve cell line. Brain Res. 1984 Jun;316(2):197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zengel J. E., Magleby K. L. Differential effects of Ba2+, Sr2+, and Ca2+ on stimulation-induced changes in transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Aug;76(2):175–211. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]