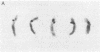Abstract
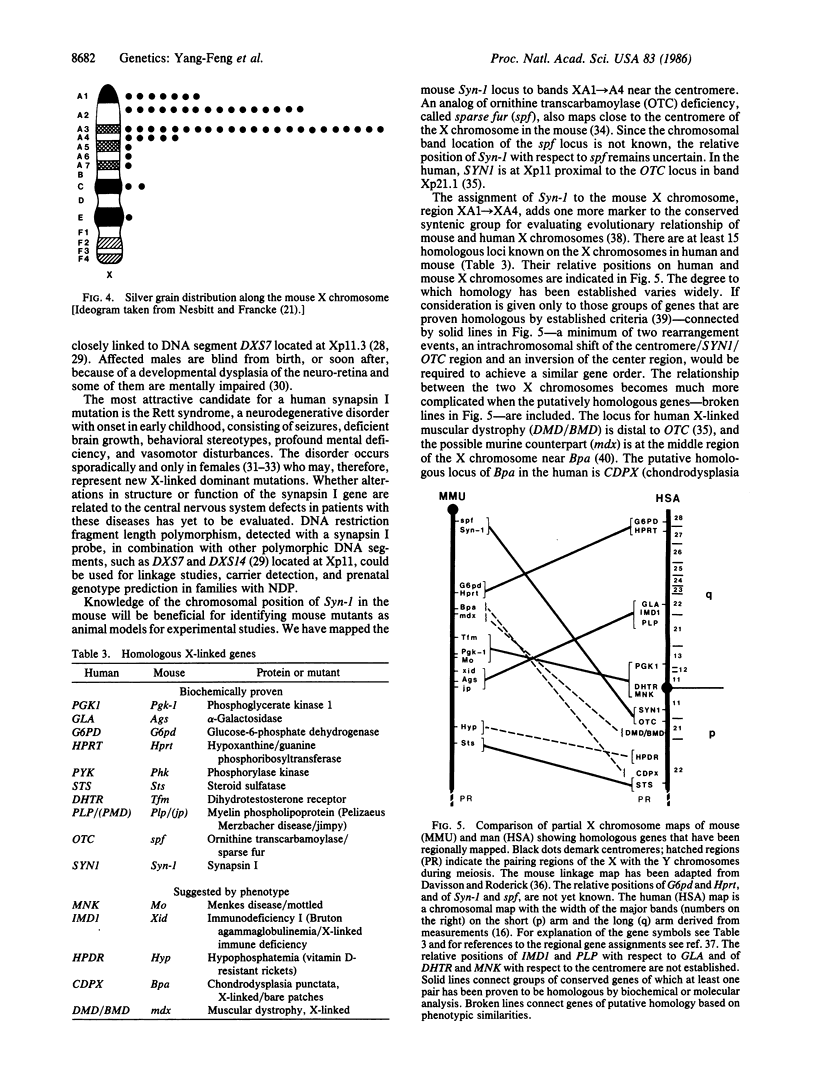
Synapsin I is a neuron-specific phosphoprotein associated with the membranes of small synaptic vesicles. Its function is not entirely clear, but evidence points to a possible role in the regulation of neurotransmitter release. Its biosynthesis is under developmental control. Assignment of the human synapsin I gene to the X chromosome at band Xp11 was accomplished by in situ hybridization, using a rat cDNA probe. Southern blot analysis of DNAs from a panel of human-Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids with defined regions of the human X chromosome confirmed the in situ mapping data. The mouse synapsin I gene was assigned to the X chromosome, proximal to band XD, by Southern blot analysis of Chinese hamster-mouse somatic cell hybrids with normal or rearranged mouse X chromosomes. In situ chromosomal hybridization experiments localized the mouse synapsin I gene more precisely to bands XA1----A4. These results add to the comparative gene map of mammalian species and support certain hypotheses regarding the evolutionary relationship between human and mouse X chromosomes. We hypothesize that the synapsin I gene could be mutated in human X-linked disorders with primary neuronal degeneration, such as the Rett syndrome.
Full text
PDF
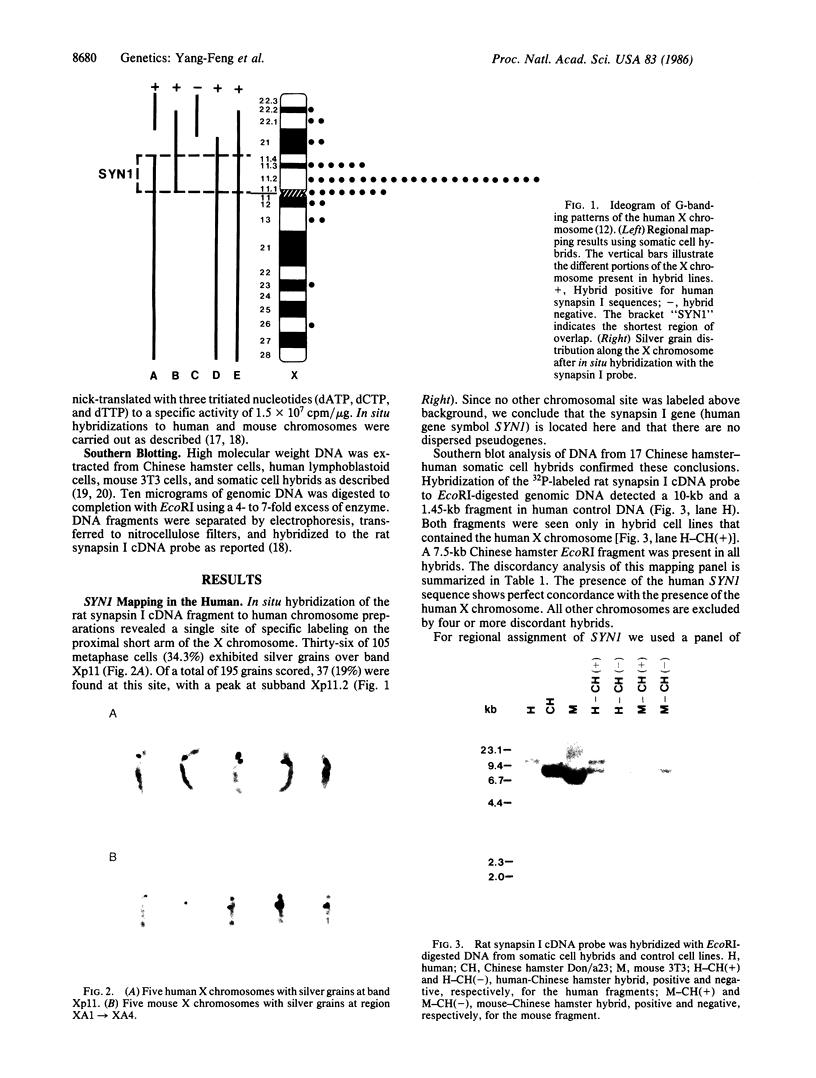
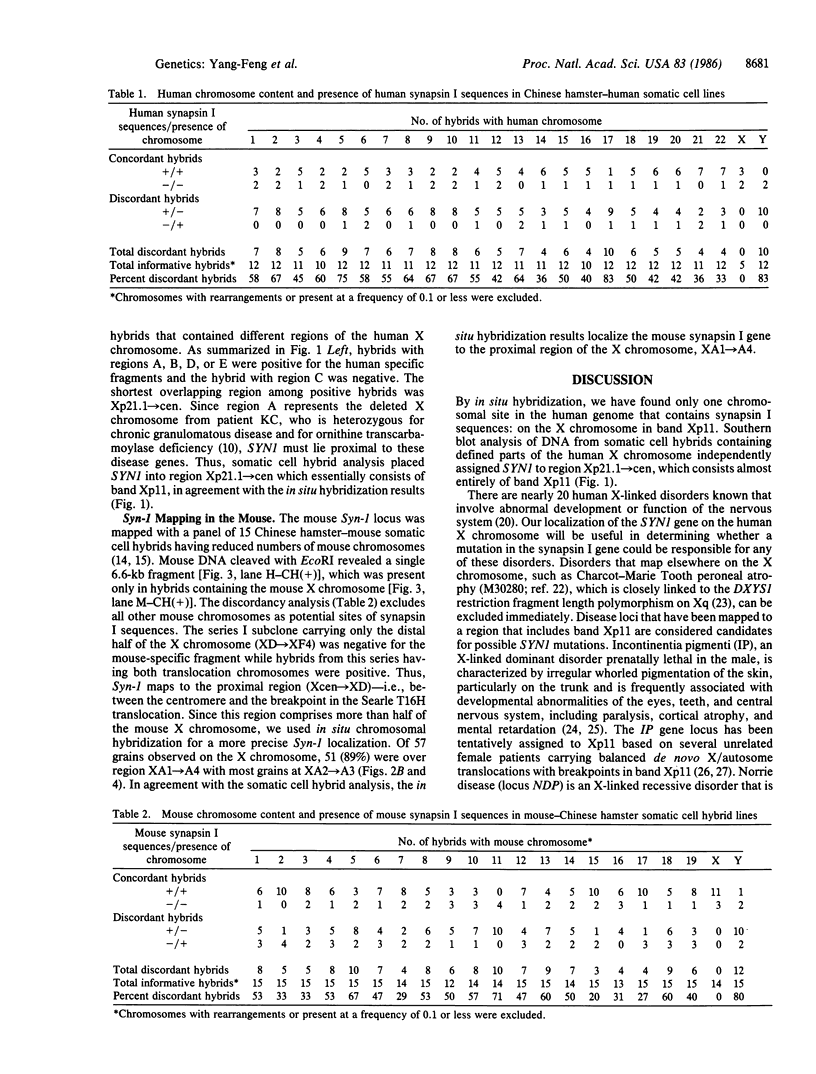

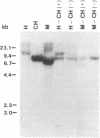
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baas F., Bikker H., van Ommen G. J., de Vijlder J. J. Unusual scarcity of restriction site polymorphism in the human thyroglobulin gene. A linkage study suggesting autosomal dominance of a defective thyroglobulin allele. Hum Genet. 1984;67(3):301–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00291357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines A. J., Bennett V. Synapsin I is a spectrin-binding protein immunologically related to erythrocyte protein 4.1. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):410–413. doi: 10.1038/315410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfield G., Siller W. G., Wight P. A., Moore K. J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1189–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney R. G. Incontinentia pigmenti. A world statistical analysis. Arch Dermatol. 1976 Apr;112(4):535–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry C. J., Magenis R. E., Brown M., Lanman J. T., Jr, Tsai J., O'Lague P., Goodfellow P., Mohandas T., Bergner E. A., Shapiro L. J. Inherited chondrodysplasia punctata due to a deletion of the terminal short arm of an X chromosome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 18;311(16):1010–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410183111603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMars R., LeVan S. L., Trend B. L., Russell L. B. Abnormal ornithine carbamoyltransferase in mice having the sparse-fur mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1693–1697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Busby N., Shaw D., Hansen S., Brown M. G. Intrachromosomal gene mapping in man: assignment of nucleoside phosphorylase to region 14cen leads to 14q21 by interspecific hybridization of cells with a t(X;14) (p22;q21) translocation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Jan;2(1):27–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01539240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Lalley P. A., Moss W., Ivy J., Minna J. D. Gene mapping in Mus musculus by interspecific cell hybridization: assignment of the genes for tripeptidase-1 to chromosome 10, dipeptidase-2 to chromosome 18, acid phosphatase-1 to chromosome 12, and adenylate kinase-1 to chromosome 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(2-3):57–84. doi: 10.1159/000130799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Oliver N. Quantitative analysis of high-resolution trypsin-giemsa bands on human prometaphase chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1978 Dec 18;45(2):137–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00286957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Random X inactivation resulting in mosaic nullisomy of region Xp21.1----p21.3 associated with heterozygosity for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency and for chronic granulomatous disease. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):298–307. doi: 10.1159/000132078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Taggart R. T. Assignment of the gene for cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase (Sod-1) to a region of chromosome 16 and of Hprt to a region of the X chromosome in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5230–5233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Taggart R. T. Comparative gene mapping: order of loci on the X chromosome is different in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3595–3599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal A., Stolzenberger C., Wienker T., Wieacker P., Ropers H. H., Friedrich U., Bleeker-Wagemakers L., Pearson P., Warburg M. Norrie's disease: close linkage with genetic markers from the proximal short arm of the X chromosome. Clin Genet. 1985 Mar;27(3):282–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilgenkrantz S., Tridon P., Pinel-Briquel N., Beurey J., Weber M. Translocation (X;9)(p11;q34) in a girl with incontinentia pigmenti (IP): implications for the regional assignment of the IP locus to Xp11? Ann Genet. 1985;28(2):90–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):296–352. doi: 10.1159/000132178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg B., Aicardi J., Dias K., Ramos O. A progressive syndrome of autism, dementia, ataxia, and loss of purposeful hand use in girls: Rett's syndrome: report of 35 cases. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):471–479. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Happle R., Phillips R. J., Roessner A., Jünemann G. Homologous genes for X-linked chondrodysplasia punctata in man and mouse. Hum Genet. 1983;63(1):24–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00285392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. V., Neville B., Jones R. W., Fear C., Bobrow M. Two cases of X/autosome translocation in females with incontinentia pigmenti. Hum Genet. 1985;71(3):231–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00284581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilimann M. W., DeGennaro L. J. Molecular cloning of cDNAs for the nerve-cell specific phosphoprotein, synapsin I. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1997–2002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., McKusick V. A. Report of the Committee on Comparative Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):536–566. doi: 10.1159/000132187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., de Martinville B., Horwich A. L., Rosenberg L. E., Francke U. Human ornithine transcarbamylase locus mapped to band Xp21.1 near the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):698–700. doi: 10.1126/science.6494904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt M. N., Francke U. A system of nomenclature for band patterns of mouse chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1973;41(2):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00319691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. Ancient linkage groups and frozen accidents. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):259–262. doi: 10.1038/244259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rett A. Uber ein eigenartiges hirnatrophisches Syndrom bei Hyperammonämie im Kindersalter. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1966 Sep 10;116(37):723–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburg M. Norrie's disease. A congenital progressive oculo-acoustico-cerebral degeneration. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1966;(Suppl):1–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund D. A., Weston W. L. Incontinentia pigmenti. A four-generation study. Arch Dermatol. 1980 Jun;116(6):701–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Seeburg P. H., Francke U. Human luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone gene (LHRH) is located on short arm of chromosome 8 (region 8p11.2----p21). Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Jan;12(1):95–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01560732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Kunkel L. M., Bruns G., Morlé F., Koenig M., Mandel J. L., Horwich A., Latt S. A., Gusella J. F., Housman D. Localization of DNA sequences in region Xp21 of the human X chromosome: search for molecular markers close to the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):235–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Wyman A. R., White R., Francke U. Assignment of first random restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) locus ((D14S1) to a region of human chromosome 14. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):216–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]