Abstract
The cell cytoskeleton interprets and responds to physical cues from the microenvironment. Applying mechanical force to mesenchymal stem cells induces formation of a stiffer cytoskeleton, which biases against adipogenic differentiation and toward osteoblastogenesis. mTORC2, the mTOR complex defined by its binding partner rictor, is implicated in resting cytoskeletal architecture and is activated by mechanical force. We asked if mTORC2 played a role in mechanical adaptation of the cytoskeleton. We found that during bi-axial strain induced cytoskeletal restructuring, mTORC2 and Akt co-localize with newly assembled focal adhesions (FA). Disrupting the function of mTORC2, or that of its downstream substrate Akt, prevented mechanically-induced F-actin stress fiber development. mTORC2 becomes associated with vinculin during strain, and knock-down of vinculin prevents mTORC2 activation. In contrast, mTORC2 is not recruited to the FA complex during its activation by insulin, nor does insulin alter cytoskeletal structure. Further, when rictor was knocked down, the ability of MSC to enter the osteoblastic lineage was reduced, and when cultured in adipogenic medium, rictor-deficient MSC showed accelerated adipogenesis. This indicated that cytoskeletal remodeling promotes osteogenesis over adipogenesis. In sum, our data show that mTORC2 is involved in stem cell responses to biophysical stimuli, regulating both signaling and cytoskeletal reorganization. As such, mechanical activation of mTORC2 signaling participates in mesenchymal stem cell lineage selection, preventing adipogenesis by preserving β-catenin and stimulating osteogenesis by generating a stiffer cytoskeleton.
Keywords: osteoblast, adipocyte, rictor, Akt, vinculin
Introduction
The ability to respond and adapt to physical signals is a critical attribute of living organisms and the physical microenvironment of cells contributes to their phenotype and function. The fate of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), in particular, is influenced by the application of dynamic mechanical signals that are generated by tissue loading (1,2). Mechanical regulation of MSC differentiation has a direct effect on cell lineage, as both static (3,4) and dynamic (5) mechanical cues modulate lineage selection in vitro, in part through stiffening of the cell cytoskeleton resulting from formation of F-actin stress fibers (6). Stress fibers are anchored through focal adhesions, where both structural and signaling molecules participate in the perception, response, and adaptation to the biophysical environment. Focal adhesion numbers increase in response to surface stiffness (7) and after dynamic load (8,9). Direct effects of mechanical stimuli on the cytoskeleton of uncommitted marrow MSCs are thought to underwrite the increased osteoblastogenesis that occurs during exercise-induced loading of the skeleton (10), while reduced loading leads to increased marrow adipocytes (11,12).
Entry into the osteoprogenitor lineage is supported by Wnt activation of β-catenin (13), a process associated with the repression of adipogenic genes (14). Mechanical stimuli activate β-catenin and inhibit adipogenesis in MSC (5), but generation of the mechanical β-catenin signal bypasses the Wnt/LRP interaction, arising instead from mechanically activated Akt’s direct phosphorylation and inhibition of GSK3β (15). Searching for the kinase responsible for mechanical activation of Akt, we ruled out both PI3-kinase and integrin-linked kinase (16). We identified mTORC2, the rictor-associated mTOR that is insensitive to rapamycin, (17,18), as proximal to Akt and necessary for mechanical activation of β-catenin (16).
Mechanical stimulation of mTORC2 requires that tension develop at focal adhesions and the signal is amplified by increased numbers of focal adhesions (9,19), an adaptation to force reminiscent of the enhanced response to shear force measured after development of focal adhesions in osteoblasts (20). Mechanical input further causes cytoskeletal reorganization in MSC; within several hours after force application MSC have a five-fold increase in focal adhesions which become highly interconnected via a radial actin cytoskeleton (9). Interestingly, cellular F-actin cytoskeletal structure is disrupted in the absence of mTORC2 (21,22). This suggests that mTORC2 serves as a trigger by which mechanical force induces cytoskeletal change.
mTORC2 has been shown to reside predominantly in the endoplasmic reticulum in resting cells (23), and was not reported in a recent analysis of the focal adhesion proteome (24). From this cytoplasmic location, mTORC2’s involvement in cytoskeletal architecture might be predicted to be at a distance. An alternative possibility would be that physical force induces a relocation of mTORC2 to sites where outside-in signaling is initiated at focal adhesions, sites which provide anchoring for F-actin radial struts. In yeast, osmotic stretch activates TORC2 through the redistribution of its partner, the pleckstrin homology domain protein Slm, from a plasma membrane domain to a separate membrane compartment, causing TORC2 to be relocate (25). Little is known regarding the regulation of mammalian TORC2 (26); it is possible that mammalian TORC2 might also be activated during a process of protein relocation.
In the work presented here we set out to determine whether mTORC2 was involved in force generated cytoskeletal reorganization. We hypothesized local activation of mTORC2 at focal adhesions would be critical to mechanically directed cytoskeletal change. As such, mTORC2’s regulation of cytoskeletal adaption would also influence MSC lineage decisions. In the data presented here, we show that during bi-axial stretch mTORC2 is recruited to newly assembling focal adhesions. Importantly, in the absence of mTORC2 signaling, strain-induced cytoskeletal reorganization is deficient, and osteoblast differentiation is impaired while adipogenesis is accelerated.
Materials and Methods
Reagents
Fetal bovine serum was from Atlanta Biologicals (Atlanta, GA). Culture media, trypsin-EDTA reagent, antibiotics, Akti1/2, KU63794, ML7, blebbistatin were from Sigma-Aldrich. KU63794 was from EMD Millipore.
Cells and Culture Conditions
Marrow-derived MSC (mdMSC cells) were harvested from murine marrow using a published protocol (27); we published that mdMSC rapidly attain both osteoblastic and adipocytic characteristics under appropriate conditions (15). mdMSC were maintained in growth medium (10% fetal bovine serum, 100 µg/ml penicillin/streptomycin). For experiments, the cells were plated at a density of 6,000–10,000 cells/cm2 in collagen-I coated silicone membrane plates (FlexCell Hillsborough, NC) and cultured for 2 days prior to application of strain. Osteogenic medium consisted of 50 µg/ml ascorbic acid and 10 µM β-glycerophosphate. Adipogenic medium included 0.5 mM IBMX, 5 µg/ml insulin and 1 µM dexamethasone. MEFs were from K. Burridge, and C3H10T1/2 cells were obtained from ATCC.
Mechanical Strain
Uniform bi-axial strain was applied to mdMSC plated on 6-well Bioflex Collagen-I coated plates using the Flexcell FX-4000 system (Flexcell International, Hillsborough, NC).The mechanical regimen consisted of 100 cycles of 2% strain at 10 cycles/min, as previously described (9). For analysis, cells were harvested for directly after 100 cycles of the last strain application.
RNA Interference
mdMSC were transfected with specific siRNA or a control siRNA (20 nM) using PepMute Plus (SignaGen Lab, Rockville, MD). Medium was replaced at 18 hours with MEM containing 10% FBS, 1.25 mM glutamine and 100 μg/ml penicillin/ streptomycin. Mechanical strain was applied 72 hours after initial transfection; osteogenic or adipogenic media were added 18 hours after transfection. siRictor and siVinculin and their respective control siRNAs (siCTL) were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). The siRNA forward sequence for Rictor target sense was 5’-UCAUCUUUCUGACUAAGCGAAGGGC and for the control (nucleotide change within same sequence) was 5’-GCCCUCGUUGACUGAAAGAAUCUGA. The siRNA to silence vinculin was sense 5’-GAGAGAUAUGCCACCAGCCUUUAUU and control 5’-GAGAUACGUCACGACUCCUUAGAUU.
Immunoprecipitation
Cell lysates were pre-cleared with 1.0 µg control IgG at 4 °C x 30 minutes. 10 µl primary antibody was added for incubation at 4 °C overnight before collecting immunoprecipitates (IP) and resuspending in 20 µl of PBS plus loading buffer for SDS-PAGE analysis.
Western Blotting
Whole cell lysates were prepared with lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris HCl, 1 mM EGTA, 0.24% sodium deoxycholate, 1% Igepal, pH 7.5) containing 25 mM NaF and 2 mM sodium vanadate. Aprotinin, leupeptin, pepstatin, and PMSF were added prior to lysis. Whole cell lysates (5–20 µg) or IP proteins were loaded onto polyacrylamide gel (7–12%) for chromatography and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. After blocking with milk (5% w/v), primary antibody was applied overnight at 4 °C including antibodies against rictor, mTOR, total-Akt, pS473-Akt (Cell Signaling, Beverly MA); vinculin and paxillin (Abcam, Cambridge MA); actin (Sigma-Aldrich) and tubulin (Santa Cruz, Dallas TX). Secondary antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase was detected with ECL plus chemiluminescence kit (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway NJ). The images were acquired with a HP Scanjet and densitometry determined using NIH ImageJ, 1.37v.
Immunofluorescence
The heterobifunctional crosslinker NHS-ester diazirine (SDAD) (Thermo Scientific, Inc.) was used to crosslink lysine residues with long-wave UV light. Briefly, 0.5 mM crosslinker was added to plates positioned at 5 cm from the 365 nm UV x 5 minutes. For microscopy, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde x 20min, permeabilized in 0.1% Triton-X 100 × 5min, blocked sequentially with 0.2M Glycine x 10 min and 5% donkey serum x 30 min separated by 3× 10min PBS washes between steps. Silicone membranes were cut from plates and transferred to 6-well plate surface. Primary Abs were added at 4°C overnight (Anti-vinculin Ab (Sigma-Aldrich), and anti-rictor, anti-mTOR, anti-Akt (Cell Signaling). Secondary antibodies were as follows: for vinculin, DyLight 649 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch Lab) and for Cell Signaling products: Rhod Red-X-AffiniPure Dnk Anti-Rabbit IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratory, Inc). Actin stress fibers were visualized with Alexa Fluor 488® conjugated phalloidin (Invitrogen). After 3× 10min washes, membranes were sealed with mounting medium on glass. Cells were imaged on an Olympus BX61 inverted microscope system using filters: DyLight 649: Semroc 4040A; Rhodamine Red-X: Semroc 4040B; Alexa Fluor® 488 Phalloidin: Semroc 3540B. mdMSC are flat such that confocal does not supply more information than simple immunofluorescence microscopy. Micrography images show cells representative of the majority within the field.
Isolation of focal adhesions
Cells were incubated with TEA-containing low ionic strength buffer [2.5 mM triethanolamine (TEA), pH 7.0] for 3 min at room temperature, 1× PBS containing protease/phosphatase inhibitors. A Waterpik (Fort Collins CO) nozzle held 0.5 cm from the plate surface at ∼90° supplied the hydrodynamic force to flush away cell bodies, membrane-bound organelles, nuclei, cytoskeleton, and soluble cytoplasmic materials (28).
Assessment of osteogenic and adipogenic phenotype
Total mRNA was isolated from mdMSC and osteogenic and adipogenic genes amplified by RT-PCR as previously described (2,29). Alkaline phosphatase staining and assay was performed with Sigma kit.
Statistical Analysis
Densitometry results compiled from at least three separate experiments, are expressed as mean ±SEM. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA analysis of variance or t test (GraphPad Prism). All experiments were replicated at least three times to assure reproducibility.
Results
mTORC2 is required for strain induced cytoskeletal reorganization
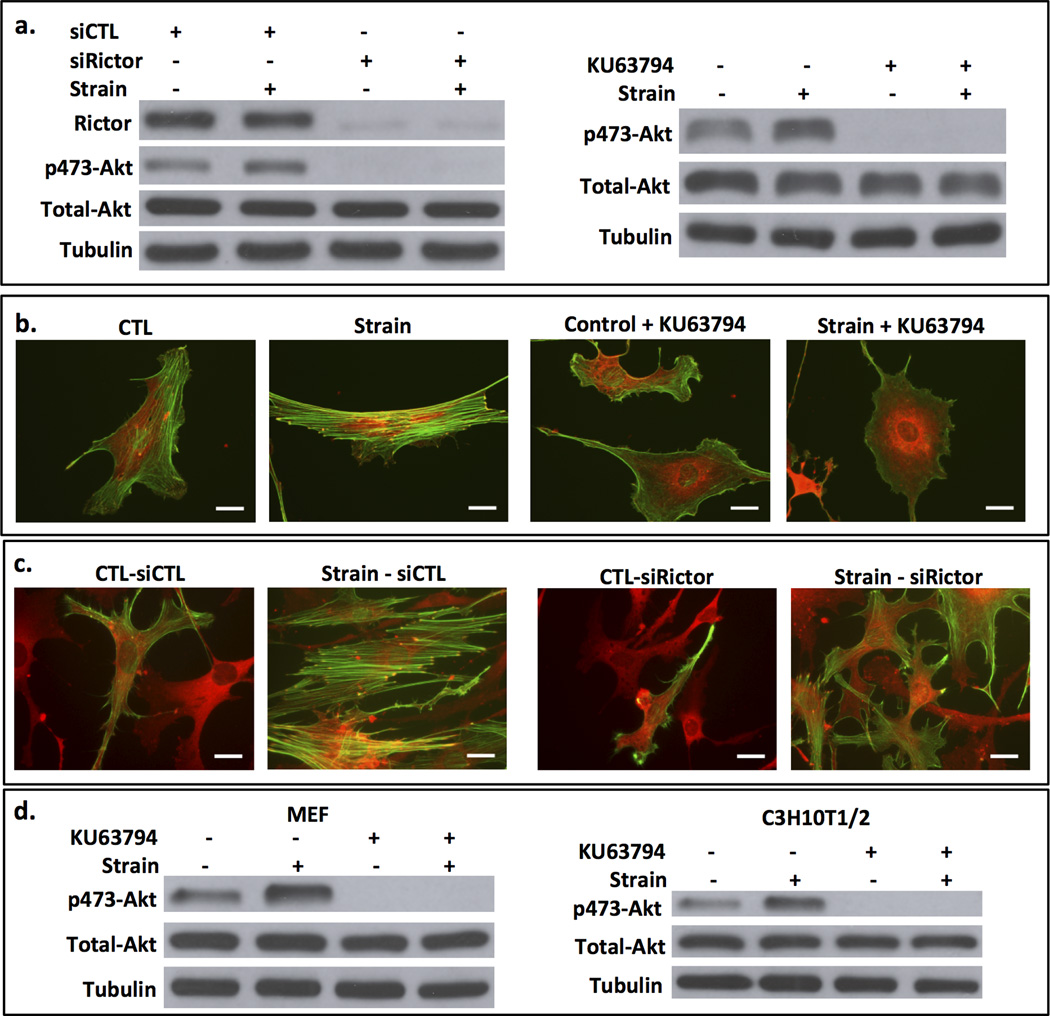
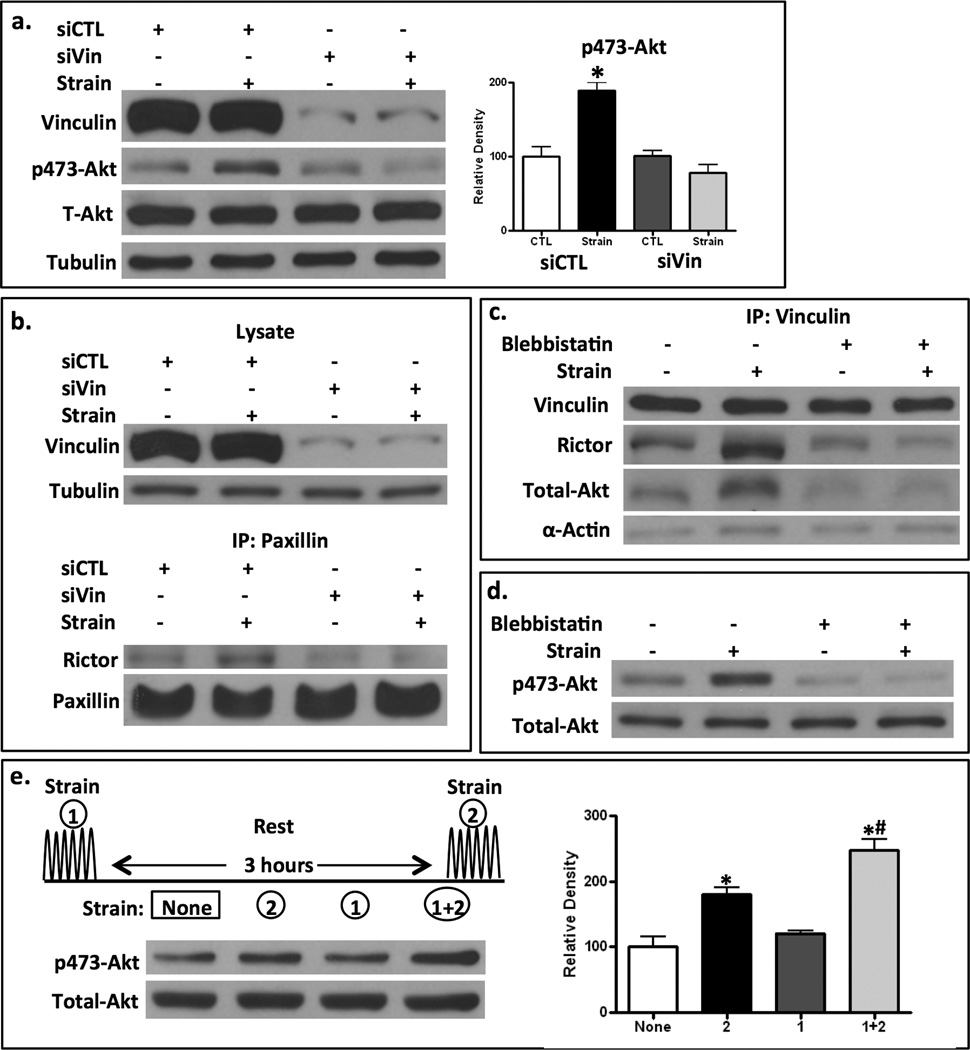
We have previously shown that strain prevents adipogenesis in marrow derived stem cells in a signaling process that culminates in increased nuclear β-catenin (2), whereby GSK3β is inactivated through phosphorylation by Akt (5). Strain induced activation of Akt depends on activation of mTORC2 (16). Here we specifically examine the role of rictor (the mTOR partner in mTORC2) in this signaling process. Akt phosphorylation on the mTORC2 targeted serine-473 was increased after 100 cycles of strain (Fig 1a). When rictor, the specific component which discriminates mTORC2 from mTORC1, is silenced, strain did not increase Akt phosphorylation. Shown in the Western blot to the right, the mTOR inhibitor KU63794 also prevented mechanical induction of Akt phosphorylation, as expected (16). The transmission of mechanical force through focal adhesions (FAs) induces cytoskeleton reorganization (30). We previously showed that strain (100 cycles, 2% strain) caused an increase in FAs that peaked at a nearly five-fold increase in number examined 3 hours after the application of force (9). This process is typified by mature focal adhesions inter-connected via actomyosin stress fibers (31). As expected, mdMSC demonstrated cytoskeletal reorganization, including the development of radial stress fibers emerging from and connecting to vinculin-containing focal adhesions 3 hours after strain (Fig 1b). To investigate whether mTORC2 signaling was required for the strain induced cytoskeletal alteration, mTOR kinase was inhibited with KU63794. In the absence of mTOR kinase activity, strain failed to induce radial stress fiber assembly (Fig 1b). To confirm the involvement of mTORC2 in cytoskeletal reorganization by mechanical strain, we depleted rictor using siRNA. Cells lacking rictor were unable to respond to strain with cytoskeletal reorganization (Fig 1c). Stress fibers, which form after application of strain as shown in mdMSC transfected with a control siRNA, were deficient when rictor was silenced; actin fibers that did form were not radial in nature. As mTORC2 is critical to strain induced radial stress fiber formation originating at FA sites, this suggested that mTORC2 should be located at focal adhesions in strained cells.
Figure 1. mTORC2 is required for mechanical Akt activation and strain induced cytoskeletal reorganization.
a. After 48 h of treatment with siRNA based on the rictor (siRictor) or mutated (siCTL) sequences. mdMSC were strained x 10 min. Immunoblot showed a loss of mechanical Akt activation when rictor is knocked down. Shown to the right, the mTOR inhibitor KU63794 (2mM) prevented mechanical Akt activation. b. Strain-induced focal adhesion assembly (vinculin = red fluorescence) and F-actin (green) and actin reorganization failed to occur when mTOR was inhibited by KU63794. Scale bars = 25 µm. c. Rictor knock down, as opposed to treatment with control siRNA, prevented strain-induced cytoskeletal reorganization. d. Mechanical strain x 10 min activated Akt in both murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) and embryonic MSC (C3H10T1/2); this was inhibited by pretreatment with KU63794.
The requirement for mTORC2 to activate Akt after mechanical strain was also studied in murine embryonic fibroblasts and the embryonic mesenchymal cell line C3H10T1/2 to assess generality of the effect. As shown in Figure 1d, mechanical strain induced Akt phosphorylation, and inhibition of mTOR with KU63794 prevented this effect, indicating that mTOR was the responsible kinase in these MSC as well.
mTORC2 is associated with strain-induced FAs
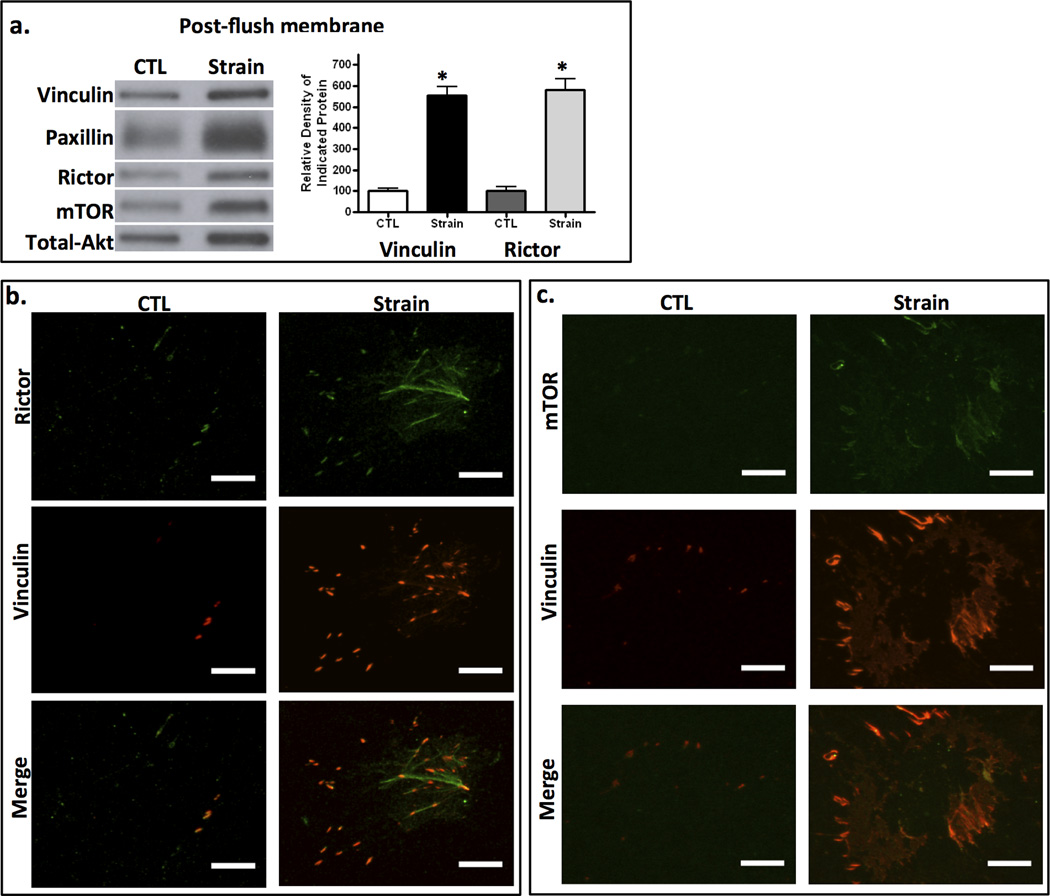
To query whether rictor was associated with newly developing focal adhesions in response to strain, we purified FAs by virtue of their strong adhesion to the collagen coated culture plate after cross-linking. Application of pulsed hydrodynamic forces flushed away cell bodies, nuclei and soluble materials of the cytoplasm, leaving FAs adherent to the substrate (24,28). Focal adhesion proteins adherent to the membrane were analyzed by immunoblot: strained plates contained more FA adherent proteins, represented by vinculin and paxillin. We previously showed that strain does not alter the total cellular vinculin level, but causes its recruitment into strain-induced focal adhesions (9) where it forms part of a link to β-integrin (32). Shown here, the components of mTORC2, rictor and mTOR, that were adherent to the membrane were increased in strained cultures (Fig 2a). The strain-induced increase in rictor paralleled that of vinculin as shown by densitometry (n = 3 experiments); this confirmed both mechanical induction of FA assembly and the presence of mTORC2 in the macromolecular FA complexes. Paxillin is also targeted to focal adhesions (33) and its increased presence in the adhesion complexes is shown as well.
Figure 2. mTORC2 is associated with strain-induced FAs.
a. 3 h after 100 strain cycles, cell bodies were removed with hydrodynamic force and remaining adherent FA proteins scraped for Western blot. Strained cells generated more focal adhesion macromolecular complexes. Densitometry of vinculin and rictor bands from 3 separate experiments in series is shown at the right; * = p < 0.05 different from control. b, c. IF of flushed membranes shows increases in punctate vinculin and rictor (b) or mTOR (c) staining after strain. Scale bars = 25 µm.
Recruitment of mTORC2 to FAs was further confirmed by co-immunofluorescence staining after membrane flushing. Shown in Fig 2b and 2c, FAs were visualized by vinculin staining 3 hours after strain application and punctate vinculin staining was more abundant in strained cells. The substrate adherent FAs also contained rictor and mTOR (Fig 2b and 2c, respectively). This confirmed that mechanical stretch promoted the development of FA complexes which contained mTORC2.
Strain induces mTORC2 association with FA proteins
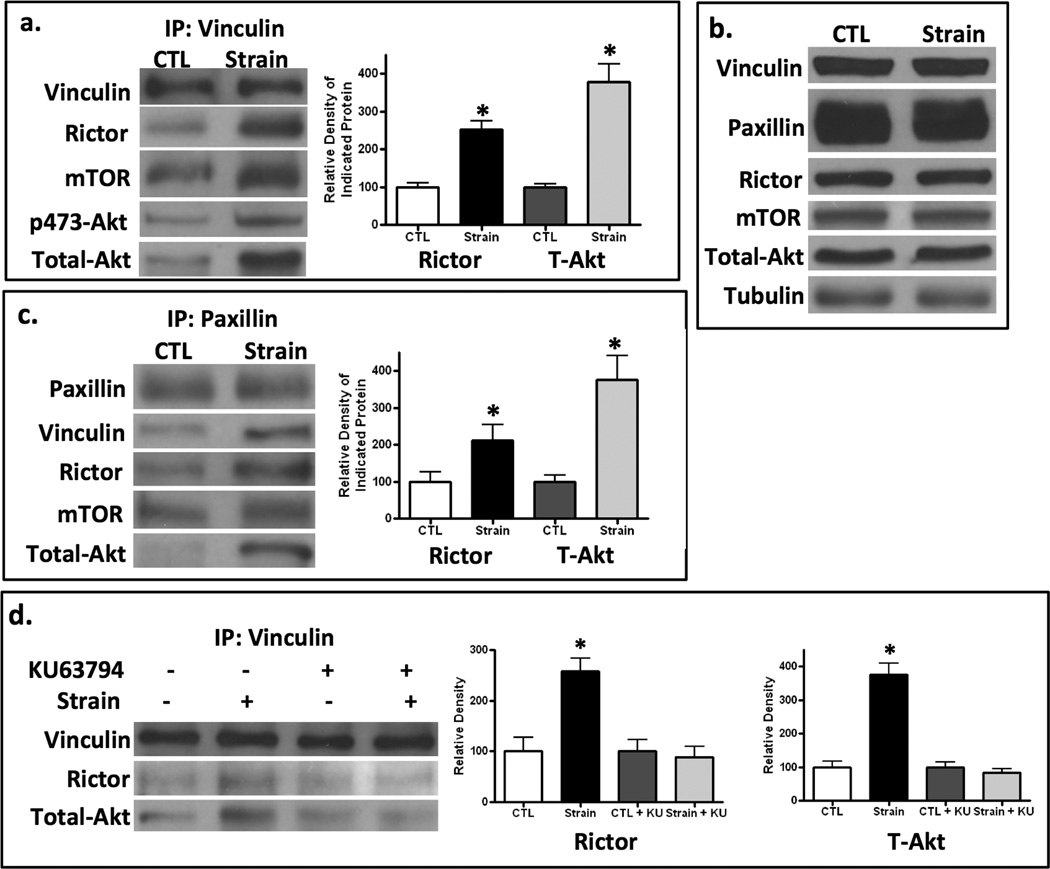
The co-localization of mTORC2 with known focal adhesion proteins led us to ask whether mechanical mTORC2/Akt signaling was propagated at FA sites. We first examined whether rictor and its Akt substrate were co-associated with vinculin, a molecule that is involved in force generation within the focal adhesion (34,35). After application of strain (100 cycles), cell lysates were immediately harvested and immunoprecipitated with vinculin. The association of both rictor and the mTOR substrate Akt with vinculin was increased with strain application in a reproducibly significant fashion, as shown by densitometry of rictor and Akt bands compiled from 3 experiments (Fig 3a). mTORC2’s rapid association with vinculin after mechanical treatment resulted in phosphorylation of Akt: phospho-Akt (pAkt) in the vinculin pull-down complex paralleled the recruitment of total Akt. Although lysates were corrected for protein prior to loading on vinculin beads, we also showed that 100 cycles of strain did not alter total amounts of FA or mTORC2 proteins, by showing no significant differences in lysates from control or strained conditions (Fig 3b).
Figure 3. Strain induces mTORC2 association with FA proteins, dependent on mTOR activity.
a. MSC cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibody to vinculin 10 min post-strain and analyzed by immunoblot, normalized to vinculin. Strain increased the association of rictor, mTOR and total and phosphorylated Akt with vinculin. Densitometry of rictor and total Akt bands is shown at the right; * = p < 0.05 different from control, n=3. b. Lysates prior to vinculin immunoprecipitation showed equivalent amounts of proteins of interest. c. Paxillin immunoprecipitation of strained cells showed that association with vinculin, rictor, mTOR and Akt was increased by strain. Densitometry of rictor and Akt bands is shown to the right; * = p < 0.05 different from control, n=3. d. IP with vinculin shows that strain failed in increase the association of rictor and Akt with vinculin when mTOR was inhibited with KU63794 (2mM). Densitometry confirms mTOR activity is necessary for association of rictor and Akt bands with vinculin; * = p < 0.05 different from control, n=3.
We confirmed strain-induced association of mTORC2 with focal adhesion proteins by pulling down paxillin. Immunoprecipitation with paxillin revealed an association of rictor and Akt with this protein after strain (Fig 3c). The significant association of rictor and Akt with paxillin was confirmed by densitometry. mTOR was also found in the paxillin immunoprecipitate after strain.
Further, inhibition of mTOR activity using the pharmacologic inhibitor KU63794 prevented the strain-induced association of both rictor and Akt with immunoprecipitated vinculin (Fig 3d). The inhibition of the strain induced vinculin/rictor association and vinculin/Akt association in the presence of KU63794 was confirmed by densitometry.
Akt must be activated to effect cytoskeletal reorganization
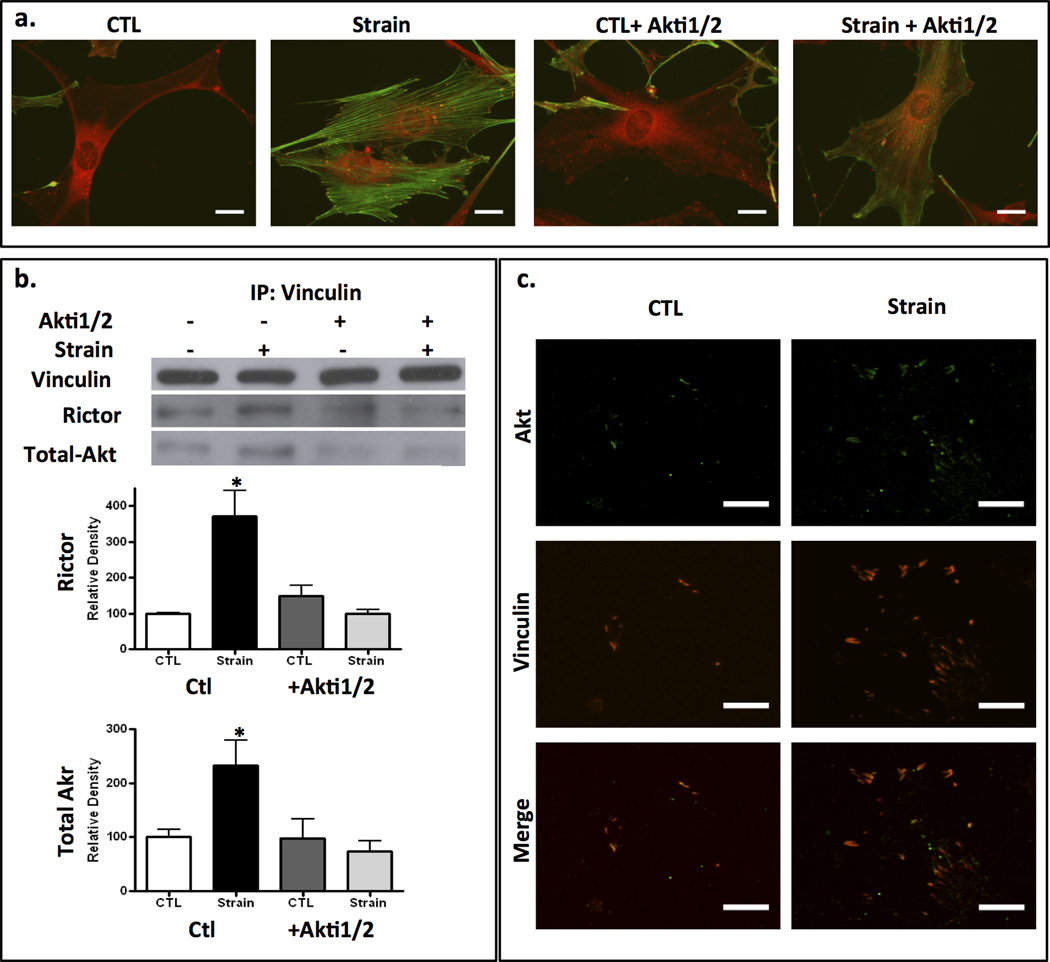
mTORC2 has a role in regulating the structure of the resting actin cytoskeleton (22,36) with suggested cytoskeletal effectors downstream of mTORC2 including PKCα and RhoA (37). As Akt is a known downstream target of mTORC2 (17) and co-localizes with mTORC2 proteins in focal adhesions in response to mechanical stimulation (Fig 3), we asked if Akt was required for mTORC2 to effect mechanical cytoskeletal reorganization. Figure 4a shows that suppressing Akt activity with the specific Akt inhibitor, Akti1/2 (38) prevented strain-induced assembly of radial stress fibers connected to peripheral FAs. Importantly, strain failed to recruit rictor or Akt to the FA macromolecular complex when Akt activity was inhibited: vinculin failed to pull down rictor or Akt after strain when mdMSC were pre-treated with Akti1/2 (Fig 4b). The requirement for Akt activation for Rictor and Akt association with vinculin was confirmed by densitometry showing that expected increases after strain in Rictor (top graph) and tAkt in the vinculin pulldown was absent when Akt was inhibited (Fig 4b). The Akti1/2 inhibitor is pleckstrin homology domain dependent (38); as such preventing Akt activation in this case likely prevents association with mTORC2 and/or vinculin.
Figure 4. Akt must be activated to effect cytoskeletal reorganization.
a. Addition of the Akt inhibitor, Akti1/2 (40 µM) prevented cytoskeletal reorganization 3h post strain. Vinculin = red, F-actin = green; scale bars = 25 µm. b. Akt activity is required for strain induced association of rictor and Akt with IP’d vinculin. Densitometry of rictor (top) and total Akt (bottom) bands are shown below a representative Western blot; * = p < 0.05 different from control, n=3. c. IF of adherent proteins after removing cell bodies with hydrodynamic force. Akt is associated with increased punctate vinculin membrane staining in strained cells. Scale bars = 25 µm.
To verify the presence of Akt in strain induced FAs, we purified focal adhesions using hydrodynamic flushing of cell bodies from the membrane substrate to leave adherent FAs; after strain, the presence of Akt in punctate vinculin complexes adherent to the membrane is shown in Fig 4c. In sum, Akt as well as mTORC2 is required at FA sites to induce assembly of radial stress fibers emerging from the new FAs.
mTORC2 association with FA vinculin is necessary for strain activation of Akt
We next wished to identify whether vinculin was critical to mTORC2 recruitment. When vinculin protein was knocked down by targeted siRNA, as shown in Fig 5a, Akt was not activated after strain, as confirmed by densitometry. Furthermore, in mdMSC where vinculin was knocked down, immunoprecipitation of cell lysates with a second component of the FA macromolecular complex, paxillin, failed to show association with rictor after strain, implicating vinculin as the co-partner for mTORC2 recruitment into the developing focal adhesion (Fig 5b). These results suggest that mechanically induced mTORC2 signaling and recruitment to the FA require mTORC2’s association with vinculin.
Figure 5. mTORC2 association with FA elements is necessary for strain activation of Akt.
a. siRNA targeting vinculin, but not control siRNA (siCTL) blocked strain-induced activation of Akt, shown as an increase phospho-473 Akt. Densitometry confirms the failure to significantly increase pAkt when vinculin is knocked down; * = p < 0.05 different from control, n=3. b. Lysates from siCTL and siVin cells shows immunoblot for vinculin and tubulin (top figure) before pull down with antibody to Paxillin (lower figure). Rictor association with paxillin increases only when vinculin is present. c. Blebbistatin (50µM) delivered prior to strain prevented strain-induced rictor, Akt and actin association with vinculin pull down. d. Blebbistatin prevented strain induced mTORC2 activity measured by increase in pAkt. e. Strain was applied at the beginning (strain 1) and/or end (strain 2) of a 3 hour period, at which point all lysates were made. pAkt rises after strain (comparing no strain, 1st lane, to strain 2, 2nd lane). pAkt returns to basal levels 3 h after strain (strain 1, 3rd lane). A 2nd strain application (strain 1+2, 4th lane) shows increased pAkt. Densitometry confirms pAkt return to baseline, and amplification at the second strain application; * ¹ control, * ¹ #, (n=4).
External forces applied to the cell generate intracellular tension which contributes to assembly and maturation of FAs (39,40). Redistribution of the integral FA complex molecule vinculin from the cytoplasm to nascent FAs is dependent both on myosin II and the stiffness of the external ECM substrate, which together generate static cytoskeletal tension (41). To ascertain the role of tension in the mechanical recruitment of mTORC2 to the focal adhesion complex, we blocked myosin II ATPase activity with blebbistatin, which results in inhibition of actomyosin contraction (42). Inactivation of myosin II prevented the recruitment of rictor and its Akt substrate to the FA complex (Fig 5c). Coincident with the interruption of rictor recruitment, blebbistatin also inhibited strain-induced Akt phosphorylation by mTORC2 (Fig 5d). This indicates that cells which lack internal tension do not respond to exogenous force with mTORC2/Akt signaling.
We queried whether the association of mTORC2 with vinculin in the FA was itself enough to induce Akt activation. Shown in Fig 5e, 100 strain cycles induced an immediate rise in mTORC2 phosphorylation of Akt (compare strained cells in 2nd lane, with unstrained cells in 1st lane), which returned to baseline levels within 3 hours (3rd lane). When the strain was applied a second time, there was enhanced Akt phosphorylation compared to only one application of strain (compare 4th with 2nd lane). Densitometry confirms this pattern of enhancement with the second strain application; e.g., that pAkt returns to normal by 3 hours, that a second treatment amplifies the signal. This result shows that despite the sustained presence of mTORC2 in FA complexes, shown in Fig 2, mTORC2 does not continuously phosphorylate Akt; however, once located at the FA site, a second strain application causes an amplification of Akt activation. As such, the presence of mTORC2 in the FA should potentiate the ability of MSC to respond to further mechanical input with signals that promote osteogenesis.
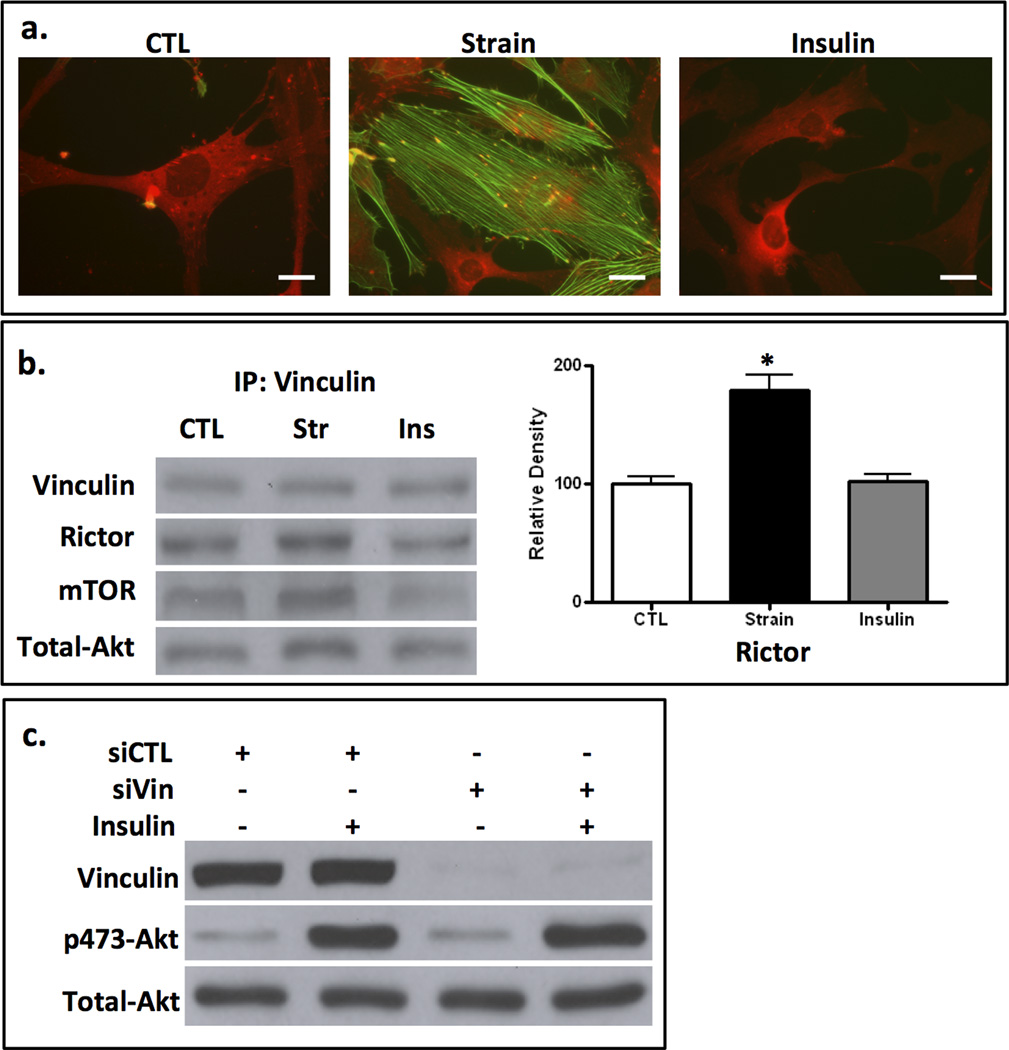
Insulin activation of Akt induces neither cytoskeletal reorganization nor mTORC2 association with vinculin
Insulin also utilizes mTORC2 during activation of Akt, although this requires the participation of PI3K (43). In a previous study we showed that insulin activation of Akt was unaffected when tension development was inhibited (9). Interestingly, PI3-K participates in the restructuring of lamellipodia (44) suggesting that insulin might participate in cytoskeletal regulation through actions on either mTORC2 or PI3K. In mdMSCs, insulin induced neither focal adhesion maturation nor F-actin assembly, in contrast to the cytoskeletal reorganization induced by strain activation of mTORC2/Akt (Fig 6a). Accordingly, mTORC2 was not recruited to FAs during insulin stimulation of Akt: insulin failed to induce association of vinculin with rictor, mTOR or Akt (Fig 6b). The absence of rictor in the vinculin immunoprecipitate of insulin treated cells was confirmed by densitometry.
Figure 6. Insulin activation of Akt induces neither cytoskeletal reorganization nor mTORC2 association with vinculin.
a. Insulin (100 ng/ml x 1 h) does not induce cytoskeletal reorganization, as does 100 cycles of strain, shown by vinculin (red) and actin (green) staining. Scale bars = 25 µm. b. Vinculin pull down after strain (str) or insulin (Ins): insulin does not induce rictor, mTOR or Akt association with vinculin as does strain. Densitometry of rictor and total Akt bands is shown at the right; * = p < 0.05 different from control, n=3. c. siRNA targeting vinculin failed to prevented insulin activation of Akt, shown as an increase phosphor-473 Akt.
Insulin induction of mTORC2 and resultant phospho-473 Akt further contrasts with mTORC2/Akt signaling via mechanical force in that it does not require mTORC2 association with vinculin. Vinculin was knocked down in mdMSC using siRNA; shown in Fig 6c, insulin stimulated Akt activation was unaffected when vinculin was deficient. In sum, insulin activation of Akt caused neither mTORC2 recruitment to FAs, nor cytoskeletal restructuring. This indicates that the compartmentalized pool of mTORC2 and Akt associating with FA complexes is functionally separate from that involved in metabolic pathways.
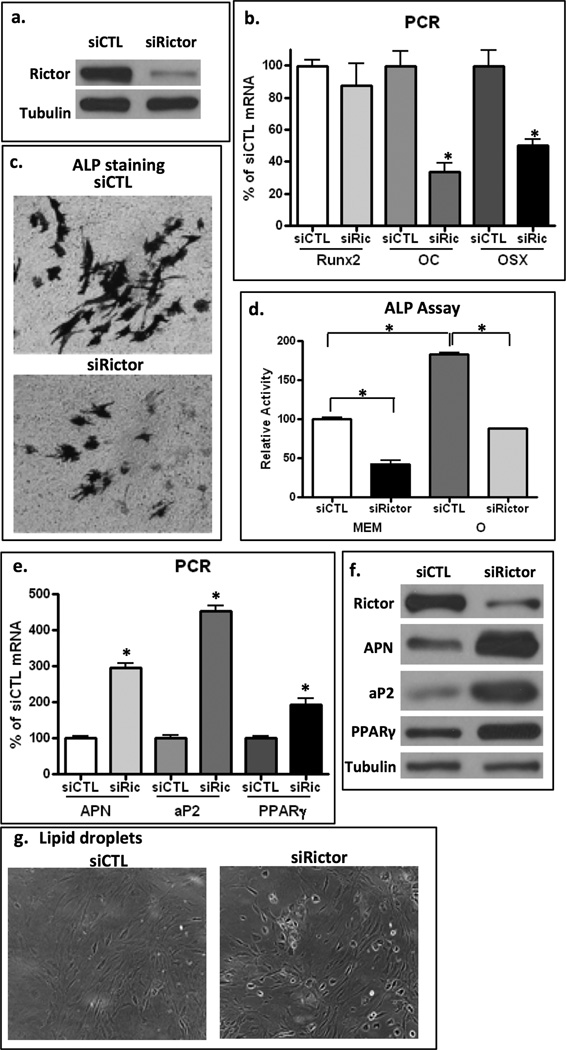
Ablation of a key component of mTORC2, Rictor, limits osteogenesis and promotes adipogenesis
Having shown that mTORC2 is recruited to focal adhesions where it participates in generating cytoskeletal structure, we wished to ascertain if limiting the availability of mTORC2 through rictor knock-down would affect differentiation of mdMSC. mdMSC treated with siRNA were transferred to osteogenic medium. After 4 days in osteogenic medium, cells treated with siRNA targeting rictor showed reduced rictor protein (Fig 7a). As these marrow-derived MSC already express high levels of RUNX2, Runx2 mRNA remains unchanged as cells enter the osteoblast lineage, but osterix and osteocalcin expressions increase (15). Cells where rictor was deficient had significantly reduced levels of osterix and osteocalcin mRNA after 4 days in osteogenic medium as compared to levels in transduced with control siRNA, shown in Fig 7b. Alkaline phosphatase positive staining developed on the cell surfaces of pre-osteoblastic mdMSC cultures, but was reduced in rictor knock-down cultures (Fig 7c). At the same time, culture alkaline phosphatase activity was reduced (Fig 7d). Together these data indicate that early osteoblast differentiation was reduced in cells where rictor was knocked down.
Figure 7. Rictor deficiency limits osteogenesis and promotes adipogenesis.
a. Western blot shows Rictor protein 4 d after transfection with siRNA targeting rictor or mutated rictor-like RNA sequence. b. mdMSC cultured in osteogenic media x 4d prior to RT-PCR for osteogenic genes. Rictor knock-down cells had significantly less osteocalcin and osterix expression, * = p < 0.05 different from cultures treated with siCTL, n=3. c,d. After 7d in osteogenic medium, stain for alkaline phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase activity are reduced in rictor knock-down cultures. e,f. mdMSC ± rictor knock-down were cultured in adipogenic media and assayed for adipogenic genes (e) and proteins (f) at 6 days; both repeated x 2. Rictor deficiency enhanced acquisition of adipogenic phenotype. g. Oil red O positive cells were increased in cultures with knock-down of rictor, low magnification shows bright lipid droplets.
Since rictor deficiency decreased osteogenic entry, we predicted that MSC with impaired cytoskeletal adaptation would be, instead, predisposed toward adipogenic lineage. To test this hypothesis, after transfection with siRNA (control and rictor), mdMSC were cultured in adipogenic medium with dexamethasone and IBMX. Shown in Fig 7e, mRNA for adiponectin, aP2 and PPARγ were highly expressed in rictor knock-down cultures, a significant difference compared to rictor-replete mdMSC at this time point. Similarly, protein expression confirmed that rictor-deficient cultures had advanced adipogenesis (Fig 7f). As well, rictor knock-down cultures showed abundant lipid-laden cells by day 6 while siCTL treated cells showed no bright lipid droplets at this time (Fig 7g).
As expected, long term inhibition of either mTOR or Akt had global effects on cell growth and proliferation preventing assessment of phenotype change at the times selected for Rictor knock-down experiments. In shorter term cultures, inhibition of Akt promoted adipogenesis, shown by expression of fat marker mRNA, and inhibited osteogenesis shown by decreased osterix expression and alkaline phosphatase activity (Supplemental Data Fig 1). Adipogenic cultures responded to inhibition of mTOR with cell death; cells in osteogenic conditions showed decreased alkaline phosphatase activity at 4 days (Supplemental Data Fig 2). Also, insulin in a dose adequate to stimulate mTORC2 (16) did not induce adipogenesis or osteogenesis of mdMSC (Supplemental Table S1).
Discussion
Both static and dynamic variables in the mechanical environment of mesenchymal stem cells participate in the regulation of MSC lineage decisions. We here show that the outside-in signaling generated by dynamic physical input results in recruitment of mTORC2 to developing focal adhesions, where mTORC2-activated Akt supports the force-induced polymerization and bundling of F-actin into discrete cytoskeletal struts. mTORC2 signaling is thus initiated by force, and reinforces the cytoskeletal apparatus that responds to the MSC external biophysical environment such that the MSC is biased away from an adipogenic cellular fate and towards the osteogenic lineage.
MSC sense the stiffness of their substrate through tension generated at focal adhesion sites, such that a rigid substrate, which mimics bone, promotes osteoblast lineage, whilst a soft substrate promotes adipogenesis (4,7). Increasing the stiffness of the MSC cytoskeleton decreases the likelihood that the cell will enter the adipogenic lineage (6). Cells respond to a stiff environment not only by cytoskeletal rearrangement, but also with increases in β-catenin (45), which in the case of the bone marrow MSC further biases it towards osteoblastogenesis and restricts adipogenesis (29). mTORC2 is a key participant in the mechanical activation of β-catenin in MSC, a process leading to Akt phosphorylation which we have shown to be independent of both PI3K and integrin linked kinase (16); we have here shown that this signaling molecule also is critical to regulation of cell architecture in response to mechanical stimulation. As might be predicted, without the ability to generate cytoskeletal rearrangement due to loss of rictor, the ability of mdMSC to respond to osteogenic stimuli with increases in osteoblastic gene markers and cell surface expression of alkaline phosphatase, factors that signify that cells have entered the osteoblast lineage, was reduced. In conjunction with this, rictor-deficient cultures underwent adipogenesis at a faster rate, supporting that mTORC2, through regulation of the cytoskeleton, is involved in MSC lineage allocation.
The bone marrow environment in which MSC reside is highly dynamic, and affected by physical use and disuse (46). The physical forces generated due to skeletal loading are complex and include variable hydrostatic pressure, fluid flow and viscosity. Resident cellular elements are known to respond to each of these factors (47) and they will be diversely affected dependent on local placement, adherence and nature of substrate at the very least (4). All of these factors are eventually sensed by the cell at its substrate attachment through focal adhesions, creating outside-in force through integrins. As such, the dynamic marrow environment will be transmuted into cell behaviors via these connections, which, as we have shown here, are continuously modified within the cell cytoskeleton.
Physical as well as soluble signals that direct MSC lineage selection are critical to bone formation. The effect of skeletal loading to promote bone formation in humans and in multiple animal models (10) is accompanied by a decrease in marrow fat (48). The mechanical antiadipogenic signal requires the transient activation and trafficking of β-catenin to the nucleus (2). This occurs through a GSK3β control node, where the inhibition of GSK3β by Akt results in increases in, and activation of, β-catenin (5). The effect on MSC lineage allocation that arises through mechanical activation of β-catenin is similar to effects of other stimuli that activate β-catenin, such as the high bone density mutation in the Lrp5 receptor, where increased osteogenesis is accompanied by decreased adipogenesis (49). Lrp5 activation also invokes GSK3β inhibition, but does not require mTORC2/Akt signaling, rather inhibiting GSK3β through sequestration (50). It is notable that soluble factors such as Wnt and insulin utilize mechanisms to regulate downstream signals - GSK3β and mTORC2/Akt respectively - that are distinct from those operated by mechanical stimuli. As shown, insulin stimulation of mTORC2 fails to induce cytoskeletal reorganization or cause redistribution of mTORC2 to FAs, which highlights the distinct co-opting of this signal by mechanical input to allow a response to the physical environment. Cytoskeletal reorganization not only adjusts the intensity of mechanical signaling through redistribution of signaling molecules, as we have shown here, but also likely modulates cellular responses to non-physical inputs. For instance, the ephrin signal causes unique responses dependent on whether the ephrin receptors are allowed to cluster, or remain separated within the cytoskeleton (51).
The initial description of the mTORC2 complex revealed that the absence of rictor led to a disruption of F-actin connectivity in resting cells (22). F-actin stress fibers can generate cell tension in response to the static environment to control lineage selection of stem cells (4). Mechanical stress at focal adhesion sites triggers reinforcement and maturation of the FAs in a process characterized by integrin clustering and recruitment of new FA proteins, followed by polymerization of actin which is anchored to FA platforms (52). Downstream of mTORC2, we show here that Akt is a necessary effector to formation of F-actin radial stress fibers connected to FAs. Importantly, the activated Akt must be associated with the FA complex for this function, and the recruitment of Akt to FAs likely depends on interactions with its pleckstrin homology domain. The Akt inhibitor used in our studies is dependent on binding to the pleckstrin homology domain, and as such, its inhibition of mTORC2’s recruitment to the FA may be through cloaking protein structure required in the redistribution of mTORC2 along with its Akt substrate. Interestingly, during osmotic stress, yeast TORC2 follows the relocation of the pleckstrin homology domain protein Slm to a separate membrane compartment (25), in a process which may be similar to the co-requirement for Akt recruitment with mTORC2 in mammalian MSC cells.
mTORC2 is not recruited to the FA in the absence of vinculin, suggesting a direct association of a unique component of mTORC2 with vinculin. A recent characterization of the FA proteome includes neither mTORC2 components nor Akt (28). It is known that Akt associates with actin (53,54) and phosphorylates actin regulatory proteins (55), suggesting that many proteins indirectly associated with FAs were not catalogued in the basal condition that was studied (28). Outside-in mechanical signaling generates force transmission across the vinculin protein and alters its geometry (34,56); this step may precede its association with mTORC2 by causing the unmasking of binding sites. As well, multiple kinases are activated upon integrin ligation which may contribute to subsequent protein associations. Our data shows that mTORC2, once associated with developing focal adhesions, does not remain in the activated state. However, when force is reapplied, we find that mTORC2 signaling is amplified, likely due to the presence of mTORC2 in the focal adhesion apparatus. This amplified signaling may explain the ability of repeated mechanical force to affect MSC lineage switching at force levels which are ineffective when applied only once daily (19).
During substrate stretch, the FA serves as a mechanosome that not only transmits mechanical information, but is itself dynamically restructured as the cell adapts to the mechanical environment. We now identify mTORC2 as a novel participant in the assembly and response of this heterogeneous mechanosome. In conclusion, mTORC2 and Akt signaling proteins serve two locally relevant cellular functions in MSC. First, their recruitment to vinculin-containing adhesion complexes is necessary to translate physical information from the external environment into intracellular signals. Second, once present at sites of FA assembly, these molecules reinforce and auto-amplify anti-adipogenic signals through regulating reorganization of the cytoskeleton. Thus, mTORC2, working through its Akt effector, is a critical signal for the regulation of MSC lineage decisions.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
JR acknowledges support from NIH AR056655, AR042360; MS acknowledges support from 5K12HD00441.
Footnotes
Disclosures - All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest
Authors’ roles - Study design: BS, ZX, NC and JR. Data collection: BS and ZX. Data analysis and interpretation: BS, ZX, NC, WRT, GU, MS and JR. Drafting and reviewing manuscript: BS, NC, WRT, GU, MS and JR.
Supplemental Data figure legends shown with supplemental data set.
References
- 1.Luu YK, Capilla E, Rosen CJ, Gilsanz V, Pessin JE, Judex S, Rubin CT. Mechanical stimulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation promotes osteogenesis while preventing dietary-induced obesity. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(1):50–61. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.080817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sen B, Xie Z, Case N, Ma M, Rubin C, Rubin J. Mechanical strain inhibits adipogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells by stimulating a durable beta-catenin signal. Endocrinology. 2008;149(12):6065–6075. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Discher DE, Mooney DJ, Zandstra PW. Growth factors, matrices, and forces combine and control stem cells. Science. 2009;324(5935):1673–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.1171643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677–689. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sen B, Styner M, Xie Z, Case N, Rubin CT, Rubin J. Mechanical loading regulates NFATc1 and beta-catenin signaling through a GSK3beta control node. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(50):34607–34617. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.039453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McBeath R, Pirone DM, Nelson CM, Bhadriraju K, Chen CS. Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev Cell. 2004;6(4):483–495. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(04)00075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shih YR, Tseng KF, Lai HY, Lin CH, Lee OK. Matrix stiffness regulation of integrin-mediated mechanotransduction during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(4):730–738. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Riveline D, Zamir E, Balaban NQ, Schwarz US, Ishizaki T, Narumiya S, Kam Z, Geiger B, Bershadsky AD. Focal contacts as mechanosensors: externally applied local mechanical force induces growth of focal contacts by an mDia1-dependent and ROCK-independent mechanism. J Cell Biol. 2001;153(6):1175–1186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.6.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sen B, Guilluy C, Xie Z, Case N, Styner M, Thomas J, Oguz I, Rubin C, Burridge K, Rubin J. Mechanically induced focal adhesion assembly amplifies anti-adipogenic pathways in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2011;29(11):1829–1836. doi: 10.1002/stem.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ozcivici E, Luu YK, Adler B, Qin YX, Rubin J, Judex S, Rubin CT. Mechanical signals as anabolic agents in bone. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(1):50–59. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Trudel G, Payne M, Madler B, Ramachandran N, Lecompte M, Wade C, Biolo G, Blanc S, Hughson R, Bear L, Uhthoff HK. Bone marrow fat accumulation after 60 days of bed rest persisted 1 year after activities were resumed along with hemopoietic stimulation: the Women International Space Simulation for Exploration study. J Appl Physiol. 2009;107(2):540–548. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.91530.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Menuki K, Mori T, Sakai A, Sakuma M, Okimoto N, Shimizu Y, Kunugita N, Nakamura T. Climbing exercise enhances osteoblast differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation with high expression of PTH/PTHrP receptor in bone marrow cells. Bone. 2008;43(3):613–620. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN, Lucas PC, Erickson RL, MacDougald OA. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt signaling. Science. 2000;289(5481):950–953. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5481.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Krishnan V, Bryant HU, Macdougald OA. Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(5):1202–1209. doi: 10.1172/JCI28551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Case N, Xie Z, Sen B, Styner M, Zou M, O'Conor C, Horowitz M, Rubin J. Mechanical activation of beta-catenin regulates phenotype in adult murine marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(11):1531–1538. doi: 10.1002/jor.21156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Case N, Thomas J, Sen B, Styner M, Xie Z, Galior K, Rubin J. Mechanical regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) in mesenchymal stem cells is dependent on Akt protein serine 473 phosphorylation via mTORC2 protein. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(45):39450–39456. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.265330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jacinto E, Facchinetti V, Liu D, Soto N, Wei S, Jung SY, Huang Q, Qin J, Su B. SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell. 2006;127(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 2005;307(5712):1098–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.1106148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sen B, Xie Z, Case N, Styner M, Rubin CT, Rubin J. Mechanical signal influence on mesenchymal stem cell fate is enhanced by incorporation of refractory periods into the loading regimen. J Biomech. 2011;44(4):593–599. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.11.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ponik SM, Pavalko FM. Formation of focal adhesions on fibronectin promotes fluid shear stress induction of COX-2 and PGE2 release in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. J Appl Physiol. 2004;97(1):135–142. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01260.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bhaskar PT, Hay N. The two TORCs and Akt. Dev Cell. 2007;12(4):487–502. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Kim DH, Guertin DA, Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sabatini DM. Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr Biol. 2004;14(14):1296–1302. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.06.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Boulbes DR, Shaiken T, Sarbassov dos D. Endoplasmic reticulum is a main localization site of mTORC2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;413(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.08.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kuo JC, Han X, Hsiao CT, Yates Iii JR, Waterman CM. Analysis of the myosin-II-responsive focal adhesion proteome reveals a role for beta-Pix in negative regulation of focal adhesion maturation. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(4):383–393. doi: 10.1038/ncb2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Berchtold D, Piccolis M, Chiaruttini N, Riezman I, Riezman H, Roux A, Walther TC, Loewith R. Plasma membrane stress induces relocalization of Slm proteins and activation of TORC2 to promote sphingolipid synthesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(5):542–547. doi: 10.1038/ncb2480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Weber JD, Gutmann DH. Deconvoluting mTOR biology. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(2):236–248. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.2.19022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Peister A, Mellad JA, Larson BL, Hall BM, Gibson LF, Prockop DJ. Adult stem cells from bone marrow (MSCs) isolated from different strains of inbred mice vary in surface epitopes, rates of proliferation, and differentiation potential. Blood. 2004;103(5):1662–1668. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-09-3070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kuo JC, Han X, Yates JR, 3rd, Waterman CM. Isolation of focal adhesion proteins for biochemical and proteomic analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;757:297–323. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-166-6_19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Case N, Thomas J, Xie Z, Sen B, Styner M, Rowe D, Rubin J. Mechanical input restrains PPARgamma2 expression and action to preserve mesenchymal stem cell multipotentiality. Bone. 2013;52(1):454–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2012.08.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Goldmann WH. Mechanotransduction and Focal Adhesions. Cell Biol Int. 2012 doi: 10.1042/CBI20120184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tojkander S, Gateva G, Lappalainen P. Actin stress fibers - assembly, dynamics and biological roles. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 8):1855–1864. doi: 10.1242/jcs.098087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ezzell RM, Goldmann WH, Wang N, Parashurama N, Ingber DE. Vinculin promotes cell spreading by mechanically coupling integrins to the cytoskeleton. Exp Cell Res. 1997;231(1):14–26. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.3451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wade R, Brimer N, Lyons C, Vande Pol S. Paxillin enables attachment-independent tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase and transformation by RAS. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(44):37932–37944. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.294504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Grashoff C, Hoffman BD, Brenner MD, Zhou R, Parsons M, Yang MT, McLean MA, Sligar SG, Chen CS, Ha T, Schwartz MA. Measuring mechanical tension across vinculin reveals regulation of focal adhesion dynamics. Nature. 2010;466(7303):263–266. doi: 10.1038/nature09198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ziegler WH, Liddington RC, Critchley DR. The structure and regulation of vinculin. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16(9):453–460. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jacinto E, Loewith R, Schmidt A, Lin S, Ruegg MA, Hall A, Hall MN. Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(11):1122–1128. doi: 10.1038/ncb1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu L, Das S, Losert W, Parent CA. mTORC2 regulates neutrophil chemotaxis in a cAMP- and RhoA-dependent fashion. Dev Cell. 2010;19(6):845–857. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Barnett SF, Defeo-Jones D, Fu S, Hancock PJ, Haskell KM, Jones RE, Kahana JA, Kral AM, Leander K, Lee LL, Malinowski J, McAvoy EM, Nahas DD, Robinson RG, Huber HE. Identification and characterization of pleckstrin-homology-domain-dependent and isoenzyme-specific Akt inhibitors. Biochem J. 2005;385((Pt 2)):399–408. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Choi CK, Vicente-Manzanares M, Zareno J, Whitmore LA, Mogilner A, Horwitz AR. Actin and alpha-actinin orchestrate the assembly and maturation of nascent adhesions in a myosin II motor-independent manner. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(9):1039–1050. doi: 10.1038/ncb1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vicente-Manzanares M, Zareno J, Whitmore L, Choi CK, Horwitz AF. Regulation of protrusion, adhesion dynamics, and polarity by myosins IIA and IIB in migrating cells. J Cell Biol. 2007;176(5):573–580. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200612043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pasapera AM, Schneider IC, Rericha E, Schlaepfer DD, Waterman CM. Myosin II activity regulates vinculin recruitment to focal adhesions through FAK-mediated paxillin phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 2010;188(6):877–890. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200906012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Straight AF, Cheung A, Limouze J, Chen I, Westwood NJ, Sellers JR, Mitchison TJ. Dissecting temporal and spatial control of cytokinesis with a myosin II Inhibitor. Science. 2003;299(5613):1743–1747. doi: 10.1126/science.1081412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gan X, Wang J, Su B, Wu D. Evidence for direct activation of mTORC2 kinase activity by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(13):10998–11002. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.195016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cain RJ, Ridley AJ. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases in cell migration. Biol Cell. 2009;101(1):13–29. doi: 10.1042/BC20080079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Samuel MS, Lopez JI, McGhee EJ, Croft DR, Strachan D, Timpson P, Munro J, Schroder E, Zhou J, Brunton VG, Barker N, Clevers H, Sansom OJ, Anderson KI, Weaver VM, Olson MF. Actomyosin-mediated cellular tension drives increased tissue stiffness and beta-catenin activation to induce epidermal hyperplasia and tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 2011;19(6):776–791. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.05.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gurkan UA, Akkus O. The Mechanical Environment of Bone Marrow: A Review. Ann Biomed Eng. 2008 doi: 10.1007/s10439-008-9577-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Thompson WR, Rubin CT, Rubin J. Mechanical regulation of signaling pathways in bone. Gene. 2012;503(2):179–193. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.04.076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.David V, Martin A, Lafage-Proust MH, Malaval L, Peyroche S, Jones DB, Vico L, Guignandon A. Mechanical loading down-regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in bone marrow stromal cells and favors osteoblastogenesis at the expense of adipogenesis. Endocrinology. 2007;148(5):2553–2562. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Qiu W, Andersen TE, Bollerslev J, Mandrup S, Abdallah BM, Kassem M. Patients with high bone mass phenotype exhibit enhanced osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(11):1720–1731. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.070721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Taelman VF, Dobrowolski R, Plouhinec JL, Fuentealba LC, Vorwald PP, Gumper I, Sabatini DD, De Robertis EM. Wnt signaling requires sequestration of glycogen synthase kinase 3 inside multivesicular endosomes. Cell. 2010;143(7):1136–1148. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Salaita K, Nair PM, Petit RS, Neve RM, Das D, Gray JW, Groves JT. Restriction of receptor movement alters cellular response: physical force sensing by EphA2. Science. 2010;327(5971):1380–1385. doi: 10.1126/science.1181729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ziegler WH, Gingras AR, Critchley DR, Emsley J. Integrin connections to the cytoskeleton through talin and vinculin. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36(Pt 2):235–239. doi: 10.1042/BST0360235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cenni V, Sirri A, Riccio M, Lattanzi G, Santi S, de Pol A, Maraldi NM, Marmiroli S. Targeting of the Akt/PKB kinase to the actin skeleton. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60(12):2710–2720. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3349-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Vandermoere F, El Yazidi-Belkoura I, Demont Y, Slomianny C, Antol J, Lemoine J, Hondermarck H. Proteomics exploration reveals that actin is a signaling target of the kinase Akt. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6(1):114–124. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M600335-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Enomoto A, Murakami H, Asai N, Morone N, Watanabe T, Kawai K, Murakumo Y, Usukura J, Kaibuchi K, Takahashi M. Akt/PKB regulates actin organization and cell motility via Girdin/APE. Dev Cell. 2005;9(3):389–402. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Vogel V, Sheetz M. Local force and geometry sensing regulate cell functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(4):265–275. doi: 10.1038/nrm1890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.