Abstract
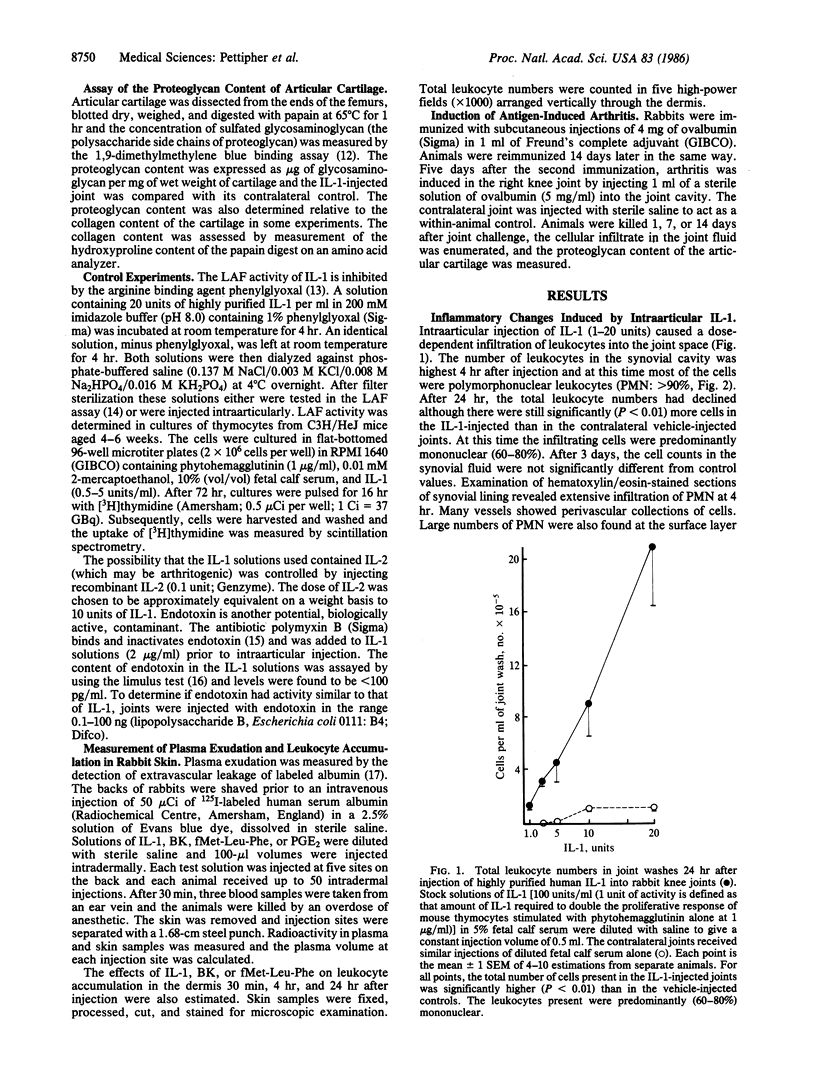
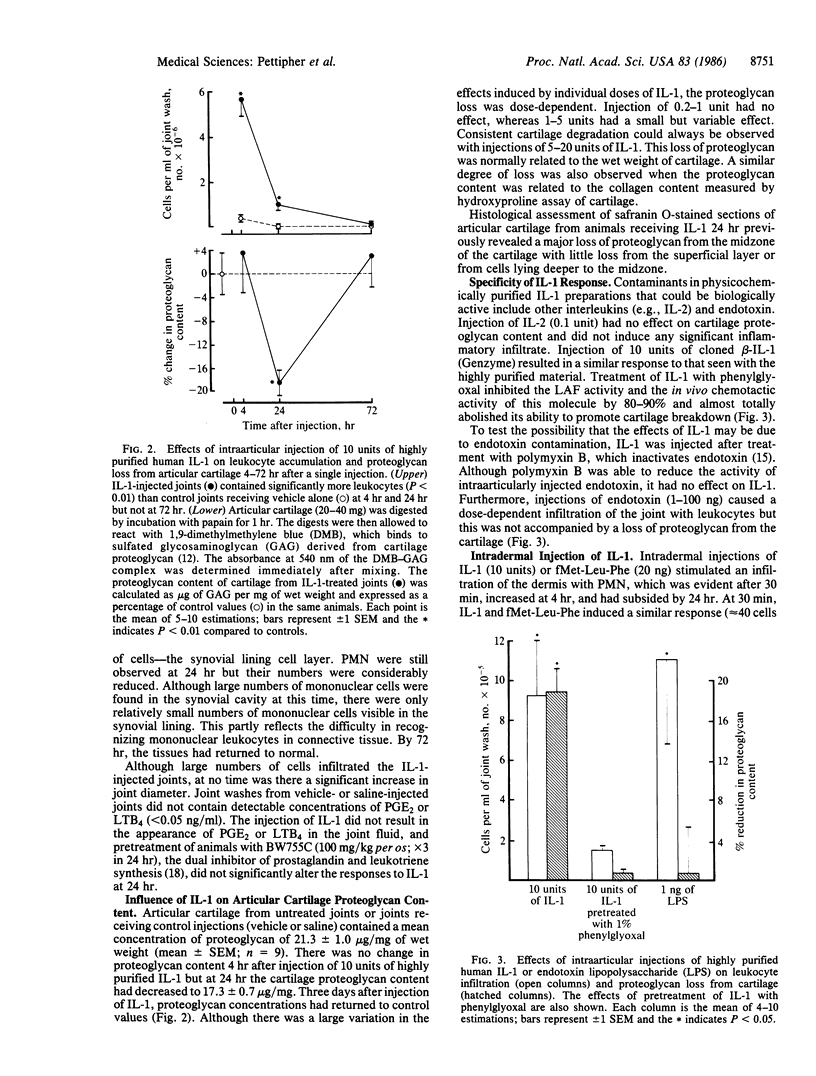
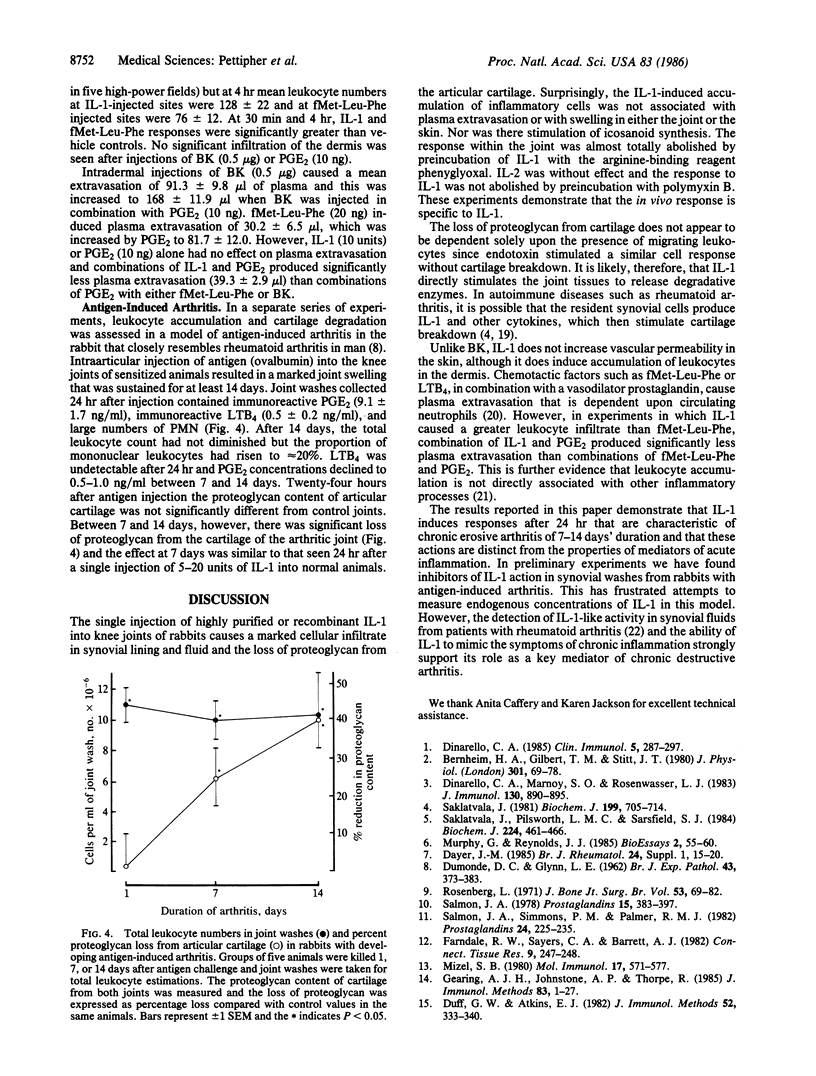
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) is a polypeptide released by activated macrophages and is thought to be a key mediator of host responses to infection and inflammation. The availability of highly purified and recombinant material has now permitted the evaluation of IL-1 as a mediator of chronic inflammatory processes in vivo. We have demonstrated that intraarticular injection of IL-1 into rabbit knee joints induces the accumulation of polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes in the joint space and the loss of proteoglycan from the articular cartilage. The effects on cartilage could not be explained solely by the presence of leukocytes, since injections of endotoxin also stimulated leukocyte accumulation in the joint but had no effect on proteoglycan loss. Responses to IL-1 were not associated with increased production of the icosanoids prostaglandin E2 or leukotriene B4 and were not reduced by an inhibitor of their synthesis. The pattern of leukocyte infiltration and cartilage breakdown 24 hr after IL-1 injection was similar to that seen in animals with antigen-induced arthritis of 1 week's duration. These observations support the hypothesis that IL-1 acts directly to mediate the erosive processes of chronic arthritis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheim H. A., Gilbert T. M., Stitt J. T. Prostaglandin E levels in third ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits during fever and changes in body temperature. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:69–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. An update on human interleukin-1: from molecular biology to clinical relevance. J Clin Immunol. 1985 Sep;5(5):287–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00918247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Marnoy S. O., Rosenwasser L. J. Role of arachidonate metabolism in the immunoregulatory function of human leukocytic pyrogen/lymphocyte-activating factor/interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):890–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The inhibitory effect of polymyxin B on endotoxin-induced endogenous pyrogen production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farndale R. W., Sayers C. A., Barrett A. J. A direct spectrophotometric microassay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cartilage cultures. Connect Tissue Res. 1982;9(4):247–248. doi: 10.3109/03008208209160269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Johnstone A. P., Thorpe R. Production and assay of the interleukins. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Oct 24;83(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1959–1961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90651-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluger M. J., Singer R., Eiger S. M. Polymyxin B use does not ensure endotoxin-free solution. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Oct 24;83(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Studies on the purification and structure-functional relationships of murine lymphocyte activating factor (Interleukin 1). Mol Immunol. 1980 May;17(5):571–577. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri A. M., Panayi G. S., Goodman S. M. Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease. I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. Chemical basis for the histological use of safranin O in the study of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Jan;53(1):69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J. Characterization of catabolin, the major product of pig synovial tissue that induces resorption of cartilage proteoglycan in vitro. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):705–714. doi: 10.1042/bj1990705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Pilsworth L. M., Sarsfield S. J., Gavrilovic J., Heath J. K. Pig catabolin is a form of interleukin 1. Cartilage and bone resorb, fibroblasts make prostaglandin and collagenase, and thymocyte proliferation is augmented in response to one protein. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):461–466. doi: 10.1042/bj2240461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A. A radioimmunoassay for 6-keto-prostaglandin F1alpha. Prostaglandins. 1978 Mar;15(3):383–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Simmons P. M., Palmer R. M. A radioimmunoassay for leukotriene B4. Prostaglandins. 1982 Aug;24(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaes G. Cell-to-cell interactions in the secretion of enzymes of connective tissue breakdown, collagenase and proteoglycan-degrading neutral proteases. A review. Agents Actions. 1980 Dec;10(6):474–485. doi: 10.1007/BF02024145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedmore C. V., Williams T. J. Control of vascular permeability by polymorphonuclear leukocytes in inflammation. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):646–650. doi: 10.1038/289646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J. Prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin I2 and the vascular changes of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;65(3):517–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby D. A., Sedgwick A. D., Giroud J. P., Al-Duaij A. Y., de Brito F. The use of the air pouch to study experimental synovitis and cartilage breakdown. Biomed Pharmacother. 1986;40(2):45–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


