Abstract
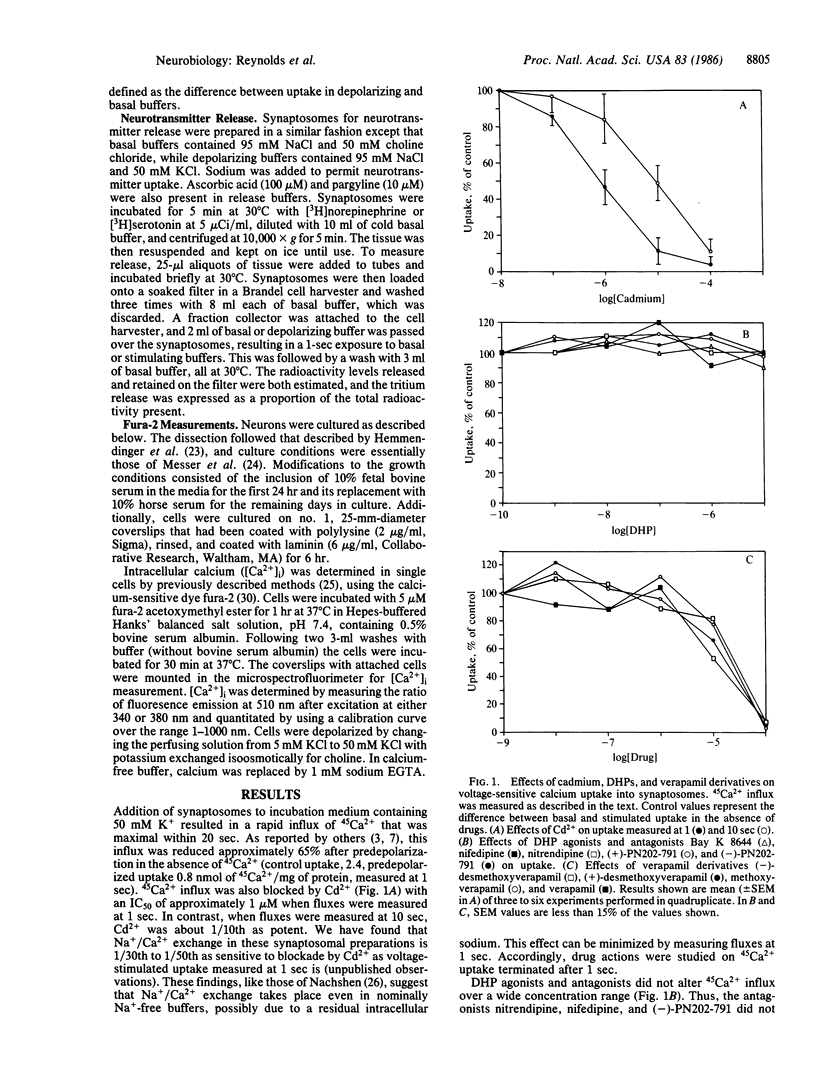
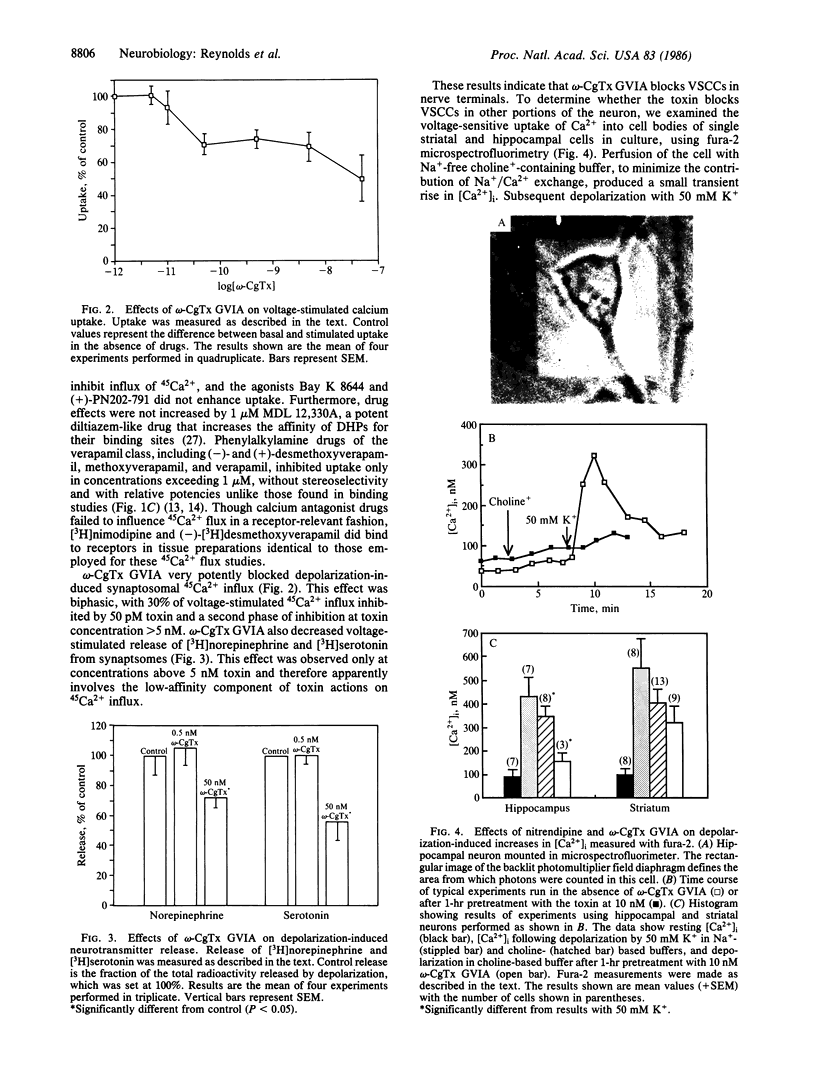
We have studied the voltage-activated influx of Ca2+ into synaptosomes. Rapid 45Ca2+ influx into synaptosomes, measured at 1 sec, was blocked by predepolarization and by low concentrations of cadmium (IC50, 1 microM), as anticipated for voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCCs). However, fluxes were insensitive to dihydropyridine drugs that block or activate VSCCs, including nitrendipine, Bay K 8644, and (+)- and (-)-PN202-791. Phenylalkylamine calcium antagonists, including verapamil and desmethoxyverapamil, blocked 45Ca2+ uptake in a nonspecific fashion. The peptide omega-conotoxin fraction GVIA (omega-CgTx GVIA) blocked 45Ca2+ uptake in a biphasic fashion, with a 30% reduction at 50 pM toxin and a further decrease at concentrations greater than 5 nM. The toxin inhibited neurotransmitter release from synaptosomes in nanomolar concentrations, corresponding to its low-affinity effects on 45Ca2+ influx. omega-CgTx GVIA also inhibited depolarization-induced increases in intracellular Ca2+ concentration in single hippocampal and striatal neurons. These findings indicate that omega-CgTx GVIA blocks VSCCs in both cell bodies and nerve terminals and that the predominant form of VSCC in nerve terminals is the dihydropyridine-insensitive N type.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Creba J. A., Karobath M. The effect of dihydropyridine calcium agonists and antagonists on neuronal voltage sensitive calcium channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1038–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M. Calcium channel antagonists. Omega-conotoxin defines a new high affinity site. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6230–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell L. C., Barr E. M., Leslie S. W. 45Ca2+ uptake into rat whole brain synaptosomes unaltered by dihydropyridine calcium antagonists. J Neurochem. 1983 Nov;41(5):1455–1459. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau P., Blaustein M. P. Initial release of [3H]dopamine from rat striatal synaptosomes: correlation with calcium entry. J Neurosci. 1983 Apr;3(4):703–713. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-04-00703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry D. R., Goll A., Gadow C., Glossmann H. (-)-3H-desmethoxyverapamil labelling of putative calcium channels in brain: autoradiographic distribution and allosteric coupling to 1,4-dihydropyridine and diltiazem binding sites. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;327(2):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00500915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmendinger L. M., Garber B. B., Hoffmann P. C., Heller A. Selective association of embryonic murine mesencephalic dopamine neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Oct 19;222(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. R., Jaros J. A., Roeske W. R., Wiech N. L., Ursillo R., Yamamura H. I. Potent enhancement of [3H]nitrendipine binding in rat cerebral cortical and cardiac homogenates: a putative mechanism for the action of MDL 12,330A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer A., Mazurkiewicz J. E., Maskin P. Growth of dissociated rat cerebellar cells using serum-free supplemented media and varied transferrin concentrations. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1981 Mar;1(1):99–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00736042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. M., Gould R. J., Largent B. L., Snyder S. H. A unitary mechanism of calcium antagonist drug action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):860–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Blaustein M. P. The effects of some organic "calcium antagonists" on calcium influx in presynaptic nerve terminals. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(2):576–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A. Selectivity of the Ca binding site in synaptosome Ca channels. Inhibition of Ca influx by multivalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Jun;83(6):941–967. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.6.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A. The early time course of potassium-stimulated calcium uptake in presynaptic nerve terminals isolated from rat brain. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:251–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura A., Takahashi M. Differential effect of a dihydropyridine derivative to Ca2+ entry pathways in neuronal preparations. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 3;301(2):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Gray W. R., Zeikus R., McIntosh J. M., Varga J., Rivier J., de Santos V., Cruz L. J. Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.4071055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J., Luque F. A., Gray W. R. Purification and sequence of a presynaptic peptide toxin from Conus geographus venom. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5087–5090. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perney T. M., Dinerstein R. J., Miller R. J. Depolarization-induced increases in intracellular free calcium detected in single cultured neuronal cells. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Oct 12;51(2):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampe D., Janis R. A., Triggle D. J. BAY K 8644, a 1,4-dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel activator: dissociation of binding and functional effects in brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1984 Dec;43(6):1688–1692. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. (-)-[3H] desmethoxyverapamil labels multiple calcium channel modulator receptors in brain and skeletal muscle membranes: differentiation by temperature and dihydropyridines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):731–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., O'Leary M. E., Murawsky M. M., Wang T. Presynaptic calcium channels in rat cortical synaptosomes: fast-kinetics of phasic calcium influx, channel inactivation, and relationship to nitrendipine receptors. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1349–1357. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01349.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., O'Leary M. E. Temporal characteristics of potassium-stimulated acetylcholine release and inactivation of calcium influx in rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):868–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium channels in rat brain synaptosomes: identification and pharmacological characterization. High affinity blockade by organic Ca2+ channel blockers. J Neurosci. 1985 Mar;5(3):841–849. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-03-00841.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward J. J., Leslie S. W. Bay K 8644 stimulation of calcium entry and endogenous dopamine release in rat striatal synaptosomes antagonized by nimodipine. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 9;370(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90502-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Schoemaker H., Boles R. G., Roeske W. R. Diltiazem enhancement of [3H]nitrendipine binding to calcium channel associated drug receptor sites in rat brain synaptosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):640–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90877-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]