Abstract
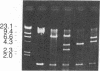
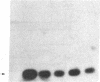
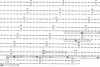
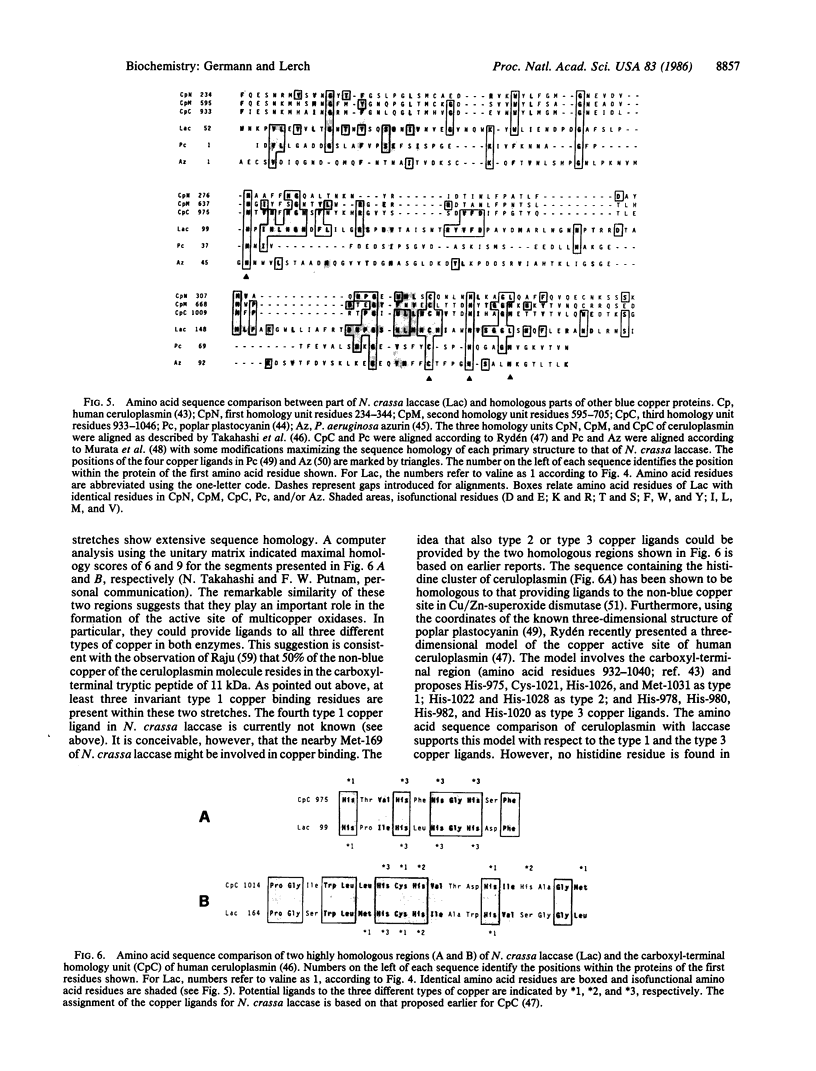
The laccase (benzenediol:oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.10.3.2) gene from Neurospora crassa was cloned and part of its nucleotide sequence corresponding to the carboxyl-terminal region of the protein has been determined. The gene was cloned by cDNA synthesis with a laccase-specific synthetic deoxyundecanucleotide as primer and poly(A) RNA isolated from cycloheximide-treated N. crassa cultures as template. Based on the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA obtained, a unique 21-mer was synthesized and used to screen a genomic DNA library from N. crassa. Five different positive clones were isolated and shown to share an overlapping DNA region with the same pattern of restriction sites. Sequence analysis of the common 1.36-kilobase Sal I fragment revealed an open reading frame of 726 nucleotides. The amino acid sequence deduced is in complete agreement with the primary structures of several tryptic peptides isolated previously from N. crassa laccase. The analyzed carboxyl-terminal region of laccase exhibits a striking sequence homology to the carboxyl-terminal part of the third homology unit of the multicopper oxidase ceruloplasmin and to a smaller extent, to the low molecular weight blue copper proteins plastocyanin and azurin. Based on amino acid sequence comparison between these proteins, putative copper ligands of N. crassa laccase are proposed. Moreover, these data further support the hypothesis that the small blue copper proteins and the multicopper oxidases have evolved from the same ancestral gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman E. T., Stenkamp R. E., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. A crystallographic model for azurin a 3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 25;123(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boel E., Vuust J., Norris F., Norris K., Wind A., Rehfeld J. F., Marcker K. A. Molecular cloning of human gastrin cDNA: evidence for evolution of gastrin by gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2866–2869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briving C., Gandvik E. K., Nyman P. O. Structural studies around cysteine and cystine residues in the "blue" oxidase fungal laccase B. Similarity in amino acid sequence with ceruloplasmin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 28;93(2):454–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Noyes B. E., Agarwal K. L., Steiner D. F. Construction and selection of recombinant plasmids containing full-length complementary DNAs corresponding to rat insulins I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5036–5040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H. Codon--anticodon pairing: the wobble hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):548–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Biro P. A., Cohen S. N., Erlich H. A., von Gabain A., Lawrance S. K., Lemaux P. G., McDevitt H. O., Peterlin B. M., Schulz M. F. Use of synthetic oligonucleotide probes complementary to genes for human HLA-DR alpha and beta as extension primers for the isolation of 5'-specific genomic clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1531–1535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinum J., Reinhammar B., Marchesini A. The stoichiometry of the three different types of copper in ascorbate oxidase from green zucchini squash. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80736-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., Putnam F. W. Internal duplication and evolution of human ceruloplasmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2805–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser K., Minuth W. The phenoloxidases of the ascomycete Podospora anserina. Communication 4. Genetic regulation of the formation of laccase. Genetics. 1970 Mar-Apr;64(3):441–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden E. Caeruloplasmin: a multi-functional metalloprotein of vertebrate plasma. Ciba Found Symp. 1980;79:93–124. doi: 10.1002/9780470720622.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Eriksson K. E. Induction of Neurospora crassa laccase with protein synthesis inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):450–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.450-457.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Eriksson K. E. Purification and properties of Neurospora crassa laccase. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):458–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.458-465.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervé M., Garnier A., Tosi L., Steinbuch M. Spectroscopic and photoreduction studies of copper chromophores in ceruloplasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston I. B., Kingston B. L., Putnam F. W. Chemical evidence that proteolytic cleavage causes the heterogeneity present in human ceruloplasmin preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5377–5381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird J. H., Fincham J. R. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Neurospora crassa am (NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase) gene. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Dawson C. R. The specific activity value based on the prosthetic copper of ascorbate oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Nov;191(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch K., Deinum J., Reinhammar B. The state of copper in Neurospora laccase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 24;534(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. C., Jacobson J. W., Giles N. H. Characterization and in vitro translation of polyadenylated messenger ribonucleic acid from Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1192-1198.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSBACH R. Purification and some properties of laccase from Polyporus versicolor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 11;73:204–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Huang T., Itakura K. Solid-phase synthesis of polynucleotides. III. Synthesis of polynucleotides with defined sequences by the block coupling phosphotriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5491–5505. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi K., Miyake T., Hozumi T., Itakura K. Solid-phase synthesis of polynucleotides. II. Synthesis of polythymidylic acids by the block coupling phosphotriester method. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5473–5489. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Begg G. S., Lambrou F., Leslie B., Simpson R. J., Freeman H. C., Morgan F. J. Amino acid sequence of a basic blue protein from cucumber seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6434–6437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Germann U. A., Lerch K. Isolation and structural organization of the Neurospora crassa copper metallothionein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2665–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA T. Purification and physico-chemical properties of laccase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Oct;30(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T. Studies on laccases of lacquer trees. I. Comparison of laccases obtained from Rhus vernicifera and Rhus succedanea. J Biochem. 1961 Sep;50:264–272. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortel T. L., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Structural model of human ceruloplasmin based on internal triplication, hydrophilic/hydrophobic character, and secondary structure of domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peisach J., Levine W. G., Blumberg W. E. Structural properties of stellacyanin, a copper mucoprotein from Rhus vernicifera, the Japanese lac tree. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2847–2858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju K. S. Isolation and characterization of copper-binding sites of human ceruloplasmin. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;56(1):81–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00228772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhammar B. Purification and properties of laccase and stellacyanin from Rhus vernicifera. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 7;205(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden L., Lundgren J. Homology relationships among the small blue proteins. Nature. 1976 May 27;261(5558):344–346. doi: 10.1038/261344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén L. Model of the active site in the blue oxidases based on the ceruloplasmin-plastocyanin homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6767–6771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechtman M. G., Yanofsky C. Structure of the trifunctional trp-1 gene from Neurospora crassa and its aberrant expression in Escherichia coli. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):83–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Bauman R. A., Ortel T. L., Dwulet F. E., Wang C. C., Putnam F. W. Internal triplication in the structure of human ceruloplasmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):115–119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Ortel T. L., Putnam F. W. Single-chain structure of human ceruloplasmin: the complete amino acid sequence of the whole molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Pastink A., Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Jansen A. E., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The genes coding for histone H3 and H4 in Neurospora crassa are unique and contain intervening sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5347–5360. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]