Abstract
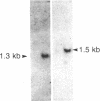
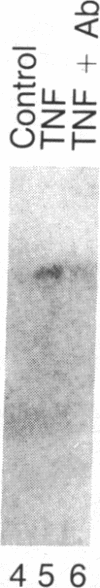
Recombinant Escherichia coli-derived human tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induces the 1.3-kilobase beta 2 interferon (IFN-beta 2) mRNA in human diploid fibroblasts (FS-4 strain). IFN-beta 2 is serologically related to the well-characterized IFN-beta 1 (respective antisera cross-neutralize the heterologous protein). Polyclonal and monoclonal anti-IFN-beta antibodies inhibit the increase in class I HLA gene expression (HLA-B7 mRNA) in TNF-treated FS-4 cells suggesting that TNF-induced IFN-beta 2 mediates the enhancing effect of TNF on HLA gene expression in human fibroblasts. The structure of this autocrine human interferon has been determined. A cDNA library was prepared from polyadenylylated RNA extracted from TNF-induced FS-4 cells, and eight IFN-beta 2 cDNA clones were isolated using a 21-nucleotide synthetic oligonucleotide probe. The 1128-nucleotide sequence of IFN-beta 2 mRNA and the 212-amino acid sequence of the IFN-beta 2 protein were deduced from these cDNA clones. The amino acid sequences of the serologically related human IFN-beta 1 and -beta 2 were compared using the Sellers TT metric algorithm for locating similarities and using the pattern scoring method for evaluating the observed similarities. IFN-beta 1 and -beta 2 each contain a segment that is approximately 100 amino acids including 39 amino acids that are aligned and identical in the two proteins. The hydropathic index plots across these segments in the two proteins are also strikingly similar. The region of similarity between IFN-beta 1 and -beta 2 includes a section that is also highly conserved in all IFN-alpha species sequenced. Thus IFN-beta 2 shares structural similarities with other human interferons that also preferentially increase class I HLA gene expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. K., Zur Nedden D., Heintzelman M., Hunkapiller M., Zoon K. Biologic activity in a fragment of recombinant human interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1045–1047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M., Mogensen K. E. Interferon receptors. Interferon. 1983;5:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheiter H., Ohno M., Smith M., Gutte B., Zoon K. C. Orientation of a human leukocyte interferon molecule on its cell surface receptor: carboxyl terminus remains accessible to a monoclonal antibody made against a synthetic interferon fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2539–2543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases mRNA levels and surface expression of HLA-A,B antigens in vascular endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Berman B., Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K., Vilcek J. Two antigenically distinct species of human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2185–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henco K., Brosius J., Fujisawa A., Fujisawa J. I., Haynes J. R., Hochstadt J., Kovacic T., Pasek M., Schamböck A., Schmid J. Structural relationship of human interferon alpha genes and pseudogenes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):227–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90401-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Landsberger F. R., Inouye M., Sehgal P. B. Significance of similarities in patterns: an application to beta interferon-related DNA on human chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4090–4094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Sehgal P. B., LaForge K. S., Inouye M. Expression of the native alpha and beta interferon genes in human cells. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Rutter W. J., Shows T. B., Gray P., Goeddel D. V., Lawn R. M. Leukocyte and fibroblast interferon genes are located on human chromosome 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M. Genetic and functional diversity of interferons in man. Interferon. 1983;5:205–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Increased nuclease sensitivity of the human interferon-alpha 1-related genes and the interferon-beta 1 gene during induction by virus. J Interferon Res. 1985 Fall;5(4):597–604. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B., May L. T., Inouye M., Slate D. L., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H. Interferon-beta-related DNA is dispersed in the human genome. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1312–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.6546621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B., May L. T., Slate D. L., Shulman L., Barker P. E., Ruddle F. H. Interferon-beta-related DNA on human chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jul;11(4):403–408. doi: 10.1007/BF01534418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B., Slate D. L., Ruddle F. H. Multiple human beta interferon genes. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):744–755. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B. How many human interferons are there? Interferon. 1982;4:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., May L. T., LaForge K. S., Inouye M. Unusually long mRNA species coding for human alpha and beta interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6932–6936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Sagar A. D. Heterogeneity of poly(I) x poly(C)-induced human fibroblast interferon mRNA species. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):95–97. doi: 10.1038/288095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B. The interferon genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 30;695(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(82)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R. M., May L. T., Ferguson-Smith A., Slate D. L., Revel M., Ruddle F. H. Human chromosome 7 carries the beta 2 interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5219–5222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slate D. L., Ruddle F. H. Fibroblast interferon in man is coded by two loci on separate chromosomes. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B. Translational activity and functional stability of human fibroblast beta 1 and beta 2 interferon mRNAs lacking 3'-terminal RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1741–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Olson S., Lawn R. M. Chromosomal localization of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferon genes by means of in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Chernajovsky Y., Zeevi M., Shulman L., Soreq H., Nir U., Wallach D., Perricaudet M., Tiollais P., Revel M. Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R., Korn J. H., Revel M. Structure and expression of cDNA and genes for human interferon-beta-2, a distinct species inducible by growth-stimulatory cytokines. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2529–2537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]