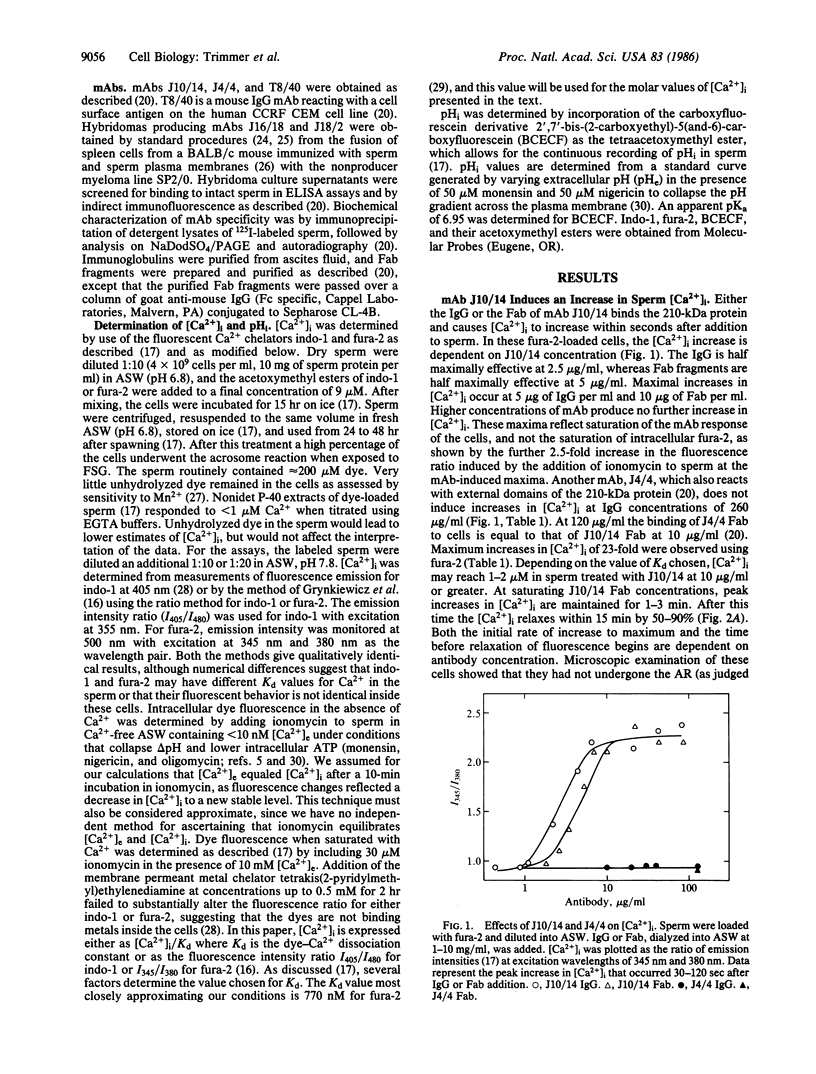
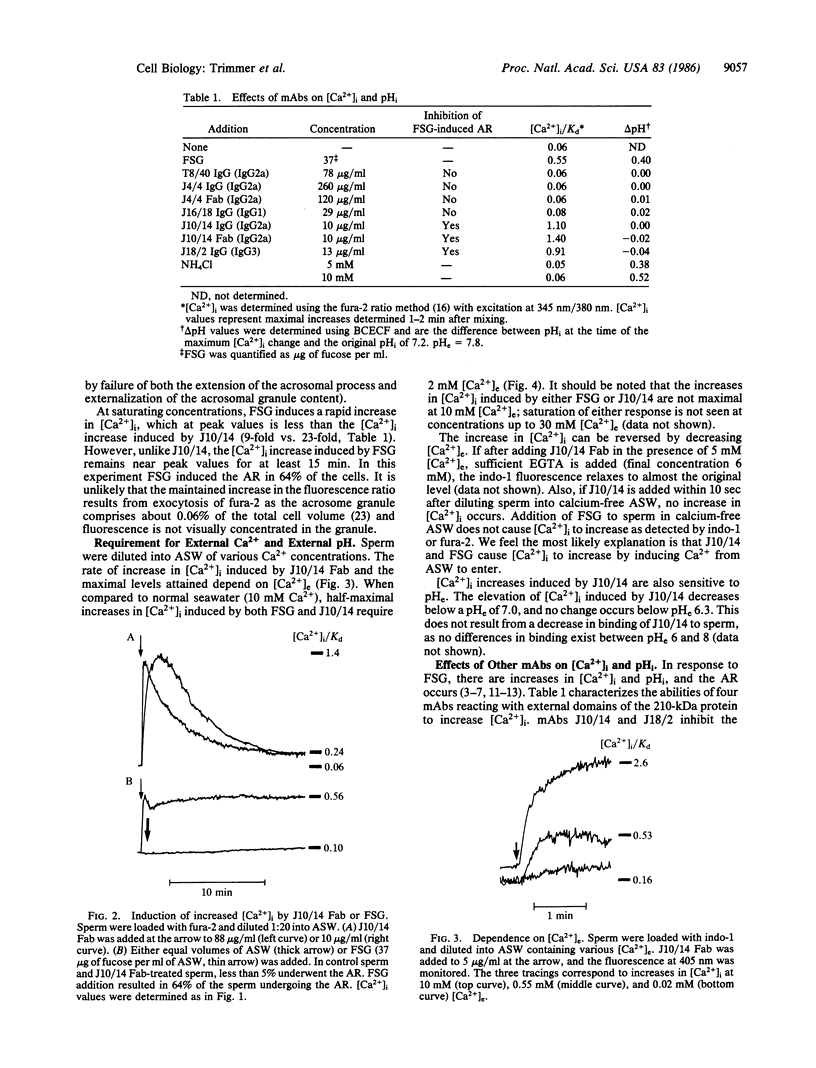
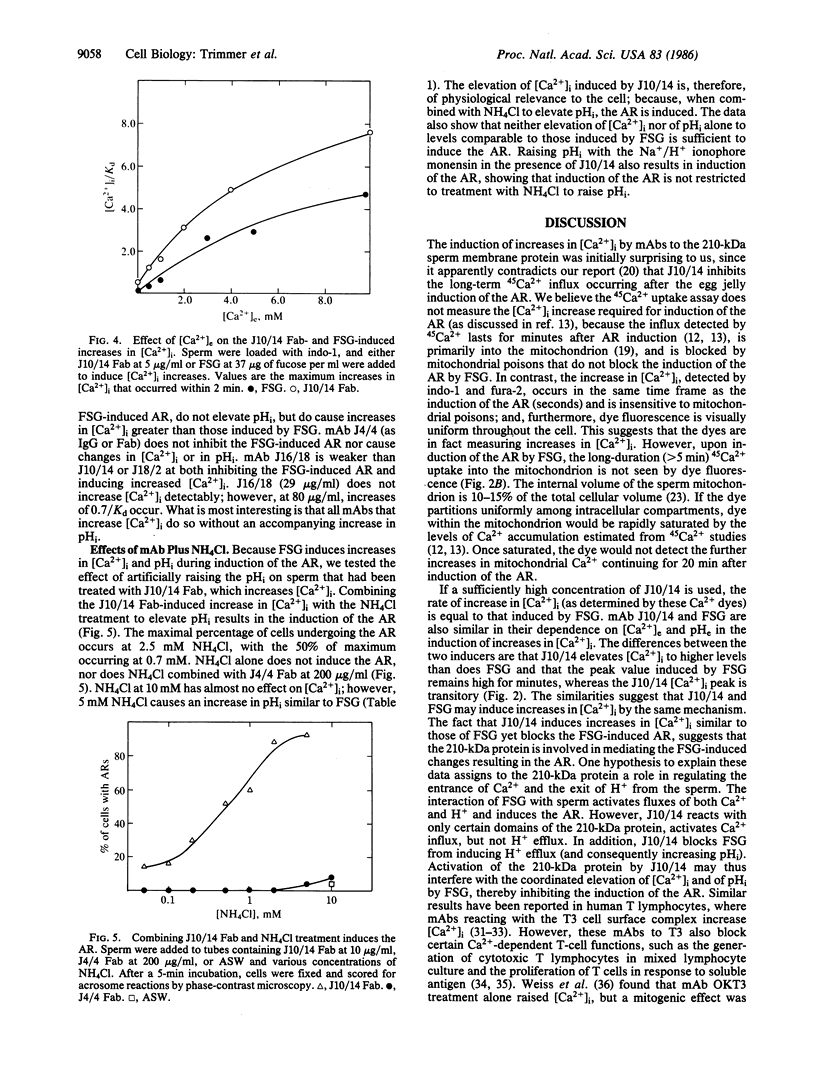
Abstract
Changes in intracellular free Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) of sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) spermatozoa were measured using the fluorescent Ca2+ indicators fura-2 and indo-1. The intracellular pH (pHi) of sperm was also determined. The fucose sulfate-rich glycoconjugate component of egg jelly induced increases in [Ca2+]i and pHi in sperm and induced the acrosome reaction. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to external domains of a 210-kDa glycoprotein of the sperm plasma membrane induced a 23-fold increase in [Ca2+]i (vs. 9-fold for fucose sulfate-rich glycoconjugate), but the mAbs did not cause the pHi to increase and did not induce the acrosome reaction. When the mAb treatment which induced an increase in [Ca2+]i was combined with an NH4Cl treatment, which increased the pHi, the acrosome reaction was induced. mAb-induced increases in [Ca2+]i were dependent on millimolar concentrations of extracellular Ca2+ and were reversed by placing sperm in Ca2+-free seawater or by chelating Ca2+ with EGTA. The mAb-induced [Ca2+]i increase was sensitive to the pH of the seawater, although mAb binding was not. The data show that increased [Ca2+]i and pHi are necessary for induction of the acrosome reaction and suggest that the 210-kDa protein may play a role in regulating Ca2+ entry into the spermatozoan. These mAbs make it possible to separate the increase in [Ca2+]i from the increase in pHi and may be useful in the elucidation of the regulatory role of Ca2+ in sperm physiology.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arslan P., Di Virgilio F., Beltrame M., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis in Ehrlich and Yoshida carcinomas. A new, membrane-permeant chelator of heavy metals reveals that these ascites tumor cell lines have normal cytosolic free Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2719–2727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantino M. E., Schackmann R. W., Johnson D. E. Changes in subcellular elemental distributions accompanying the acrosome reaction in sea urchin sperm. J Exp Zool. 1983 May;226(2):255–268. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402260211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Kung P. C., Gingras S. P., Goldstein G. Does OKT3 monoclonal antibody react with an antigen-recognition structure on human T cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1805–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen R., Schackmann R. W., Dahlquist F. W., Shapiro B. M. 31P-NMR analysis of sea urchin sperm activation. Reversible formation of high energy phosphate compounds by changes in intracellular pH. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Nov;149(1):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen R., Schackmann R. W., Shapiro B. M. Elevation of the intracellular pH activates respiration and motility of sperm of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14881–14890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen R., Schackmann R. W., Shapiro B. M. Metabolism of sea urchin sperm. Interrelationships between intracellular pH, ATPase activity, and mitochondrial respiration. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5392–5399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Moore J. P., Morris J. D., Taylor M. V., Rogers J., Smith G. A., Metcalfe J. C. A common sequence of calcium and pH signals in the mitogenic stimulation of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):481–484. doi: 10.1038/313481a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P., Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C. Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4876–4882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. H., Clapper D. L., Winkler M. M., Lee H. C., Epel D. A volatile inhibitor immobilizes sea urchin sperm in semen by depressing the intracellular pH. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):493–501. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. C., Johnson C., Epel D. Changes in internal pH associated with initiation of motility and acrosome reaction of sea urchin sperm. Dev Biol. 1983 Jan;95(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Linch D. C., Tatham P. E. The effect of mitogenic lectins and monoclonal antibodies on intracellular free calcium concentration in human T-lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):661–666. doi: 10.1042/bj2190661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Terhorst C., Cantley L. C., Rosoff P. M. Stimulation of the T3-T cell receptor complex induces a membrane-potential-sensitive calcium influx. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podell S. B., Moy G. W., Vacquier V. D. Isolation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from sea urchin sperm exhibiting species specific recognition of the egg surface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 21;778(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90444-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Changes of free calcium levels with stages of the cell division cycle. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):147–149. doi: 10.1038/315147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. C., Vacquier V. D. Phosphorylation of sperm histone H1 is induced by the egg jelly layer in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1986 Jul;116(1):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Hussey R. E., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody blocking human T cell function. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Oct;10(10):758–762. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Cantley L. C. Stimulation of the T3-T cell receptor-associated Ca2+ influx enhances the activity of the Na+/H+ exchanger in a leukemic human T cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14053–14059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schackmann R. W., Chock P. B. Alteration of intracellular [Ca2+] in sea urchin sperm by the egg peptide speract. Evidence that increased intracellular Ca2+ is coupled to Na+ entry and increased intracellular pH. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8719–8728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schackmann R. W., Christen R., Shapiro B. M. Measurement of plasma membrane and mitochondrial potentials in sea urchin sperm. Changes upon activation and induction of the acrosome reaction. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13914–13922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schackmann R. W., Christen R., Shapiro B. M. Membrane potential depolarization and increased intracellular pH accompany the acrosome reaction of sea urchin sperm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6066–6070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schackmann R. W., Eddy E. M., Shapiro B. M. The acrosome reaction of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus sperm. Ion requirements and movements. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):483–495. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schackmann R. W., Shapiro B. M. A partial sequence of ionic changes associated with the acrosome reaction of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1981 Jan 15;81(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schackmann R. Ion measurements in sea urchin sperm. Methods Cell Biol. 1986;27:57–71. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SeGall G. K., Lennarz W. J. Chemical characterization of the component of the jelly coat from sea urchin eggs responsible for induction of the acrosome reaction. Dev Biol. 1979 Jul;71(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Kiehart D. P., Sardet C., Tilney M. Polymerization of actin. IV. Role of Ca++ and H+ in the assembly of actin and in membrane fusion in the acrosomal reaction of echinoderm sperm. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):536–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Trowbridge I. S., Vacquier V. D. Monoclonal antibody to a membrane glycoprotein inhibits the acrosome reaction and associated Ca2+ and H+ fluxes of sea urchin sperm. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):697–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Vacquier V. D. Activation of sea urchin gametes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:1–26. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S. Interspecies spleen-myeloma hybrid producing monoclonal antibodies against mouse lymphocyte surface glycoprotein, T200. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):313–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacquier V. D. Rapid immunoassays for the acrosome reaction of sea urchin sperm utilizing antibody to bindin. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Aug;153(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90600-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Shoback D., Stobo J. Role of T3 surface molecules in human T-cell activation: T3-dependent activation results in an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



