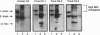Abstract
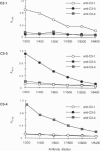
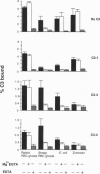
In all other species analyzed to date, the functionally active form of complement component C3 exists as the product of a single gene. We have now identified and characterized three functional C3 proteins (C3-1, C3-3, and C3-4) in trout that are the products of at least two distinct C3 genes. All three proteins are composed of an alpha-and a beta-chain and contain a thioester bond in the alpha-chain. However, they differ in their electrophoretic mobility, glycosylation, reactivity with monospecific C3 antibodies, and relative ability to bind to various surfaces (zymosan, Escherichia coli, erythrocytes). A comparison of the partial amino acid sequences of the three proteins showed that the amino acid sequence identity/similarity of C3-3 to C3-4 is 87/91%, while that of C3-3 and C3-4 to C3-1 is 51.5/65.5% and 60/73% respectively. Thus, trout possess multiple forms of functional C3 that represent the products of several distinct genes and differ in their ability to bind covalently to various complement activators.
Full text
PDF


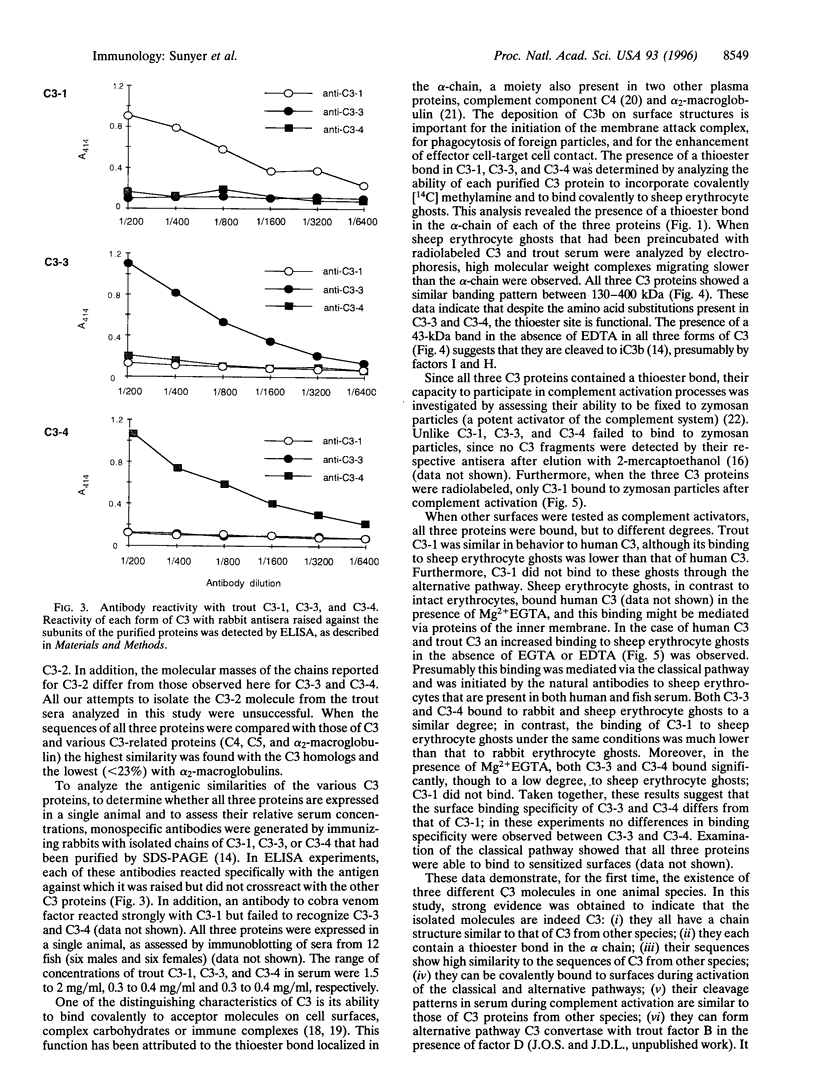
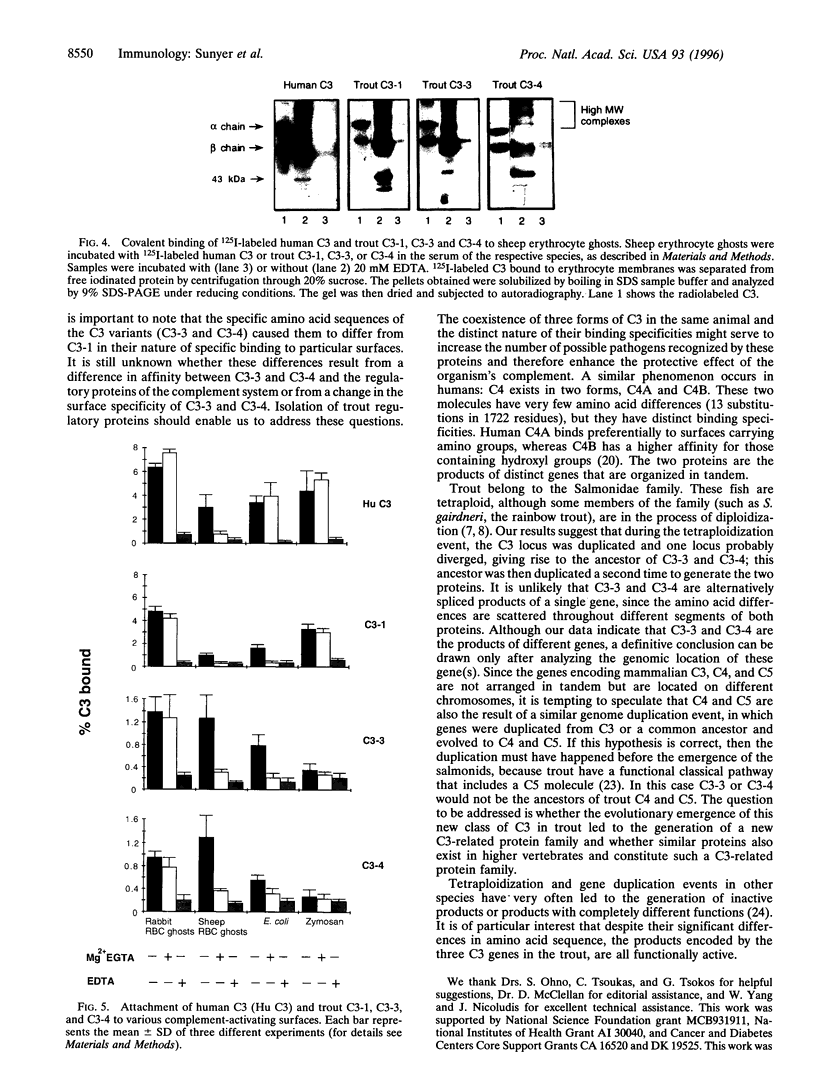

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alsenz J., Avila D., Huemer H. P., Esparza I., Becherer J. D., Kinoshita T., Wang Y., Oppermann S., Lambris J. D. Phylogeny of the third component of complement, C3: analysis of the conservation of human CR1, CR2, H, and B binding sites, concanavalin A binding sites, and thiolester bond in the C3 from different species. Dev Comp Immunol. 1992 Jan-Feb;16(1):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(92)90052-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila D., Lambris J. D. Isolation and characterization of the third complement component of axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum). Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1990;95(4):839–845. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(90)90326-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Law S. K. The complement component C4 of mammals. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):495–502. doi: 10.1042/bj2650495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Activation of the alternative complement pathway due to resistance of zymosan-bound amplification convertase to endogenous regulatory mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1683–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzinger D. C., Bredehorst R., Vogel C. W. Molecular cloning and derived primary structure of cobra venom factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12775–12779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Austen K. F. Phylogeny and function of the complement system. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:309–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Lao Z., Pang J., Alsenz J. Third component of trout complement. cDNA cloning and conservation of functional sites. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6123–6134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. P., Dodds A. W. The thioester bond of C3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;153:73–82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74977-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavroidis M., Sunyer J. O., Lambris J. D. Isolation, primary structure, and evolution of the third component of chicken complement and evidence for a new member of the alpha 2-macroglobulin family. J Immunol. 1995 Mar 1;154(5):2164–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization and function of the complement system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:321–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Iwaki M., Nakai C., Nozaki M., Kaidoh T., Nonaka M., Natsuume-Sakai S., Takahashi M. Purification of a major serum protein of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) homologous to the third component of mammalian complement. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6327–6333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Natsuume-Sakai S., Takahashi M. The complement system in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). II. Purification and characterization of the fifth component (C5). J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1495–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Nonaka M., Irie M., Tanabe K., Kaidoh T., Natsuume-Sakai S., Takahashi M. Identification and characterization of a variant of the third component of complement (C3) in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) serum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Yamaguchi N., Natsuume-Sakai S., Takahashi M. The complement system of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). I. Identification of the serum lytic system homologous to mammalian complement. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1489–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S. Patterns in genome evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Dec;3(6):911–914. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90013-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risinger C., Larhammar D. Multiple loci for synapse protein SNAP-25 in the tetraploid goldfish. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10598–10602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu A., Kozel T. R., Pangburn M. K. Specificity of the thioester-containing reactive site of human C3 and its significance to complement activation. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 1;302(Pt 2):429–436. doi: 10.1042/bj3020429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. A thiol-ester in alpha 2-macroglobulin cleaved during proteinase complex formation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson S., Stanley K. K., Esser A. F. Domain structure, functional activity, and polymerization of trout complement protein C9. Dev Comp Immunol. 1993 Jan-Feb;17(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(93)90016-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]