Abstract
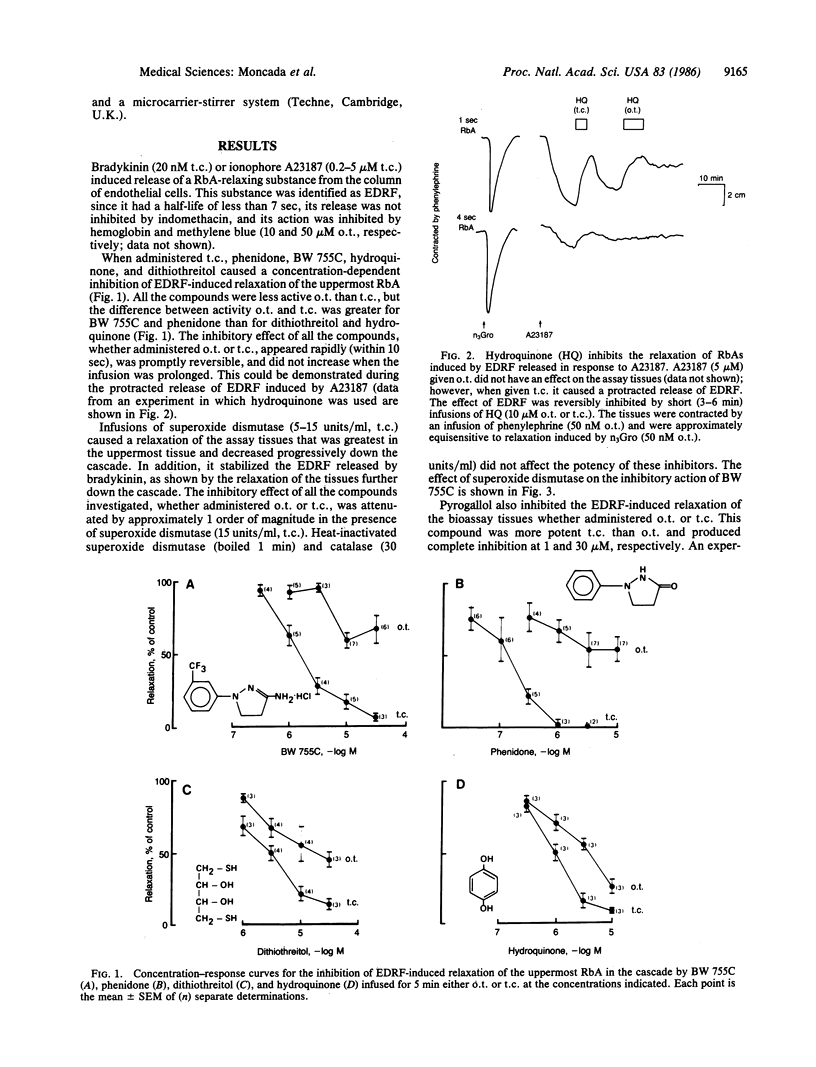
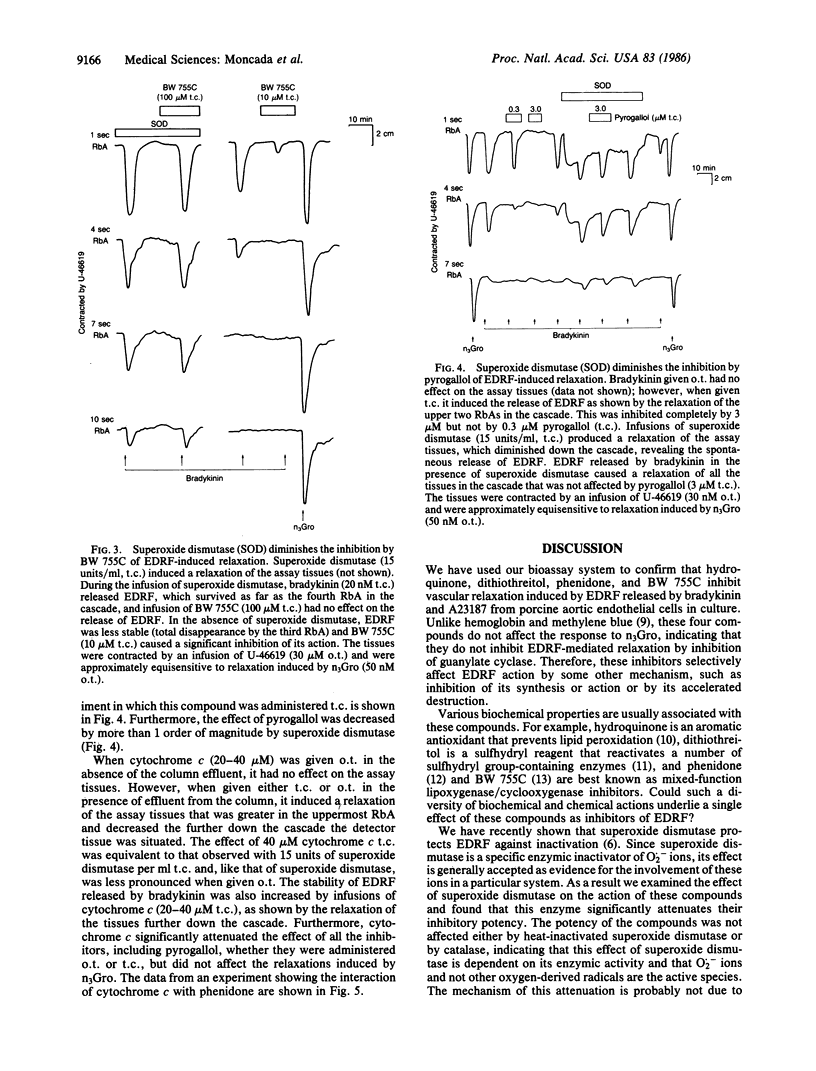
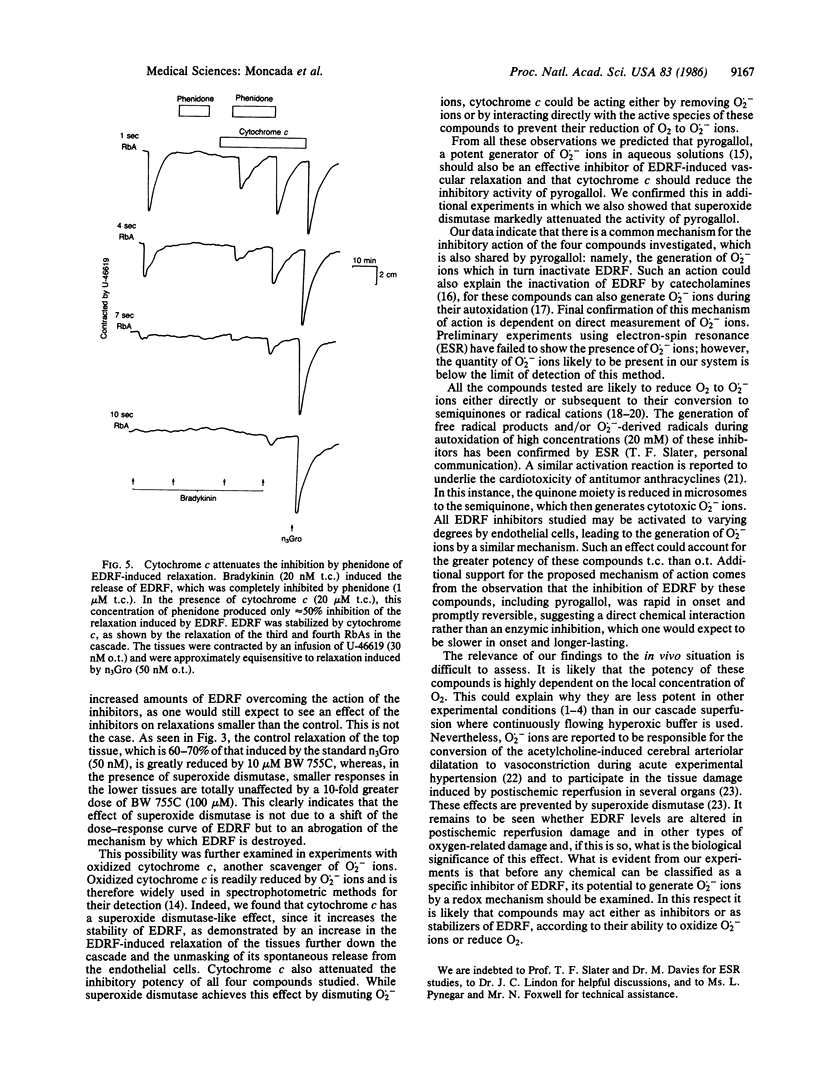
The mechanism of the inhibitory action of phenidone, 3-amino-1-[m-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-pyrazoline (BW 755C), dithiothreitol, hydroquinone, and pyrogallol on the vascular relaxation induced by endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) was investigated. EDRF was released from porcine aortic endothelial cells in culture and bioassayed on a cascade of superfused rabbit aortic strips. These compounds inhibited EDRF-induced relaxation of vascular strips, without affecting the relaxation induced by glyceryl trinitrate, and their inhibitory potency was markedly attenuated (by more than 1 order of magnitude) by the addition of superoxide dismutase (5-15 units/ml) or oxidized cytochrome c (20-40 microM) but not by catalase (30 units/ml) or heat-inactivated superoxide dismutase. These data indicate that the above five inhibitors inactivate EDRF through the formation of superoxide ions, which have recently been shown to destroy EDRF. The inhibition of EDRF by these compounds is therefore attributable to their redox properties rather than to any specific biological action.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J. 1-phenyl-3-pyrazolidone: an inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenase and lipoxygenase pathways in lung and platelets. Prostaglandins. 1978 Sep;16(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. The role of endothelium in the responses of vascular smooth muscle to drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:175–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Edwards D. H., Lewis M. J., Newby A. C., Henderson A. H. The nature of endothelium-derived vascular relaxant factor. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):645–647. doi: 10.1038/308645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Moncada S., Palmer R. M. Bioassay of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) from porcine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):685–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Superoxide anion is involved in the breakdown of endothelium-derived vascular relaxing factor. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):454–456. doi: 10.1038/320454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. The importance of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human diseases. Mol Aspects Med. 1985;8(2):89–193. doi: 10.1016/0098-2997(85)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Flower R. J., Vane J. R. A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;28(12):1959–1961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90651-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S., Marklund G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):469–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marnett L. J., Siedlik P. H., Fung L. W. Oxidation of phenidone and BW755C by prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6957–6964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P., Fridovich I. The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3170–3175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P. Generation of superoxide free radical during the autoxidation of thiols. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Gordon G. R., Kashiwase D., Lown J. W., Yen S. F., Plambeck J. A. Redox activities of antitumor anthracyclines determined by microsomal oxygen consumption and assays for superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical generation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 15;35(8):1309–1323. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A., Abraham N. G., Mullane K. M. Cytochrome P-450-dependent monooxygenase activity and endothelial-dependent relaxations induced by arachidonic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):445–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubanyi G. M., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Bioassay of endothelium-derived relaxing factor(s): inactivation by catecholamines. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 2):H95–101. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.1.H95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer H. A., Peach M. J. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit aorta. II. Inhibition of relaxation stimulated by methacholine and A23187 with antagonists of arachidonic acid metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Sep;226(3):796–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANE J. R. THE USE OF ISOLATED ORGANS FOR DETECTING ACTIVE SUBSTANCES IN THE CIRCULATING BLOOD. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:360–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E. P., Kontos H. A., Christman C. W., DeWitt D. S., Povlishock J. T. Superoxide generation and reversal of acetylcholine-induced cerebral arteriolar dilation after acute hypertension. Circ Res. 1985 Nov;57(5):781–787. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.5.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



