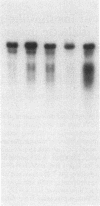
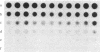
Abstract
The growth and development of the placenta is critical to fetal growth and development; however, little is known regarding the mechanisms controlling placental growth and development. Human placental membranes are known to possess receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II (IGF-I and IGF-II) from early gestation, and increasing evidence supports a major role for IGF-I and/or IGF-II in fetal growth and development. Therefore, the IGFs may also play a significant role in regulating placental growth and development. We report here that an adult human liver IGF-II cDNA hybridizes to poly(A)+ RNAs of human placentas from different gestational ages. There are four placental poly(A)+ RNA species that hybridize to IGF-II cDNA, the major one of which is about 6000 bases. The sizes of the hybridized transcripts are the same for placentas of different gestational ages. Furthermore, the IGF-II sequences expressed in the human placenta were quantitated by dot blot hybridization. The second trimester placenta expresses more IGF-II mRNA sequences than placenta of first trimester and term. Interestingly, the term placentas from diabetic pregnancies also express more of these sequences than those from normal pregnancies. These results suggest that there are developmental changes in the expression of the IGF-II gene in the placenta and that IGF-II may promote placental growth by way of an autocrine and/or paracrine mechanism. Moreover, fetuses developing in diabetic pregnancies receive a large influx of glucose, which in turn may stimulate the expression of IGF-II sequences in placenta, resulting in higher utilization of glucose and overgrowth of placenta. This may explain the macrosomia and high incidence of malformations and stillbirths known to result from pregnancies in diabetics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam P. A., Teramo K., Raiha N., Gitlin D., Schwartz R. Human fetal insulin metabolismearly in gestation. Response to acutelevation of the fetal glucose concentration and placental tranfer of human insulin-I-131. Diabetes. 1969 Jun;18(6):409–416. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.6.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Handwerger S., Rechler M. M. Developmental patterns of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II synthesis and regulation in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):150–153. doi: 10.1038/302150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton I. K., Francis M. J. Response of chondrocytes isolated from human foetal cartilage to plasma somatomedin activity. J Endocrinol. 1978 Mar;76(3):473–477. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0760473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkison P. R., Weidman E. R., Bhaumick B., Bala R. M. Release of somatomedin-like activity by cultured WI-38 human fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1980 Jun;106(6):2006–2012. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-6-2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Gerhard D. S., Fong N. M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Rall L. B. Isolation of the human insulin-like growth factor genes: insulin-like growth factor II and insulin genes are contiguous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Merryweather J. P., Sanchez-Pescador R., Stempien M. M., Priestley L., Scott J., Rall L. B. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding human preproinsulin-like growth factor II. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):775–777. doi: 10.1038/310775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Wilson D. M., Liu F., Nagashima R., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Levels of insulin-like growth factors I and II in human cord blood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Sep;57(3):609–612. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-3-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Applewhite G. T., Underwood L. E. Evidence that somatomedin is synthesized by multiple tissues in the fetus. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar 15;75(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Stiles A. D., Underwood L. E. Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal C. L., Guyda H. J., Lai W. H., Posner B. I. Ontogeny of growth factor receptors in the human placenta. Pediatr Res. 1982 Oct;16(10):820–826. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198210000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa de los Monteros, Driscoll S. G., Steinke J. Insulin release from isolated human fetal pancreatic islets. Science. 1970 May 29;168(3935):1111–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3935.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbe S. G., Quilligan E. J. Fetal carbohydrate metabolism: its clinical importance. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Jan 1;127(1):92–103. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(77)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDRICKS C. H. PATTERNS OF FETAL AND PLACENTAL GROWTH: THE SECOND HALF OF NORMAL PREGNANCY. Obstet Gynecol. 1964 Sep;24:357–365. doi: 10.1097/00006250-196409000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen M., van Schaik F. M., van Tol H., Van den Brande J. L., Sussenbach J. S. Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs encoding precursors of human insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) and an IGF-II variant. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 7;179(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalhan S. C., Schwartz R., Adam P. A. Placental barrier to human insulin-I125 in insulin-dependent diabetic mothers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jan;40(1):139–142. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-1-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K. S., Wang C. Y., Mills N., Gyves M., Ilan J. Insulin-related genes expressed in human placenta from normal and diabetic pregnancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3868–3870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills N. C., Gyves M. T., Ilan J. Comparisons of human placental lactogen mRNA levels from placentas of diabetics and normal term. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Jan;39(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilistine S. J., Moses A. C., Munro H. N. Placental lactogen administration reverses the effect of low-protein diet on maternal and fetal serum somatomedin levels in the pregnant rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5853–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R., Thorsson A. V., Hintz R. L. Increased somatomedin receptor sites in newborn circulating mononuclear cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):456–461. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K., Misaki M., Fryklund L., Christensen N., Wetterberg L. Ontogenesis of somatomedin and insulin receptors in the human fetus. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1084–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI110858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. Metabolic fuels in the foetus. Proc R Soc Med. 1968 Nov;61(11 Pt 2):1231–1236. doi: 10.1177/003591576806111P208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley H. J., Bassett J. M., Milner R. D. Control of carbohydrate metabolism in the fetus and newborn. Br Med Bull. 1975 Jan;31(1):37–43. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood L. E., D'Ercole A. J. Insulin and insulin-like growth factors/somatomedins in fetal and neonatal development. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):69–89. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE P. Pregnancy complicating diabetes. Am J Med. 1949 Nov;7(5):609–616. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(49)90382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman E. R., Bala R. M. Direct mitogenic effects of human somatomedin on human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90372-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson E. M., Crabb D. E., Milner R. D. Cellular development of some human organs before birth. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Aug;47(254):652–655. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.254.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schmid C., Froesch E. R. Biological and immunological properties of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) I and II. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):3–30. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]