Abstract
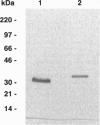
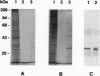
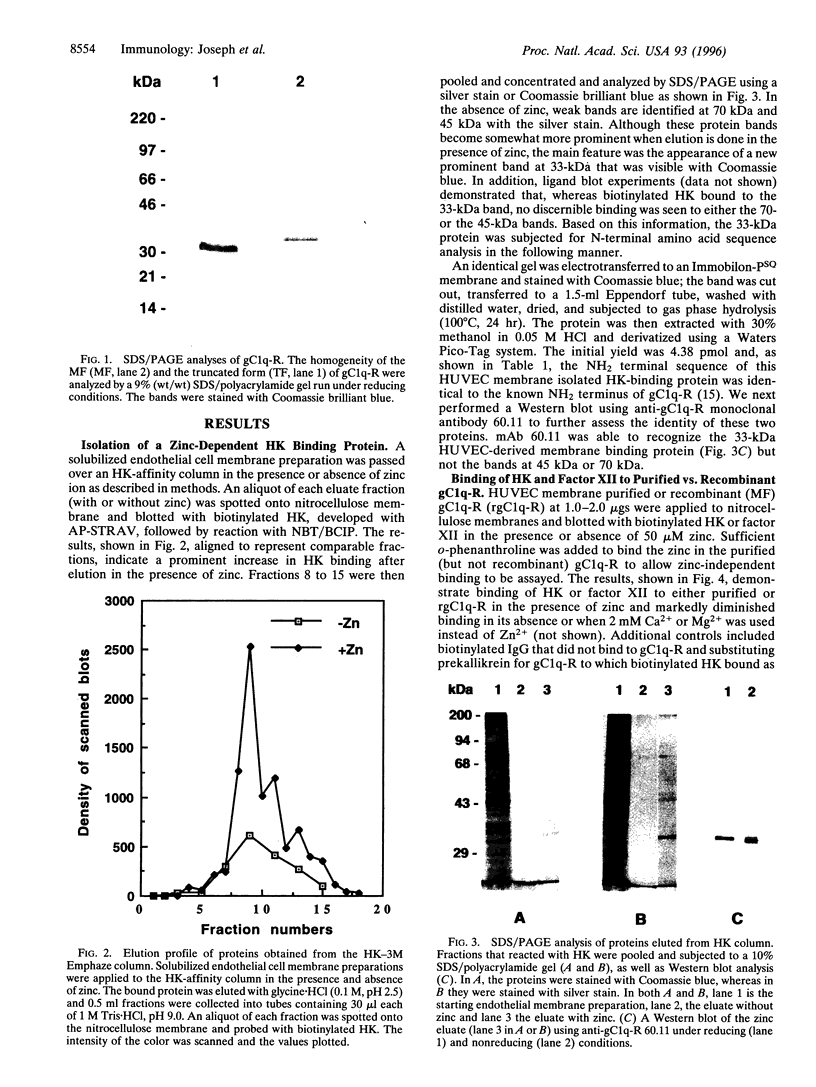
High molecular weight kininogen (HK) and factor XII are known to bind to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in a zinc-dependent and saturable manner indicating that HUVEC express specific binding site(s) for those proteins. However, identification and immunochemical characterization of the putative receptor site(s) has not been previously accomplished. In this report, we have identified a cell surface glycoprotein that is a likely candidate for the HK binding site on HUVECs. When solubilized HUVEC membranes were subjected to an HK-affinity column in the presence or absence of 50 microM ZnCl2 and the bound membrane proteins eluted, a single major protein peak was obtained only in the presence of zinc. SDS/PAGE analysis and silver staining of the protein peak revealed this protein to be 33 kDa and partial sequence analysis matched the NH2 terminus of gC1q-R, a membrane glycoprotein that binds to the globular "heads" of C1q. Two other minor proteins of approximately 70 kDa and 45 kDa were also obtained. Upon analysis by Western blotting, the 33-kDa band was found to react with several monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) recognizing different epitopes on gC1q-R. Ligand and dot blot analyses revealed zinc-dependent binding of biotinylated HK as well as biotinylated factor XII to the isolated 33-kDa HUVEC molecule as well as recombinant gC1q-R. In addition, binding of 125I-HK to HUVEC cells was inhibited by selected monoclonal anti-gC1q-R antibodies. C1q, however, did not inhibit 125I-HK binding to HUVEC nor did those monoclonals known to inhibit C1q binding to gC1q-R. Taken together, the data suggest that HK (and factor XII) bind to HUVECs via a 33-kDa cell surface glycoprotein that appears to be identical to gC1q-R but interact with a site on gC1q-R distinct from that which binds C1q.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrettini M., Schleef R. R., Heeb M. J., Hopmeier P., Griffin J. H. Assembly and expression of an intrinsic factor IX activator complex on the surface of cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19833–19839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLa Cadena R. A., Wyshock E. G., Kunapuli S. P., Schultze R. L., Miller M., Walz D. A., Colman R. W. Platelet thrombospondin interactions with human high and low molecular weight kininogens. Thromb Haemost. 1994 Jul;72(1):125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleton P., Ghebrehiwet B., Sastry K. N., Coburn J. P., Zaner K. S., Reid K. B., Tauber A. I. Identification of a gC1q-binding protein (gC1q-R) on the surface of human neutrophils. Subcellular localization and binding properties in comparison with the cC1q-R. J Clin Invest. 1995 Apr;95(4):1569–1578. doi: 10.1172/JCI117830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B. Functions associated with the C1q receptor. Behring Inst Mitt. 1989 Jul;(84):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Kew R. R., Gruber B. L., Marchese M. J., Peerschke E. I., Reid K. B. Murine mast cells express two types of C1q receptors that are involved in the induction of chemotaxis and chemokinesis. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 1;155(5):2614–2619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghebrehiwet B., Lim B. L., Peerschke E. I., Willis A. C., Reid K. B. Isolation, cDNA cloning, and overexpression of a 33-kD cell surface glycoprotein that binds to the globular "heads" of C1q. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1809–1821. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard J. S., Griffin J. H. Receptors for high molecular weight kininogen on stimulated washed human platelets. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6863–6869. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson E. J., Schmaier A. H., Wachtfogel Y. T., Kaufman N., Kucich U., Colman R. W. Human neutrophils contain and bind high molecular weight kininogen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):28–35. doi: 10.1172/JCI114151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson E. J., Schutsky D., Knight L. C., Schmaier A. H. High molecular weight kininogen binds to unstimulated platelets. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):310–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI112567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan A. A., Cines D. B., Herwald H., Schmaier A. H., Müller-Esterl W. Mapping the cell binding site on high molecular weight kininogen domain 5. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 18;270(33):19256–19261. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.33.19256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan A. A., Cines D. B., Zhang J., Schmaier A. H. The carboxyl terminus of bradykinin and amino terminus of the light chain of kininogens comprise an endothelial cell binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31822–31830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. M., Figueroa C. D., Müller-Esterl W., Bhoola K. D. Assembly of contact-phase factors on the surface of the human neutrophil membrane. Blood. 1994 Jul 15;84(2):474–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herwald H., Dedio J., Kellner R., Loos M., Müller-Esterl W. Isolation and characterization of the kininogen-binding protein p33 from endothelial cells. Identity with the gC1q receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 31;271(22):13040–13047. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.22.13040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herwald H., Hasan A. A., Godovac-Zimmermann J., Schmaier A. H., Müller-Esterl W. Identification of an endothelial cell binding site on kininogen domain D3. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14634–14642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A. Culture of human endothelial cells. Transplant Proc. 1980 Sep;12(3 Suppl 1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandle R. J., Colman R. W., Kaplan A. P. Identification of prekallikrein and high-molecular-weight kininogen as a complex in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4179–4183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni F. J., Gustafson E. J., Schmaier A. H. High molecular weight kininogen binds to platelets by its heavy and light chains and when bound has altered susceptibility to kallikrein cleavage. Blood. 1992 Mar 1;79(5):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Shibayama Y., Kuna P., Calcaterra E., Kaplan A. P., Reddigari S. R. Generation of vasoactive peptide bradykinin from human umbilical vein endothelium-bound high molecular weight kininogen by plasma kallikrein. Blood. 1992 Oct 15;80(8):1980–1988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Malhotra R., Ghebrehiwet B., Reid K. B., Willis A. C., Sim R. B. Isolation of a human endothelial cell C1q receptor (C1qR). J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Feb;53(2):179–184. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I., Reid K. B., Ghebrehiwet B. Identification of a novel 33-kDa C1q-binding site on human blood platelets. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5896–5901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri R. N., Zhou F., Hu C. J., Colman R. F., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen inhibits thrombin-induced platelet aggregation and cleavage of aggregin by inhibiting binding of thrombin to platelets. Blood. 1991 Feb 1;77(3):500–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddigari S. R., Kuna P., Miragliotta G., Shibayama Y., Nishikawa K., Kaplan A. P. Human high molecular weight kininogen binds to human umbilical vein endothelial cells via its heavy and light chains. Blood. 1993 Mar 1;81(5):1306–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddigari S. R., Shibayama Y., Brunnée T., Kaplan A. P. Human Hageman factor (factor XII) and high molecular weight kininogen compete for the same binding site on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11982–11987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaier A. H., Kuo A., Lundberg D., Murray S., Cines D. B. The expression of high molecular weight kininogen on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16327–16333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait J. F., Fujikawa K. Primary structure requirements for the binding of human high molecular weight kininogen to plasma prekallikrein and factor XI. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11651–11656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. E., Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Association of factor XI and high molecular weight kininogen in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1376–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI108898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. E., Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Characterization of human high molecular weight kininogen. Procoagulant activity associated with the light chain of kinin-free high molecular weight kininogen. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):488–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtfogel Y. T., DeLa Cadena R. A., Kunapuli S. P., Rick L., Miller M., Schultze R. L., Altieri D. C., Edgington T. S., Colman R. W. High molecular weight kininogen binds to Mac-1 on neutrophils by its heavy chain (domain 3) and its light chain (domain 5). J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19307–19312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins R. C., Bouma B. N., Cochrane C. G., Griffin J. H. Role of high-molecular-weight kininogen in surface-binding and activation of coagulation Factor XI and prekallikrein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4636–4640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iwaarden F., de Groot P. G., Bouma B. N. The binding of high molecular weight kininogen to cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4698–4703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]