Abstract
In the immune system, T-lymphocyte proliferation depends on interleukin 2 [IL-2 (T-cell growth factor)] interaction with specific receptors. In this study we show that IL-2 can specifically inhibit the proliferation of neonatal rat oligodendrocyte progenitor cells cultured in a serumless, chemically defined medium (oligodendrocyte-defined medium; ODM). IL-2 inhibited both [3H]thymidine incorporation and increase in cell number. Specificity was shown by precipitating IL-2 activity with anti-IL-2 antiserum. Furthermore, growth inhibition depended on the expression of Tac (an anti-IL-2 receptor monoclonal antibody)-positive receptors (IL-2 receptor). When cells were cultured in the presence of IL-2, both Tac-positive staining and growth inhibition were no longer expressed. The addition of interleukin 1 had no effect on [3H]thymidine incorporation or changes in cell number. However, when IL-1 was subsequently added together with IL-2, Tac expression and IL-2-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation was induced. This inhibitory effect was not due to a sensitive subpopulation because greater than 90% of the culture was Tac positive. Taken together, these data show that IL-2 can specifically inhibit oligodendrocyte proliferation and acts via Tac-positive receptors.
Full text
PDF
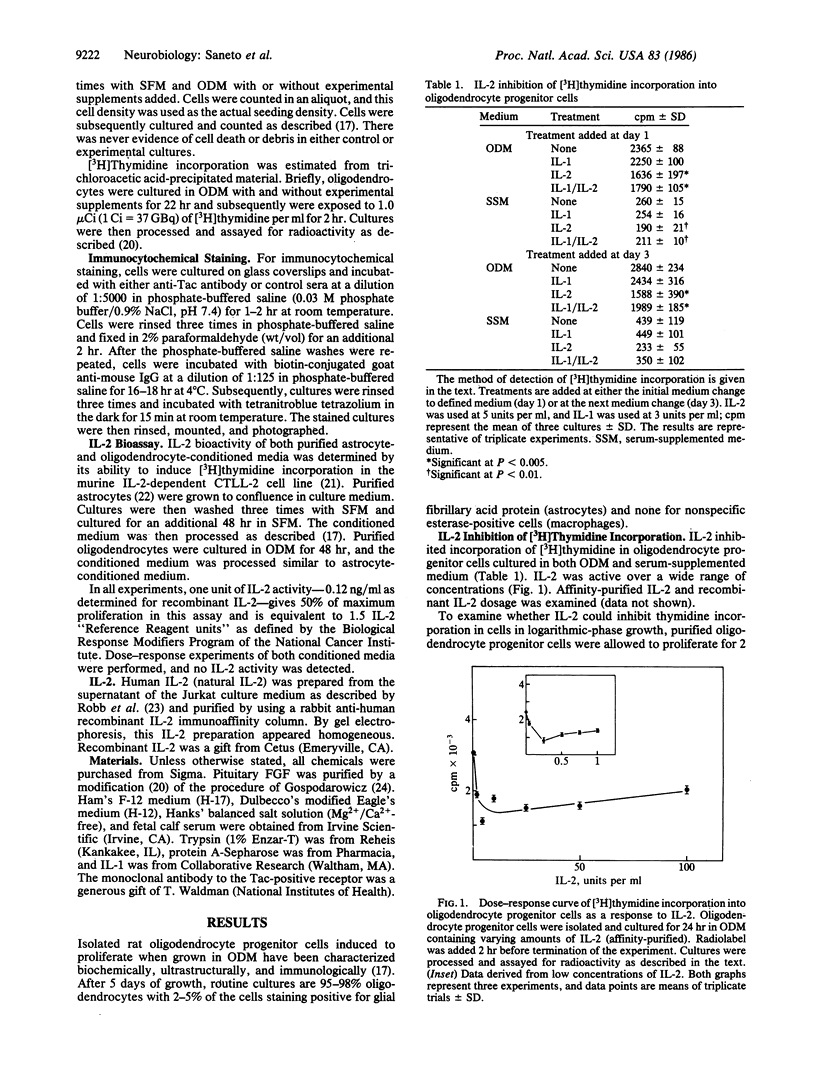



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abney E. R., Bartlett P. P., Raff M. C. Astrocytes, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes develop on schedule in dissociated cell cultures of embryonic rat brain. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90476-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenella L. S., Herndon R. M. Mature oligodendrocytes. Division following experimental demyelination in adult animals. Arch Neurol. 1984 Nov;41(11):1162–1165. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050220060015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste E. N., Merrill J. E., Kaufman S. E., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Purification and characterization of a human T-lymphocyte-derived glial growth-promoting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3930–3934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Harbour-McMenamin D., Smith E. M. Peptide hormones shared by the neuroendocrine and immunologic systems. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):858s–861s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman S. C., Schwartz J. M., Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Feldman J. D. beta-Endorphin enhances lymphocyte proliferative responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4226–4230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Baker T. J. Peptides released by ameboid microglia regulate astroglial proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2411–2415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 stimulation of astroglial proliferation after brain injury. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3872478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Purification of a fibroblast growth factor from bovine pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2515–2520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Minamoto S., Uchiyama T., Hardy R. R., Yamada G., Taniguchi T. Reconstitution of functional receptor for human interleukin-2 in mouse cells. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):467–470. doi: 10.1038/318467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Brenner M. B., McLean J. M., Strominger J. L. Antigenic stimulation regulates the level of expression of interleukin 2 receptor on human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Smith E. M., Torres B. A., Blalock J. E. Regulation of the in vitro antibody response by neuroendocrine hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4171–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Braciale V. L., Braciale T. J. Antigen-dependent regulation of interleukin 2 receptor expression on cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1966–1969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Andrus L., Prowse S. J. Role of lymphokine and antigen in the control of specific T cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:279–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Robb R. J., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Characterization of the human receptor for T-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6957–6961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveille P. J., McGinnis J. F., Maxwell D. S., de Vellis J. Immunocytochemical localization of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in rat oligodendrocytes. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 8;196(2):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer H. R. Potential pitfalls of [3H]thymidine techniques to measure cell proliferation. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1981 Mar;14(2):111–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1981.tb00516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. D., de Vellis J. Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):890–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Kutsunai S., Mohlstrom C., Hofman F., Groopman J., Golde D. W. Proliferation of astroglia and oligodendroglia in response to human T cell-derived factors. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1428–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.6610212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Cantrell D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Smith K. A., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex results in clonal T-cell proliferation through an interleukin 2-dependent autocrine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W., Kwon E. E., Sternberger N. H., Lennon V. A. The distribution of myelin-associated glycoprotein and myelin basic protein in actively demyelinating multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuroimmunol. 1984 Jul;6(4):251–264. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(84)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Miller R. H., Noble M. A glial progenitor cell that develops in vitro into an astrocyte or an oligodendrocyte depending on culture medium. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):390–396. doi: 10.1038/303390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Barnett L. B., Brown A., Behar T., McFarlin D. E. Neuropathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in inbred strains of mice. Lab Invest. 1980 Aug;43(2):150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg-Wollheim M. Lymphocyte populations in the cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood of patients with multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis. Scand J Immunol. 1983 Jun;17(6):575–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1983.tb00826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saneto R. P., de Vellis J. Characterization of cultured rat oligodendrocytes proliferating in a serum-free, chemically defined medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3509–3513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saneto R. P., de Vellis J. Effect of mitogens in various organs and cell culture conditioned media on rat oligodendrocytes. Dev Neurosci. 1985;7(5-6):340–350. doi: 10.1159/000112301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Favata M. F., Oroszlan S. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to human interleukin 2: strategy and tactics. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1808–1815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szuchet S., Stefansson K., Wollmann R. L., Dawson G., Arnason B. G. Maintenance of isolated oligodendrocytes in long-term culture. Brain Res. 1980 Oct 27;200(1):151–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple S., Raff M. C. Clonal analysis of oligodendrocyte development in culture: evidence for a developmental clock that counts cell divisions. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):773–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90843-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Reinherz E. L., Raine C. S. Multiple sclerosis: distribution of T cell subsets within active chronic lesions. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.6217550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Hardt C., Heeg K., Pfizenmaier K., Solbach W., Bartlett R., Stockinger H., Röllinghoff M. T-T cell interactions during cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses: T cell derived helper factor (Interleukin 2) as a probe to analyze CTL responsiveness and thymic maturation of CTL progenitors. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:215–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. Mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):104–105. doi: 10.1038/318104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A. M., Harford J. B., Svetlik P. B., Leonard W. L., Depper J. M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C., Klausner R. D. Only high-affinity receptors for interleukin 2 mediate internalization of ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1463–1466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. A., Hart D. N., Fabre J. W., Morris P. J. Distribution and quantitation of HLA-ABC and DR (Ia) antigens on human kidney and other tissues. Transplantation. 1980 Apr;29(4):274–279. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198004000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., Battye F., Schrader J. W. Inducible expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):688–691. doi: 10.1038/310688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]