Abstract
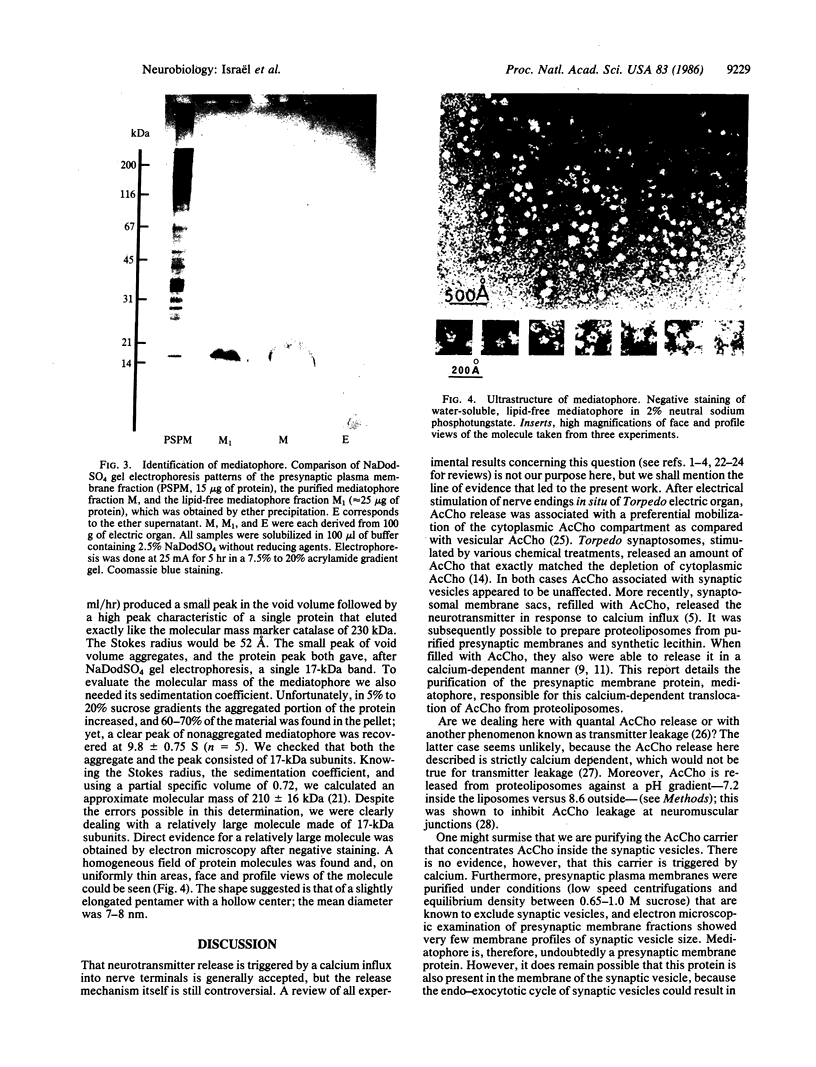
A protein, which we call "mediatophore," that mediates calcium-dependent release of acetylcholine from proteoliposomes has been purified from the presynaptic plasma membrane. About 250 micrograms of this material was obtained from 500 g of Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Precipitation of the protein and subsequent removal of associated lipids inactivated the protein, which then became water soluble; this permitted evaluation of its Stokes radius (52 A) and its sedimentation coefficient (9.8 +/- 0.75 S) and, hence, an approximate molecular mass of 210 +/- 16 kDa could be determined. PAGE analysis showed that the protein is made of 17-kDa subunits, not linked by disulfide bonds. When this material was observed by electron microscopy after negative staining, the apparently pentameric structures had an average diameter of about 7 nm.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birman S., Israël M., Lesbats B., Morel N. Solubilization and partial purification of a presynaptic membrane protein ensuring calcium-dependent acetylcholine release from proteoliposomes. J Neurochem. 1986 Aug;47(2):433–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb04520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P. Vesicle hypothesis of the release of quanta of acetylcholine. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):396–441. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducis I., Whittaker V. P. High-affinity, sodium-gradient-dependent transport of choline into vesiculated presynaptic plasma membrane fragments from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata and reconstitution of the solubilized transporter into liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 26;815(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Gautron J., Israël M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R. Evolution de la décharge de l'organe électrique de la Torpille et variations simultanées de l'acétylcholine au cours de la stimulation. J Neurochem. 1974 Oct;23(4):635–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Israël M. The release of acetylcholine. Sci Am. 1985 Apr;252(4):58–66. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0485-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Dolezal V., Tucek S., Zemková H., Vyskocil F. Is an acetylcholine transport system responsible for nonquantal release of acetylcholine at the rodent myoneural junction? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M. Proteolipides, a new type of tissue lipoproteins; their isolation from brain. J Biol Chem. 1951 Aug;191(2):807–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch-Pi J., Stoffyn P. J. Proteolipids from membrane systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:86–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helynck G., Luu B., Nussbaum J. L., Picken D., Skalidis G., Trifilieff E., Van Dorsselaer A., Seta P., Sandeaux R., Gavach C. Brain proteolipids. Isolation, purification and effect on ionic permeability of membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;133(3):689–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M., Dunant Y., Manaranche R. The present status of the vesicular hypothesis. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;13(3):237–275. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël M., Lesbats B. Continuous determination by a chemiluminescent method of acetylcholine release and compartmentation in Torpedo electric organ synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1981 Dec;37(6):1475–1483. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb06317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R. ACh release from osmotically shocked synaptosomes refilled with transmitter. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):474–475. doi: 10.1038/294474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël M., Lesbats B., Morel N., Manaranche R., Gulik-Krzywicki T., Dedieu J. C. Reconstitution of a functional synaptosomal membrane possessing the protein constituents involved in acetylcholine translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):277–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Transmitter leakage from motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Feb 11;196(1122):59–72. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B., Deutsch J. W., Carlson S. S., Wagner J. A. Biochemistry of neurotransmitter release. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:399–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. G., Marchbanks R. M. The incorporation of solubilized choline-transport activity into liposomes. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):565–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2040565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. M., Cooper J. R. High affinity choline uptake and calcium-dependent acetylcholine release in proteoliposomes derived from rat cortical synaptosomes. J Neurosci. 1983 May;3(5):987–994. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-05-00987.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel N., Marsal J., Manaranche R., Lazereg S., Mazie J. C., Israel M. Large-scale purification of presynaptic plasma membranes from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1757–1762. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel N., Thieffry M., Manaranche R. Binding of a Glycera convoluta neurotoxin to cholinergic nerve terminal plasma membranes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1737–1744. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Eytan E., Notsani B. E., Sigrist H., Sigrist-Nelson K., Gitler C. Isolation of a chloroplast N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding proteolipid, active in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2375–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. A simple assay for the study of solubilized acetylcholine receptors. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauc L. Non vesicular release of neurotransmitter. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jul;62(3):857–893. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.3.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Vyskocil F. Changes in total and quantal release of acetylcholine in the mouse diaphragm during activation and inhibition of membrane ATPase. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:1–14. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas S., O'Regan S. Reconstitution of carrier-mediated choline transport in proteoliposomes prepared from presynaptic membranes of Torpedo electric organ, and its internal and external ionic requirements. J Membr Biol. 1985;85(2):111–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01871264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Vesicle recycling and transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1979;4(12):1773–1804. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]