Abstract
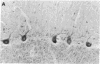
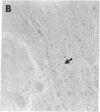
An endogenous brain substance that binds to the central-type benzodiazepine receptors with agonist properties is present in both rat and bovine brains. This substance has been purified to homogeneity from bovine brain by immunoaffinity chromatography on immobilized monoclonal anti-benzodiazepine antibody followed by gel filtration on Sephadex G-25 and two reversed-phase HPLC steps. The purified substance was characterized as the benzodiazepine N-desmethyldiazepam (nordiazepam). The techniques used for the identification were mass spectrometry, HPLC, spectrophotometry, benzodiazepine receptor binding, and immunological techniques. Benzodiazepine-like immunoreactivity was also found in all the human brains tested, including six brains that had been stored in paraffin since 1940, fifteen years before the first synthesis of benzodiazepines. These results show that benzodiazepine-like molecules of natural origin--and possibly benzodiazepines themselves--are present in human and other mammalian brains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Costa E., Ferrero P., Fujimoto M., Cosenza-Murphy D., Guidotti A. Diazepam-binding inhibitor: a neuropeptide located in selected neuronal populations of rat brain. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):179–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3892688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda M. G., Ferrari M., Guidotti A., Konkel D., Costa E. Isolation, purification and partial sequence of a neuropeptide (diazepam-binding inhibitor) precursor of an anxiogenic putative ligand for benzodiazepine recognition site. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 29;47(3):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90533-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Corda M. G., Guidotti A. On a brain polypeptide functioning as a putative effector for the recognition sites of benzodiazepine and beta-carboline derivatives. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Dec;22(12B):1481–1492. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Ferrari M., Ferrero P., Guidotti A. Multiple signals in GABAergic transmission: pharmacological consequences. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Aug;23(8):989–991. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Blas A. L., Sangameswaran L., Haney S. A., Park D., Abraham C. J., Jr, Rayner C. A. Monoclonal antibodies to benzodiazepines. J Neurochem. 1985 Dec;45(6):1748–1753. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb10530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Blas A., Kuljis R. O., Cherwinski H. M. Mammalian brain antigens defined by monoclonal antibodies. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 26;322(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnerer J., Oka K., Brossi A., Rice K. C., Spector S. Presence and formation of codeine and morphine in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4566–4567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero P., Guidotti A., Conti-Tronconi B., Costa E. A brain octadecaneuropeptide generated by tryptic digestion of DBI (diazepam binding inhibitor) functions as a proconflict ligand of benzodiazepine recognition sites. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Nov;23(11):1359–1362. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R., Gershon M. D., Spector S. A nonpeptide morphine-like compound: immunocytochemical localization in the mouse brain. Science. 1978 Jan 27;199(4327):447–448. doi: 10.1126/science.339350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintzler A. R., Levy A., Spector S. Antibodies as a means of isolating and characterizing biologically active substances: presence of a non-peptide, morphine-like compound in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Barrett R. W., James I. F., Lowney L. I., Weitz C. J., Knipmeyer L. L., Rapoport H. Morphine and other opiates from beef brain and adrenal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5203–5207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazum E., Sabatka J. J., Chang K. J., Brent D. A., Findlay J. W., Cuatrecasas P. Morphine in cow and human milk: could dietary morphine constitute a ligand for specific morphine (mu) receptors? Science. 1981 Aug 28;213(4511):1010–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.6267691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka K., Kantrowitz J. D., Spector S. Isolation of morphine from toad skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1852–1854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangameswaran L., de Blas A. L. Demonstration of benzodiazepine-like molecules in the mammalian brain with a monoclonal antibody to benzodiazepines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Blas A. L. Monoclonal antibodies to specific astroglial and neuronal antigens reveal the cytoarchitecture of the Bergmann glia fibers in the cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):265–273. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00265.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]