Abstract
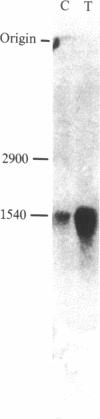
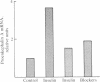
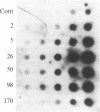
The effect of reflex splanchnic nerve stimulation on proenkephalin A biosynthesis was investigated in the rat adrenal medulla. Tissue levels of native [Met5]enkephalin-like immunoreactivity (IR) (measured by direct RIA of tissue extracts), cryptic [Met5]enkephalin-like IR (calculated as the increase in [Met5]enkephalin-like IR detected in tissue extracts after sequential digestion with trypsin and carboxypeptidase B), and proenkephalin A mRNA were determined in adrenal medulla from rats sacrificed at various times after a period of insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Two hours of insulin hypoglycemia, which produced intense reflex stimulation of the splanchnic nerves as evidenced by a 55% decrease in the adrenal medulla catecholamine levels, resulted in a 3-fold increase in proenkephalin A mRNA levels in this tissue. The proenkephalin A mRNA levels reached a maximum 15-fold increase over control values 24 hr after this period of hypoglycemic stress and then gradually declined with an approximate half-life of 4 days. Native and cryptic [Met5]enkephalin-like IR had increased 9-fold and 12-fold, respectively, 24 hr after this period of hypoglycemia, and both demonstrated maximum increases of 130-fold and 50-fold, respectively, after 96 hr. Combined pretreatment (i.p. administration) with the ganglionic and muscarinic blocking agents chlorisondamine (5 mg/kg of body weight) and atropine (1 mg/kg) blocked the increase in levels of proenkephalin A mRNA seen in the rat adrenal medulla following insulin hypoglycemia. These data indicate that reflex splanchnic nerve discharge stimulates proenkephalin biosynthesis, probably at the level of gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupo A., Pontarotti P. A., Jarry T., Delaage M. A new immunological approach to the detection and the quantitation of the Met5-enkephalin precursors in rat brain. Neuropeptides. 1984 Sep;4(5):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Yang H. Y., Fratta W., Costa E. Rat striatal methionine-enkephalin content after chronic treatment with cataleptogenic and noncataleptogenic antischizophrenic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Apr;205(1):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamatsu T., Obie J., Grimes L., McGinty J. F., Yoshikawa K., Sabol S., Hong J. S. Kainic acid alters the metabolism of Met5-enkephalin and the level of dynorphin A in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):3094–3102. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-03094.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Howells R. D., Fleminger G., Udenfriend S. Denervation of rat adrenal glands markedly increases preproenkephalin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7221–7223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGamma E. F., Adler J. E., Black I. B. Impulse activity differentially regulates [Leu]enkephalin and catecholamine characters in the adrenal medulla. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1102–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.6144183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGamma E. F., White J. D., Adler J. E., Krause J. E., McKelvy J. F., Black I. B. Depolarization regulates adrenal preproenkephalin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8252–8255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Stern A. S., Kilpatrick D. L., Gerber L. D., Rossier J., Stein S., Udenfriend S. Marked increases in large enkephalin-containing polypeptides in the rat adrenal gland following denervation. J Neurosci. 1981 Jan;1(1):80–82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-01-00080.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liston D., Patey G., Rossier J., Verbanck P., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Processing of proenkephalin is tissue-specific. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):734–737. doi: 10.1126/science.6547780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Schwartz J. P., Costa E. Use of mRNA hybridization and radioimmunoassay to study mechanisms of drug-induced accumulation of enkephalins in rat brain structures. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;28(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quach T. T., Tang F., Kageyama H., Mocchetti I., Guidotti A., Meek J. L., Costa E., Schwartz J. P. Enkephalin biosynthesis in adrenal medulla. Modulation of proenkephalin mRNA content of cultured chromaffin cells by 8-bromo-adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):255–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabol S. L., Liang C. M., Dandekar S., Kranzler L. S. In vitro biosynthesis and processing of immunologically identified methionine-enkephalin precursor protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2697–2704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. E., Eiden L. E., Affolter H. U. Elevated potassium stimulates enkephalin biosynthesis in bovine chromaffin cells. Neuropeptides. 1985 Dec;6(6):543–552. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Wilson S. P. The adrenal chromaffin cell as a model to study the co-secretion of enkephalins and catecholamines. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Jan;7(1):41–58. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Abou-Donia M. M., Chang K. J., Viveros O. H. Reserpine increases opiate-like peptide content and tyrosine hydroxylase activity in adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in culture. Neuroscience. 1981;6(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90244-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Chang K. J., Viveros O. H. Proportional secretion of opioid peptides and catecholamines from adrenal chromaffin cells in culture. J Neurosci. 1982 Aug;2(8):1150–1156. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-08-01150.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Unsworth C. D., Viveros O. H. Regulation of opioid peptide synthesis and processing in adrenal chromaffin cells by catecholamines and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Neurosci. 1984 Dec;4(12):2993–3001. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-12-02993.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Hong J. S., Sabol S. L. Electroconvulsive shock increases preproenkephalin messenger RNA abundance in rat hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):589–593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Williams C., Sabol S. L. Rat brain preproenkephalin mRNA. cDNA cloning, primary structure, and distribution in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14301–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]