Abstract
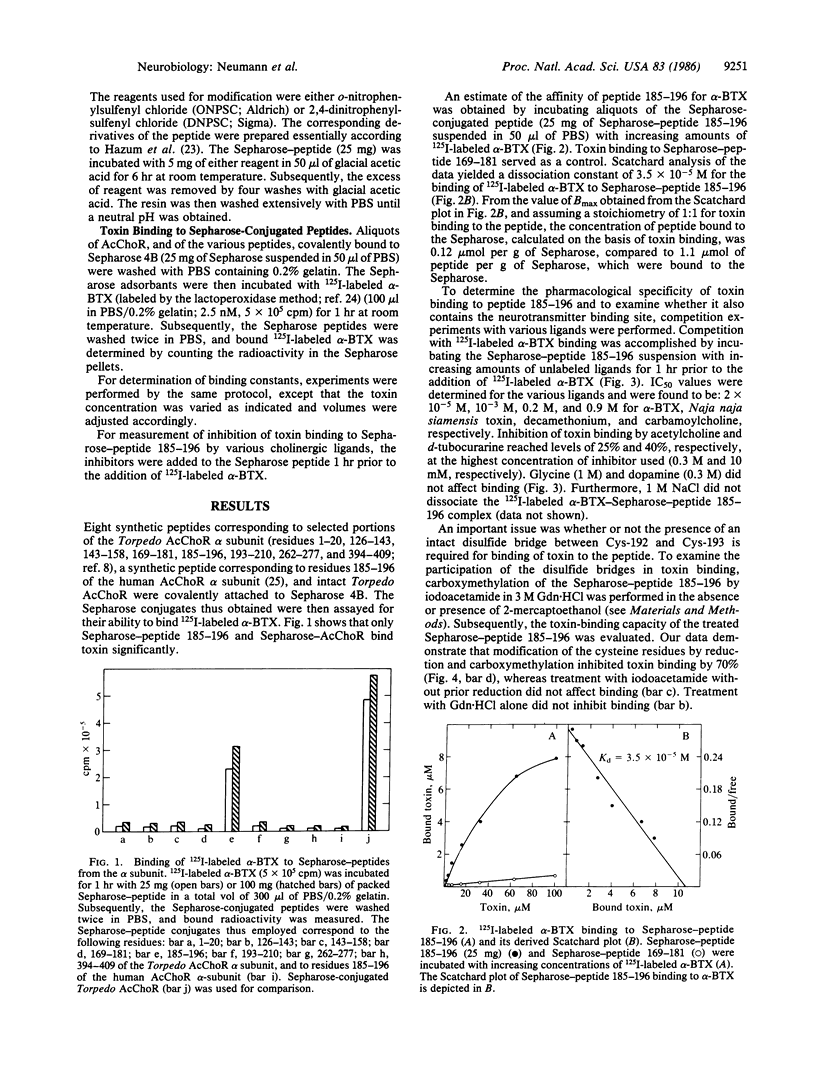
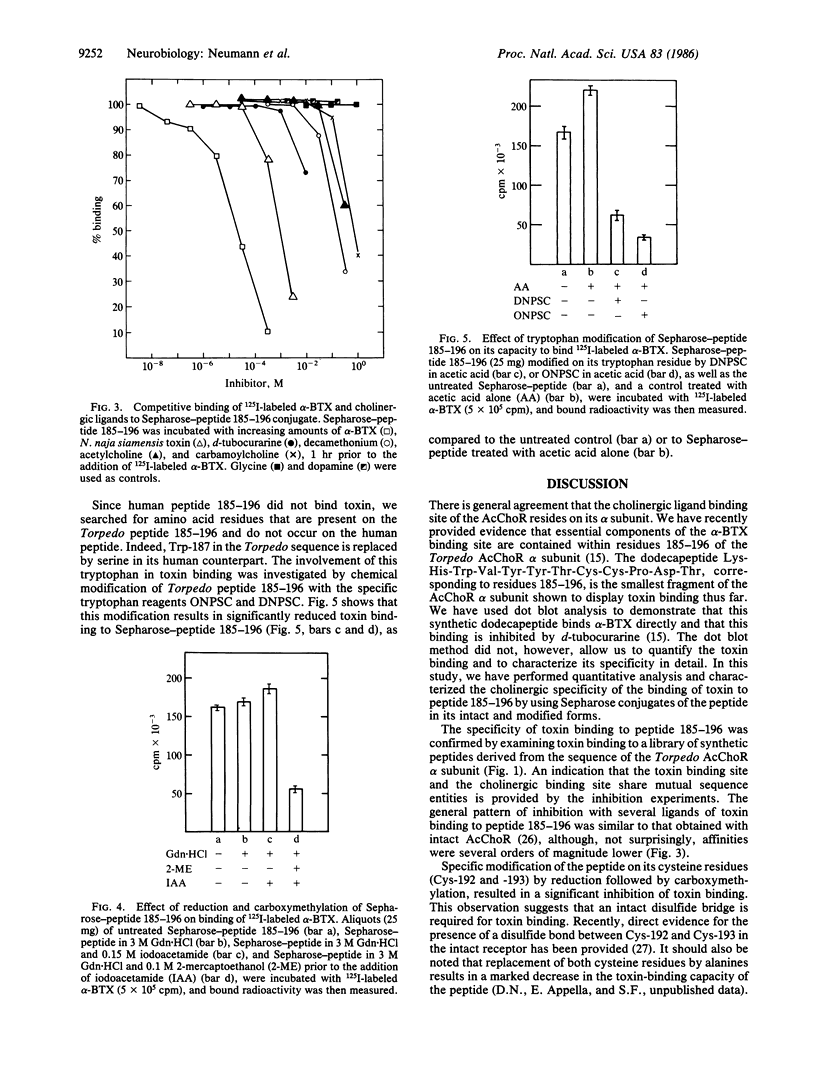
A synthetic dodecapeptide corresponding to residues 185-196 of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit, which contains the adjacent cysteine residues at positions 192 and 193, was recently shown by us to contain the essential elements for alpha-bungarotoxin binding. In the present study, we have used Sepharose-linked peptides for quantitative analysis of the cholinergic binding properties of this and other synthetic peptides. Sepharose-linked peptides corresponding to residues 1-20, 126-143, 143-158, 169-181, 185-196, 193-210, and 394-409 of the alpha subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor, as well as a peptide corresponding to residues 185-196 of the alpha subunit of human acetylcholine receptor, were tested for their toxin-binding capacity. Of these immobilized peptides, only peptide 185-196 of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor bound toxin significantly, thus verifying that this synthetic peptide contains essential components of the receptor toxin-binding site. Analysis of toxin binding to the peptide yielded a dissociation constant of 3.5 X 10(-5) M. This binding was inhibited by various cholinergic ligands. The inhibition potency obtained was alpha-bungarotoxin greater than Naja naja siamensis toxin greater than d-tubocurarine greater than decamethonium greater than acetylcholine greater than carbamoylcholine. This pharmacological profile resembles that of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and therefore suggests that the synthetic dodecapeptide also includes the neurotransmitter binding site. Reduction and carboxymethylation of the cysteine residues on peptide 185-196 inhibit its capacity to bind toxin, demonstrating that an intact disulfide is required for toxin binding. A decrease in toxin binding was also obtained following chemical modification of the tryptophan residue at position 187, thus implying its possible involvement in toxin binding. The failure to detect binding of toxin to the corresponding human sequence 185-196, in which the tryptophan residue is replaced by serine, supports this hypothesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonov A., Tarrab-Hazdai R., Silman I., Fuchs S. Immunochemical studies on acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Immunochemistry. 1977 Feb;14(2):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballivet M., Nef P., Stalder R., Fulpius B. Genomic sequences encoding the alpha-subunit of acetylcholine receptor are conserved in evolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):83–87. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfeld D., Fuchs S. Specific immunosuppression of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis by denatured acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Evans K., Goldman D., Martin G., Treco D., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a possible neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):368–374. doi: 10.1038/319368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Luyten W., Evans K., Mason P., Ballivet M., Goldman D., Stengelin S., Martin G., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a clone coding for the alpha-subunit of a mouse acetylcholine receptor. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2545–2552. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill S., Schmidt J. An immunochemical approach to the identification of the MBTA binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):602–608. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Devillers-Thiéry A., Chemouilli P. Acetylcholine receptor: an allosteric protein. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1335–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.6382611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Hawrot E., Lentz T. L. Binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to isolated alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica: quantitative analysis with protein blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4973–4977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Froehner S. C. Restoration of 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity to the alpha subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor isolated by gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8294–8297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazum E., Fridkin M., Meidan R., Koch Y. On the role of tryptophan in luteinizing-hormone-releasing hormone (luliberin). Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep 15;79(1):269–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Dwork A. J., Kaldany R. R., Silver M. L., Wideman J., Stein S., Karlin A. Identification of the alpha subunit half-cystine specifically labeled by an affinity reagent for the acetylcholine receptor binding site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11662–11665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. J., Atassi M. Z. Localization and synthesis of the acetylcholine-binding site in the alpha-chain of the Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):995–1000. doi: 10.1042/bj2240995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Automated synthesis of peptides. Science. 1965 Oct 8;150(3693):178–185. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3693.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi M. Y., Lennon V. A. Evidence for structural dissimilarity in the neurotransmitter binding region of purified acetylcholine receptors from human muscle and Torpedo electric organ. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):76–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulac-Jericevic B., Atassi M. Z. Segment alpha 182-198 of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor contains second toxin-binding region and binds anti-receptor antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 7;199(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Barchan D., Safran A., Gershoni J. M., Fuchs S. Mapping of the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site within the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3008–3011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Gershoni J. M., Fridkin M., Fuchs S. Antibodies to synthetic peptides as probes for the binding site on the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3490–3493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Tanabe T., Shimizu S., Kikyotani S., Kayano T., Hirose T., Inayama S. Cloning and sequence analysis of calf cDNA and human genomic DNA encoding alpha-subunit precursor of muscle acetylcholine receptor. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):818–823. doi: 10.1038/305818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblas B., Boyd N. D., Singer R. H. Analysis of receptor-ligand interactions using nitrocellulose gel transfer: application to Torpedo acetylcholine receptor and alpha-bungarotoxin. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Changeux J. P. High affinity binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to the purified alpha-subunit and to its 27,000-dalton proteolytic peptide from Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor. Requirement for sodium dodecyl sulfate. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):381–387. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. T., Gershoni J. M., Hawrot E., Lentz T. L. Binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to proteolytic fragments of the alpha subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor analyzed by protein transfer on positively charged membrane filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2553–2557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. T., Lentz T. L., Hawrot E. Determination of the primary amino acid sequence specifying the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site on the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8790–8794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



