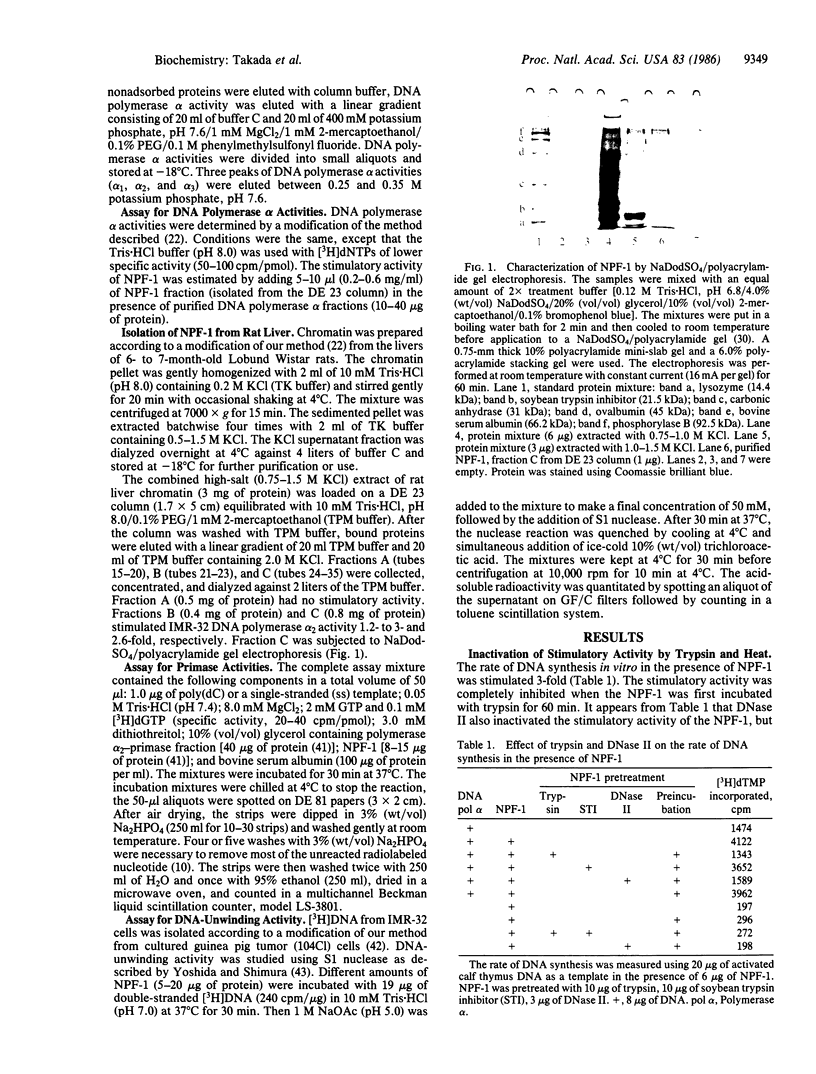
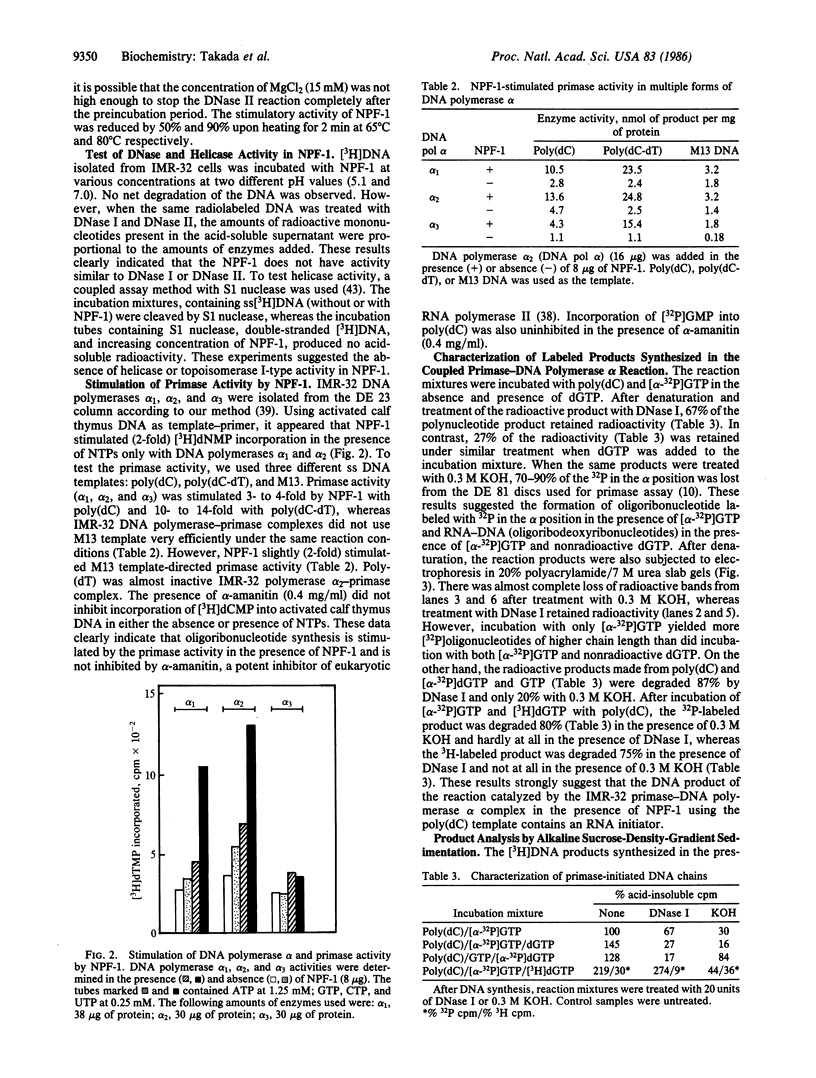
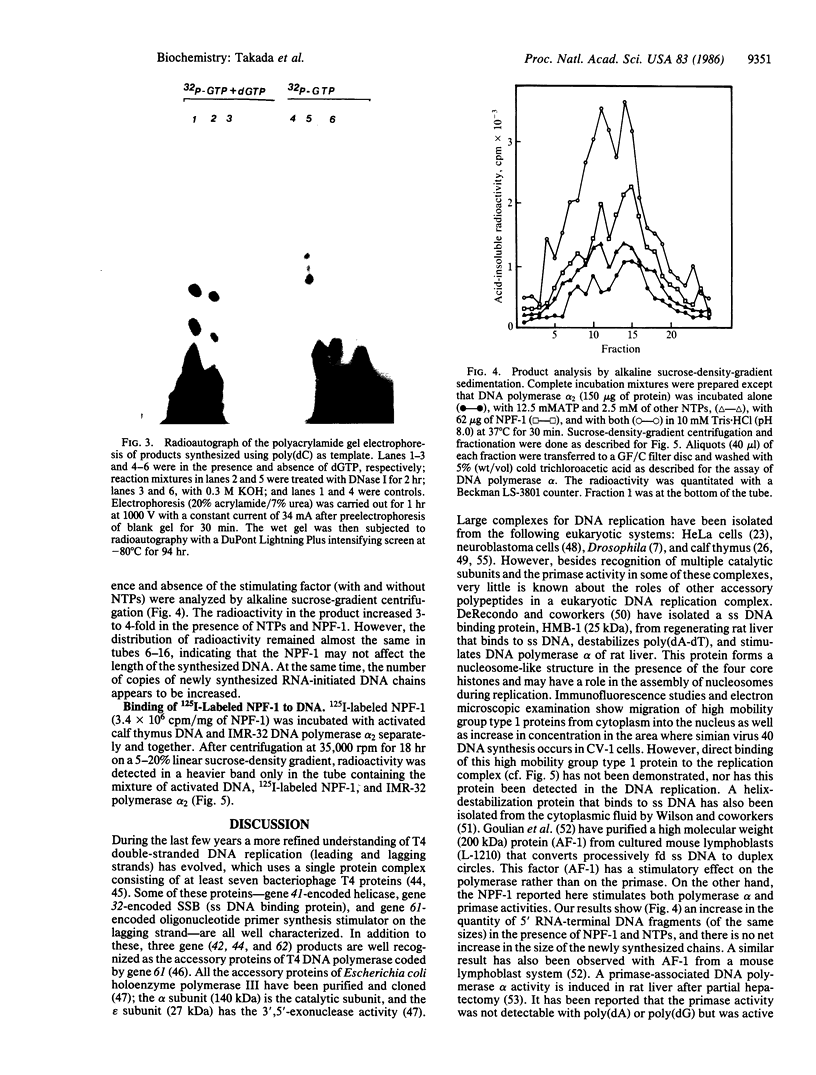
Abstract
Nuclear protein factor type 1 (NPF-1) that simulates IMR-32 primase-associated DNA polymerase alpha 1 and alpha 2 activities has been purified from a high-salt extract of liver chromatin from 6-month-old rats. The final purified factor lacks DNA polymerase alpha, RNA polymerase, and DNA-unwinding or topoisomerase type I activities. The stimulatory activity is destroyed by trypsin (60 min at 37 degrees C), DNase II (60 min at 37 degrees C), and heat treatment (2 min at 68 degrees C). The 125I-labeled NPF-1 does not bind to activated calf thymus DNA or poly(dC). However, it forms a ternary complex with DNA in the presence of DNA polymerase alpha-primase complex (alpha 1 and alpha 2). The ternary complex sediments on sucrose density gradient as a heavier band (11S). The NPF-1 also stimulates (2.5-fold) primase-catalyzed incorporation of GMP and dGMP from the corresponding triphosphates on poly(dC) template even in the presence of a high concentration of alpha-amanitin (400 micrograms/ml). The labeled duplex containing the poly(dC) template, [32P]-GTP, and [3H]dGTP loses 80% of the 32P label and 70% of the 3H label after treatment with 0.3 M KOH and DNase I, respectively. The products were isolated from reaction mixtures incubated with and without NPF-1 and subjected to alkaline sucrose-density-gradient sedimentation analysis. The results suggest that the rate of synthesis of DNA short chains is increased in the presence of NPF-1 without a concomitant increase in the chain length of the newly synthesized products.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert W., Grummt F., Hübscher U., Wilson S. H. Structural homology among calf thymus alpha-polymerase polypeptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):935–946. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts B. M. The DNA enzymology of protein machines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:1–12. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya P., Basu S. Probable involvement of a glycoconjugate in IMR-32 DNA synthesis: decrease of DNA polymerase alpha 2 activity after tunicamycin treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1488–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya P., Moskal J. R., Basu S. Embryonic chicken brain and mouse neuroblastoma cells N1E-115 and N-18 contain an inhibitor of acid deoxyribonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):842–845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya P., Simet I., Basu S. Differential inhibition of multiple forms of DNA polymerase alpha from IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2683–2687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya P., Simet I., Basu S. Inhibition of human neuroblastoma DNA polymerase activities by plant lectins and toxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2218–2221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F., Plummer J., Huberman A. J., Evans M. J. Restriction fragment primed phi X174 single-stranded DNA as template for DNA polymerase alpha and beta. Detection and partial purification of a polymerase alpha stimulating factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 19;609(2):205–223. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Rafter E., Augl C., Bollum F. J. Purification of a DNA polymerase-DNA primase complex from calf thymus glands. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14679–14687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. C., Bohn E. W., Planck S. R., Wilson S. H. Mouse DNA polymerase alpha. Subunit structure and identification of a species with associated exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11678–11687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Lehman I. R. A DNA primase activity associated with DNA polymerase alpha from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortijo M., Barón C., Jiménez J. S., Mateo P. L. Calorimetric titration of phosphorylase b with AMP. Anomalous thermal ligand-binding profiles induced by an enzymic impurity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1121–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., Soussi T., Rossignol J. M., Méchali M., De Recondo A. M. Stimulation of rat liver alpha- and beta-type DNA polymerases by an homologous DNA-unwinding protein. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Nagy R., Davey S. K. Mouse DNA polymerase alpha-primase terminates and reinitiates DNA synthesis 2-14 nucleotides upstream of C2A1-2(C2-3/T2) sequences on a minute virus of mice DNA template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4023–4027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. M., Huberman J. A. In vitro HeLa cell DNA synthesis. II. Partial characterization of soluble factors stimulating nuclear dna synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 27;520(2):271–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse F., Krauss G. The primase activity of DNA polymerase alpha from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1881–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmer A. M., Hesslewood I. P., Johnston I. R. The occurrence of multiple activities in the high-molecular-weight DNA polymerase fraction of mammalian tissues. A preliminary study of some of their properties. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):487–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. M., Cheriathundam E., Bollum F. J., Chang L. M. Immunological analysis of the polypeptide structure of calf thymus DNA polymerase-primase complex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11924–11930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. M., Cheriathundam E., Bollum F. J., Chang L. M. Initiation of DNA synthesis by the calf thymus DNA polymerase-primase complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10840–10846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U. DNA polymerases in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: mode of action and biological implications. Experientia. 1983 Jan 15;39(1):1–25. doi: 10.1007/BF01960616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Spanos A., Albert W., Grummt F., Banks G. R. Evidence that a high molecular weight replicative DNA polymerase is conserved during evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6771–6775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazwinski S. M., Edelman G. M. A DNA primase from yeast. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4995–5002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., DiFrancesco R. A., Lehman I. R. The DNA polymerase-primase from drosophila melanogaster embryos. Rate and fidelity of polymerization on single-stranded DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9314–9319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki K., Nagata K., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Purification and characterization of a factor stimulating DNA polymerase alpha activity from mouse FM3A cells. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):485–493. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamothe P., Baril B., Chi A., Lee L., Baril E. Accessory proteins for DNA polymerase alpha activity with single-strand DNA templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4723–4727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: specificity of initiation and evidence for bidirectional replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukage A., Bohn E. W., Wilson S. H. Multiple forms of DNA polymerase in mouse myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):578–582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe M., Rossignol J. M., De Recondo A. M. DNA polymerase alpha associated primase from rat liver: physiological variations. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1611–1615. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planck S. R., Wilson S. H. Studies on the structure of mouse helix-destabilizing protein-1. DNA binding and controlled proteolysis with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11547–11556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevani P., Badaracco G., Augl C., Chang L. M. DNA polymerase I and DNA primase complex in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7532–7539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevani P., Foiani M., Valsasnini P., Badaracco G., Cheriathundam E., Chang L. M. Polypeptide structure of DNA primase from a yeast DNA polymerase-primase complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7102–7107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. G., Weaver D. T., Baril E. F., DePamphilis M. L. DNA polymerase alpha cofactors C1C2 function as primer recognition proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9810–9819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda M., Nelson E. M., Bayne M. L., Benbow R. M. DNA primase activity associated with DNA polymerase alpha from Xenopus laevis ovaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7209–7213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Dumas L. B. A DNA primase that copurifies with the major DNA polymerase from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7936–7940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanos A., Sedgwick S. G., Yarranton G. T., Hübscher U., Banks G. R. Detection of the catalytic activities of DNA polymerases and their associated exonucleases following SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1825–1839. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg J. A., Otten M., Grindey G. B. Isolation of a DNA polymerase alpha-associated regulatory protein from calf thymus. Cancer Res. 1979 Nov;39(11):4330–4335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng B. Y., Ahlem C. N. Mouse primase initiation sites in the origin region of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2342–2346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Hu S. Z., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Characterization of a primase activity tightly associated with immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1854–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. E., Sugino A. Purification of a DNA primase activity from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Primase can be separated from DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8173–8181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagura T., Kozu T., Seno T. Mouse DNA polymerase accompanied by a novel RNA polymerase activity: purification and partial characterization. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):607–618. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagura T., Kozu T., Seno T., Saneyoshi M., Hiraga S., Nagano H. Novel form of DNA polymerase alpha associated with DNA primase activity of vertebrates. Detection with mouse stimulating factor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13070–13075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Shimura K. Unwinding of DNA by nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG(1 + 2) from pig thymus as determined with endonuclease. J Biochem. 1984 Jan;95(1):117–124. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Kondo T., Ando T. Multiple molecular species of cytoplasmic DNA polymerase from calf thymus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 24;353(4):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]