Abstract
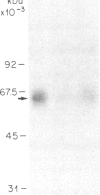
A functionalized derivative of the alpha 2-selective antagonist rauwolscine formed the basis for a photoaffinity adduct that has allowed identification of the hormone-binding subunit of the brain alpha 2-adrenergic receptor protein. Rauwolscine carboxylate underwent reaction with 4-N-t-butyloxycarbonyl-aminoaniline, leading to the synthesis of rauwolscine 4-aminophenyl carboxamide (Rau-AmPC). Rau-AmPC was radioiodinated and converted to the arylazide derivative, 17 alpha-hydroxy-20 alpha-yohimban-16 beta-[N-(4-azido-3-[125I]iodo)phenyl] carboxamide (125I-Rau-AzPC), via a diazonium salt intermediate. The characterization of 125I-Rau-AzPC as a photolabile probe employed alpha 2-adrenergic receptors, which were first solubilized from porcine brain membranes and partially purified by affinity chromatography utilizing a yohimbine-agarose affinity matrix. In the partially purified receptor preparation incubated with 125I-Rau-AzPC, photolysis resulted in covalent labeling of a major (Mr, 62,000) peptide as determined by NaDodSO4/PAGE and autoradiography. Labeling of this peptide was inhibited by the alpha 2-selective antagonist, yohimbine, and the non-subtype-selective alpha-antagonist, phentolamine, but not by the alpha 1-antagonist, prazosin, or the beta-receptor antagonist, (-)-alprenolol. The alpha-adrenergic agonist epinephrine also inhibited labeling in a stereoselective manner. These data indicate that the photolabeled Mr 62,000 peptide is the hormone-binding subunit of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor protein. The availability of this radioiodinated photoaffinity probe for the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor should facilitate further structural and biophysical characterization of the receptor protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bylund D. B., U'Prichard D. C. Characterization of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1983;24:343–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Regan J. W., Nakata H., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Gierschik P., Somers R. L., Spiegel A. M., Birnbaumer L., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional reconstitution of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3901–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. [3H]Rauwolscine and [3H]yohimbine binding to rat cerebral and human platelet membranes: possible heterogeneity of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;84(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90159-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Graham R. M. Molecular characterization of adrenergic receptors. Circ Res. 1985 May;56(5):635–650. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.5.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal R. K., Sharma R. K. Purification and biochemical characterization of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor from the rat adrenocortical carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 16;130(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara R. S., Bylund D. B. Solubilization and characterization of putative alpha-2 adrenergic isoceptors from the human platelet and the rat cerebral cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):603–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Hess H. J., Grodski A., Graham R. M., Homcy C. J. Synthesis and characterization of a high affinity radioiodinated probe for the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;29(3):219–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Dickinson K. E., Heald S. L., Wikberg J. E., Hagen P. O., DeBernardis J. F., Winn M., Arendsen D. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Photoaffinity labeling of mammalian alpha 1-adrenergic receptors. Identification of the ligand binding subunit with a high affinity radioiodinated probe. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2579–2587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Ruoho A. E. Iodoazidobenzylpindolol, a photoaffinity probe for the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Barden N., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., DeMarinis R. M., Krog A. J., Holden K. G., Matthews W. D., Hieble J. P. Affinity chromatography of human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7223–7227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., DeMarinis R. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of the subunit-binding site of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors using [3H]phenoxybenzamine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7864–7869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Nakata H., DeMarinis R. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Purification and characterization of the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3894–3900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman C. E., Hess H. J., Homcy C. J., Graham R. M. Photoaffinity labeling of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor using an 125I-labeled aryl azide analogue of prazosin. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3765–3770. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorr R. G., Heald S. L., Jeffs P. W., Lavin T. N., Strohsacker M. W., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. The beta-adrenergic receptor: rapid purification and covalent labeling by photoaffinity crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2778–2782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreeve S. M., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Molecular comparison of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors suggests that these proteins are structurally related "isoreceptors". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4842–4846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. K., Limbird L. E. Evidence that human platelet alpha-adrenergic receptors coupled to inhibition of adenylate cyclase are not associated with the subunit of adenylate cyclase ADP-ribosylated by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10471–10478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. K., Limbird L. E. Solubilization of human platelet alpha-adrenergic receptors: evidence that agonist occupancy of the receptor stabilizes receptor--effector interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4026–4030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mammalian beta-adrenergic receptors. Distinct glycoprotein populations containing high mannose or complex type carbohydrate chains. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8655–8663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatt J. D., Johnson S. L., Cragoe E. J., Limbird L. E. Inhibitors of Na+/H+ exchange block stimulus-provoked arachidonic acid release in human platelets. Selective effects on platelet activation by epinephrine, ADP, and lower concentrations of thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):12910–12919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. alpha 2 adrenoceptors: classification, localization, mechanisms, and targets for drugs. J Med Chem. 1982 Dec;25(12):1389–1401. doi: 10.1021/jm00354a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B. Islet cyclic AMP levels are not lowered during alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of insulin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4111–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]