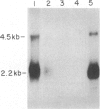
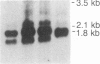
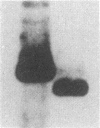
Abstract
Steroid 21-hydroxylase [21-OHase; steroid 21-monooxygenase; steroid, hydrogen-donor:oxygen oxidoreductase (21-hydroxylating); EC 1.14.99.10] is a cytochrome P-450 enzyme required for the adrenal synthesis of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. The gene encoding this protein is present in two copies (21-OHase A and B) in the S region of the murine major histocompatibility complex. Previous studies utilizing gene-specific oligonucleotide probes and gene transfer showed that only the 21-OHase A gene is expressed in the BALB/c mouse. Here, we present the complete primary structures of both BALB/c 21-OHase encoding genes. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences defines a deletion of 215 nucleotides spanning the second exon of the 21-OHase B gene; other nucleotide changes in the 21-OHase B gene introduce frame shifts and premature termination codons. Southern blot analysis of C57BL/6 and DBA/2J mice indicates that a similar deletion is present in these strains; however the C3H/HeJ strain is a structural variant. A hybrid gene composed of the 21-OHase B promoter placed 5' of the 21-OHase A structural sequences was efficiently transcribed following transfection into Y1 adrenocortical tumor cells. These findings demonstrate that the 21-OHase B gene promoter is functional and suggest that mutations within the 21-OHase B structural gene are responsible for its lack of expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amor M., Tosi M., Duponchel C., Steinmetz M., Meo T. Liver mRNA probes disclose two cytochrome P-450 genes duplicated in tandem with the complement C4 loci of the mouse H-2S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4453–4457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski M. J., Haniu M., Nakajin S., Shinoda M., Yanagibashi K., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Peptide alignment of the porcine 21-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 using a cDNA sequence of the corresponding bovine enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):734–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90600-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. beta 0 thalassemia, a nonsense mutation in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
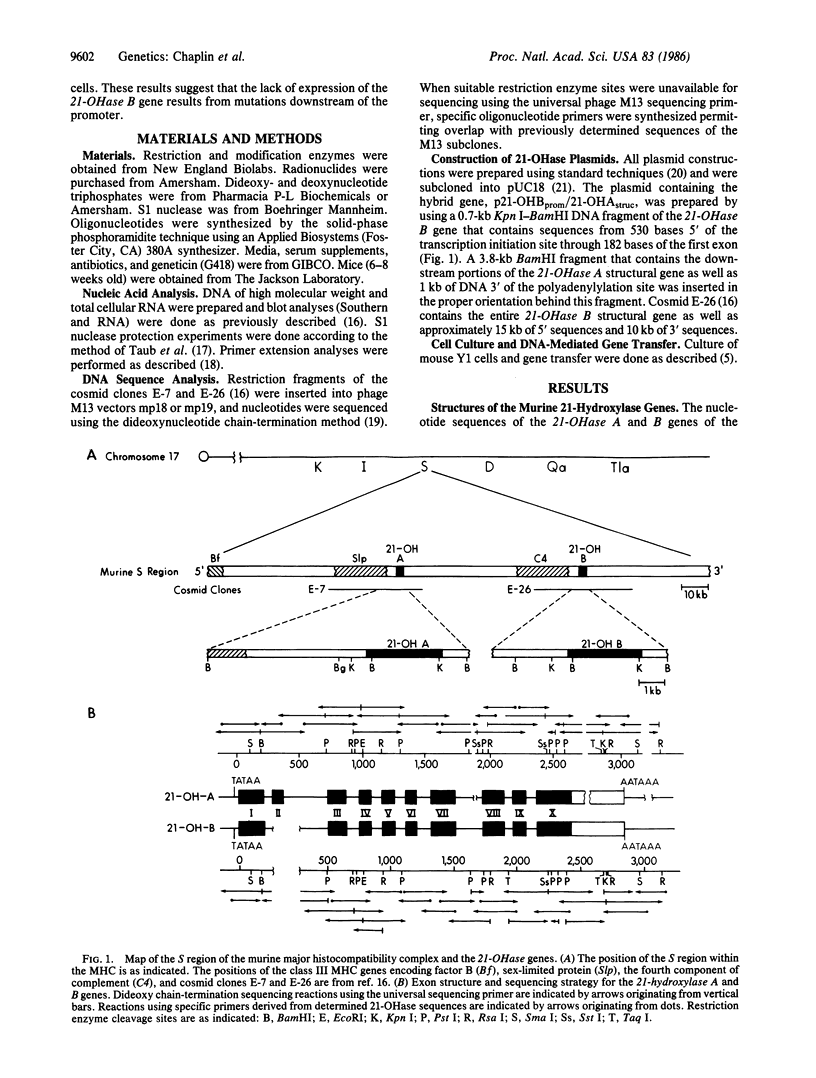
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Cloning and characterization of the bovine gene for steroid 21-hydroxylase (P-450c21). DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):211–219. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Yoshioka H., Yamane M., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2841–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. E., McCarthy J. L., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Effects of ACTH on steroidogenesis in bovine adrenocortical cells in primary culture--increased secretion of 17 alpha-hydroxylated steroids associated with a refractoriness in total steroid output. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Jun;18(6):715–723. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Okada Y., Sogawa K., Hirose T., Inayama S., Omura T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for mRNA of mitochondrial cytochrome P-450(SCC) of bovine adrenal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4647–4651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Negishi M. Multiple forms of cytochrome P-450 and the importance of molecular biology and evolution. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 15;31(14):2311–2317. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Chaplin D. D., Wong M., Seidman J. G., Smith J. A., Schimmer B. P. Expression of murine 21-hydroxylase in mouse adrenal glands and in transfected Y1 adrenocortical tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. II. Identification of cAMP and glucocorticoid regulatory domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9721–9726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Roach A., Teplow D. B., Prusiner S. B., Hood L. Cloning and characterization of the myelin basic protein gene from mouse: one gene can encode both 14 kd and 18.5 kd MBPs by alternate use of exons. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Moulding C., Battey J., Murphy W., Vasicek T., Lenoir G. M., Leder P. Activation and somatic mutation of the translocated c-myc gene in burkitt lymphoma cells. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. R., Simpson E. R. Regulation of the biosynthesis of cytochromes P-450 involved in steroid hormone synthesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Feb;39(2):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Chaplin D. D., Weis J. H., Dupont B., New M. I., Seidman J. G. Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):465–467. doi: 10.1038/312465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a bovine adrenal cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1986–1990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Structure of human steroid 21-hydroxylase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5111–5115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka H., Morohashi K., Sogawa K., Yamane M., Kominami S., Takemori S., Okada Y., Omura T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Structural analysis of cloned cDNA for mRNA of microsomal cytochrome P-450(C21) which catalyzes steroid 21-hydroxylation in bovine adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4106–4109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan P. M., Nakajin S., Haniu M., Shinoda M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Steroid 21-hydroxylase (cytochrome P-450) from porcine adrenocortical microsomes: microsequence analysis of cysteine-containing peptides. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):143–149. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]