Abstract
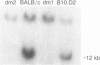
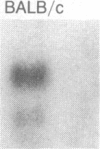
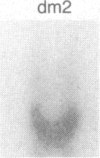
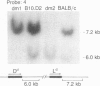
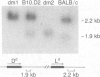
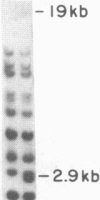
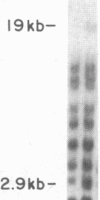
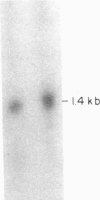
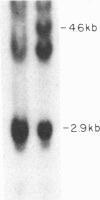
Inbred mouse strains carrying spontaneous mutations in class I genes have been extremely informative in studies of the genetic mechanisms generating polymorphism in the major histocompatibility gene complex. In this report, we determine the molecular basis of the spontaneous loss mutation in BALB/c-H-2dm2 mice, which were previously shown not to express Ld antigens while maintaining normal expression of two other class I antigens, Kd and Dd. We show BALB/c-H-2dm2 mice do not transcribe detectable levels of Ld mRNA, indicating they do not produce a truncated Ld molecule as previously reported. Furthermore, in Southern blot comparisons using a series of low-copy genomic probes, the deletion was found to be approximately 140 kilobases and include the entire Ld gene along with three or more other class I genes mapping between Dd and Ld. These data represent direct genetic evidence for a spontaneous contraction in the genes encoding class I histocompatibility antigens, which in this case probably resulted from the misalignment of the 3' flanking regions of the Dd and Ld genes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnside S. S., Hunt P., Ozato K., Sears D. W. A molecular hybrid of the H-2Dd and H-2Ld genes expressed in the dm1 mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5204–5208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H., Dmitrovsky E., Hieter P. A., Mitchell K., Leder P., Turoczi L., Kirsch I. R., Hollis G. F. Identification of three new Ig lambda-like genes in man. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):425–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J., Nairn R., Nathenson S. G., Sachs D. H., Hansen T. H. Primary structural studies of an H-2L molecule confirm that it is a unique gene product with homology to H-2K and H-2D antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1134–1138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démant P., Iványi D. Further molecular complexities of H-2 K- and D-region antigens. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):146–149. doi: 10.1038/290146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Camerini-Otero R. D., Ozato K., Seidman J. G. Structure and expression of a mouse major histocompatibility antigen gene, H-2Ld. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1994–1998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty L., DiBiase K., Lynes M. A., Seidman J. G., Weinberger O., Rinchik E. M. Characterization of a Q subregion gene in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1503–1507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow R. S., McMillan M., Nicolson M., Sher B. T., Eakle K., Davidson N., Hood L. Identification of the class I genes of the mouse major histocompatibility complex by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):231–237. doi: 10.1038/300231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow R. S., McMillan M., Orn A., Nicolson M., Davidson N., Frelinger J. A., Hood L. Identification of a BALB/c H-2Ld gene by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.7058331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Cullen S. E., Melvold R., Kohn H., Flaherty L., Sachs D. H. Mutation in a new H-2-associated histocompatibility gene closely linked to H-2D. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1550–1558. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Ozato K., Melino M. R., Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J., Jandinski J. J., Sachs D. H. Immunochemical evidence in two haplotypes for at least three D region-encoded molecules, D, L, and R. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1713–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Sachs D. H. Isolation and antigenic characterization of the product of a third polymorphic H-2 locus, H-2L. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1469–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iványi D., Démant P. Molecular heterogeneity of D-end products detected by anti-H-2.28 sera. II. B10.D2(M504) (H-2dm1) mutant fails to express one of the two H-2.4-, 28 + Dd region molecules. Immunogenetics. 1982;15(5):467–476. doi: 10.1007/BF00345906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. The major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):516–521. doi: 10.1126/science.104386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. B., Hansen T. H. Functional studies of the products of H-2L locus. Immunogenetics. 1980;10(1):7–17. doi: 10.1007/BF01561548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehoj E. P., Hansen T. H., Sachs D. H., Coligan J. E. Primary structural evidence that the H-2Dq region encodes at least three distinct gene products: Dq, Lq, and Rq. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2499–2503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehoj E. P., Walsh W. D., Potter T., Lee D. R., Coligan J. E., Hansen T. H. Chemical and serologic definition of two unique D region-encoded molecules in the wild-derived mouse strain B10.GAA37. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3138–3142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies D. H., Evans G. A., Ozato K., Camerini-Otero R. D., Tanaka K., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Expression of H-2Dd and H-2Ld mouse major histocompatibility antigen genes in L cells after DNA-mediated gene transfer. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):463–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Golden L., Weiss E., Bullman H., Hurst J., Simpson E., James R. F., Townsend A. R., Taylor P. M., Schmidt W. Expression of murine H-2Kb histocompatibility antigen in cells transformed with cloned H-2 genes. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):529–534. doi: 10.1038/298529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Sher B. T., Sun Y. H., Eakle K. A., Hood L. DNA sequence of a gene encoding a BALB/c mouse Ld transplantation antigen. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):679–682. doi: 10.1126/science.7058332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn R., Yamaga K., Nathenson S. G. Biochemistry of the gene products from murine MHC mutants. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:241–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Geliebter J., Pfaffenbach G. M., Zeff R. A. Murine major histocompatibility complex class-I mutants: molecular analysis and structure-function implications. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:471–502. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipps C., McMillan M., Flood P. M., Murphy D. B., Forman J., Lancki D., Womack J. E., Goodenow R. S., Schreiber H. Identification of a unique tumor-specific antigen as a novel class I major histocompatibility molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J. Synthesis of a defective H-2 histocompatibility antigen by mutant mouse strain BALB/c-H-2dm2. Immunogenetics. 1982;15(4):333–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00364257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Darnell J. E. Competition hybridization by "pre-saturation" of HeLa cell DNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):551–562. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Stephan D., Fischer Lindahl K. Gene organization and recombinational hotspots in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan D., Sun H., Lindahl K. F., Meyer E., Hämmerling G., Hood L., Steinmetz M. Organization and evolution of D region class I genes in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1227–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. H., Goodenow R. S., Hood L. Molecular basis of the dm1 mutation in the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse: a D/L hybrid gene. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1588–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Steinmetz M., Hood L. Genetic mapping in the major histocompatibility complex by restriction enzyme site polymorphisms: most mouse class I genes map to the Tla complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3425–3429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):701–702. doi: 10.1038/248701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]